“Our findings suggest that the omicron variant, in particular, leads to premature senescence in in vitro, ex vivo, and in lung tissue models.”
Credit: 2023 Hornung et al.
“Our findings suggest that the omicron variant, in particular, leads to premature senescence in in vitro, ex vivo, and in lung tissue models.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 15, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Uncovering a unique pathogenic mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant: selective induction of cellular senescence.”
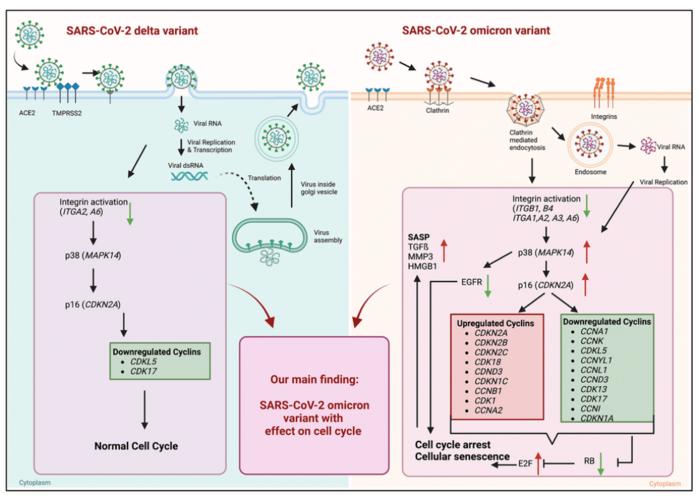
SARS-CoV-2 variants are constantly emerging with a variety of changes in the conformation of the spike protein, resulting in alterations of virus entry mechanisms. Solely omicron variants use the endosomal clathrin-mediated entry.
In this new study, researchers Franziska Hornung, Nilay Köse-Vogel, Claude Jourdan Le Saux, Antje Häder, Lea Herrmann, Luise Schulz, Lukáš Radosa, Thurid Lauf, Tim Sandhaus, Patrick Samson, Torsten Doenst, Daniel Wittschieber, Gita Mall, Bettina Löffler, and Stefanie Deinhardt-Emmer from Jena University, Leibniz Centre for Photonics in Infection Research (LPI), University of California San Francisco, Klinik für Herz- und Thoraxchirurgie, and University Hospital Bonn investigated the influence of defined altered spike formations to study their impact on premature cellular senescence.
“In our study, in vitro infections of SARS-CoV-2 variants delta (B.1.617.2) and omicron (B.1.1.529) were analyzed by using human primary small alveolar epithelial cells and human ex vivo lung slices. We confirmed cellular senescence in human lungs of COVID-19 patients. Hence, global gene expression patterns of infected human primary alveolar epithelial cells were identified via mRNA sequencing.”
Solely omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2 influenced the expression of cell cycle genes, highlighted by an increased p21 expression in human primary lung cells and human ex vivo lungs. Additionally, an upregulated senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) was detected. Transcriptomic data indicate an increased gene expression of p16, and p38 in omicron-infected lung cells. Significant changes due to different SARS-CoV-2 infections in human primary alveolar epithelial cells with an overall impact on premature aging could be identified. A substantially different cellular response with an upregulation of cell cycle, inflammation- and integrin-associated pathways in omicron infected cells indicates premature cellular senescence.
“This difference may be attributed to the distinct endocytic cell entry and intracellular pathways of the omicron variant when compared to the delta variant. The induction of cellular senescence in lung tissue following acute SARS-CoV-2 infection could potentially contribute to the reported cytokine storm and the development of long-COVID.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205297
Corresponding Author: Stefanie Deinhardt-Emmer – [email protected]
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, variant of concern, cellular senescence, lung airway cells
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.205297
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud
- X, formerly known as Twitter
- YouTube
- LabTube
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.205297
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Uncovering a unique pathogenic mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant: selective induction of cellular senescence
Article Publication Date
12-Dec-2023




