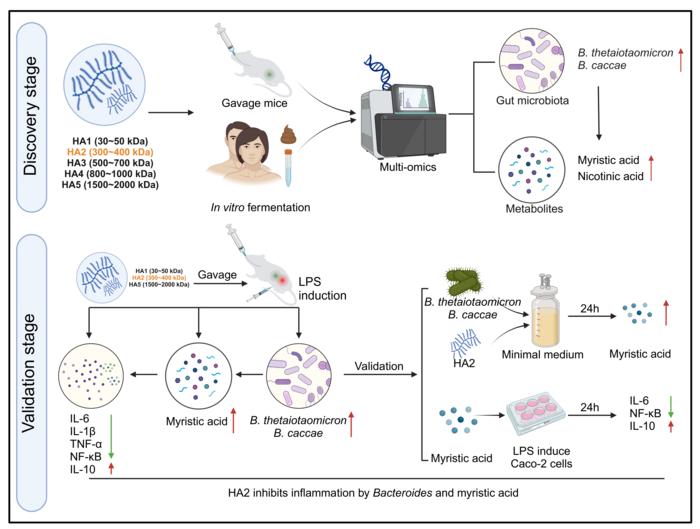
Previous studies on the function of glycosaminoglycans have primarily focused on improving host physiological indices. However, little attention has been paid to the material basis and mechanism of their mediated improvement of host health by gut microbiota. In this study, the research team focused on investigating the effect of hyaluronic acid with various molecular weights. Utilizing a combination of multi-model and multi-omics technologies, the researchers established that hyaluronic acid with a specific molecular weight (300-400 kDa) can significantly mitigate inflammatory responses in mice. This effect is dependent on gut Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Bacteroides caccae, along with their crucial metabolite-myristic acid.
Credit: ©Science China Press
Previous studies on the function of glycosaminoglycans have primarily focused on improving host physiological indices. However, little attention has been paid to the material basis and mechanism of their mediated improvement of host health by gut microbiota. In this study, the research team focused on investigating the effect of hyaluronic acid with various molecular weights. Utilizing a combination of multi-model and multi-omics technologies, the researchers established that hyaluronic acid with a specific molecular weight (300-400 kDa) can significantly mitigate inflammatory responses in mice. This effect is dependent on gut Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Bacteroides caccae, along with their crucial metabolite-myristic acid.
Furthermore, the authors validated that Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Bacteroides caccae can degrade hyaluronic acid in vitro, producing the beneficial metabolite myristic acid. This finding is based on the extensive repository of over 25,000 human gut microbiota strains established by the Center for Food Biotechnology at Jiangnan University’s School of Food Science and Technology. Simultaneously, they demonstrated that Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Bacteroides caccae exhibit high intra-species consistency, indicating the existence of specific genetic clusters among these hyaluronic acid-responsive strains.
Additionally, the research team found that hyaluronic acid stimulates Bacteroides to produce myristic acid, which in turn inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby reducing cellular inflammation. This study identified the optimal molecular weight range of hyaluronic acid to improve host inflammation, elucidated the material basis and molecular mechanisms of gut effect strains, provided biomarkers for dietary polysaccharide strategies to alleviate host inflammation, and offered new strategies and insights for the efficient screening of microbiota-directed foods.
See the article:
Hyaluronic acid modulates gut microbiota and metabolites relieving inflammation: a molecular weight-dependent study
Journal
Science Bulletin
DOI
10.1016/j.scib.2024.04.010