A new study conducted by the Centre for Urban Mental Health at the University of Amsterdam finds that, in a sample of 156,000 UK residents aged 40 and up, urban living is linked to lower levels of well-being, social satisfaction, and economic satisfaction. Urban residents also exhibit greater psychological inequality. The study identifies a ‘Goldilocks zone’ between cities and rural areas, where the highest satisfaction and most equal scores are observed.
Credit: Finnemann et al
A new study conducted by the Centre for Urban Mental Health at the University of Amsterdam finds that, in a sample of 156,000 UK residents aged 40 and up, urban living is linked to lower levels of well-being, social satisfaction, and economic satisfaction. Urban residents also exhibit greater psychological inequality. The study identifies a ‘Goldilocks zone’ between cities and rural areas, where the highest satisfaction and most equal scores are observed.
The percentage of people living in cities has surged from 10% in the 1910s to a projected 68% by 2050. This shift means that cities are increasingly shaping our psychological lives, making it crucial to understand urban well-being. This popularity of cities is largely driven by the abundance of social and economic opportunities. In response to this observation, psychologist and lead author Adam Finnemann investigated with colleagues whether the popularity of cities makes sense from a psychological perspective. In other words, does the abundance of economic opportunities translate into higher urban economic satisfaction? Does the wealth of people lead to urban social satisfaction? Do urban residents experience higher well-being compared to those living farther from cities?
A sample of 156,000 people from multiple cities
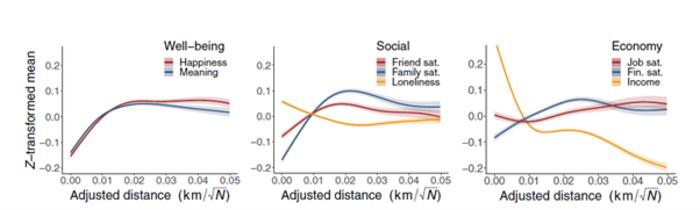
The study aimed to answer these questions by comparing urban and rural areas using large samples ranging from 40,000 to 156,000 individuals aged 40 to 70 from the UK Biobank. ‘A central challenge in urban psychology is defining urban, suburban, peri-urban, and rural areas’, states Finnemann. ‘To address this problem, we propose a novel measure of urbanicity based on the distance between individuals and their nearest city centre. This measure also accounts for the fact that living 15 km from London differs from living 15 km from Leeds—one is still urbanized while the other is countryside.’
The urban desirability paradox
The study finds that while urban residents have the highest incomes, this does not translate into psychological advantages. On the contrary, residents in highly urban areas score worse on all eight measures covering well-being, social satisfaction, and economic satisfaction. The researchers conclude that there exists a conundrum, which they term the ‘urban desirability paradox;’ highlighting the contrast between the popularity of cities and the psychological state of their residents.
Benefiting the already advantaged
The study also finds increased inequality in satisfaction, particularly regarding income and financial satisfaction, with the highest satisfaction inequality near city centers. ‘This increased social and economic satisfaction inequality aligns with theories that suggest cities disproportionately benefit the already advantaged,’ Finnemann notes.
Optimal distances
Finally, the novel measure of urbanicity allowed the researchers to examine the effects between highly urban and highly rural areas. They identified optimal distances for five variables: meaningful life, family satisfaction, friendship satisfaction, loneliness, and financial satisfaction. ‘Areas near cities but beyond their boundaries, the hinterlands, show the highest and most equal levels of psychological satisfaction,’ explains Finnemann. ‘These optimal distances might result from happy individuals moving there rather than the locations themselves enhancing individual well-being. Thus, our findings do not imply that anyone will benefit psychologically from moving to these areas.’
This study was funded by The Centre for Urban Mental Health (UMH). UMH is the largest Research Priority Area of the University of Amsterdam and comprises 3 faculties: the Faculty of Social & Behavioural Sciences, the Faculty of Science, and the Faculty of Medicine. The aim of UMH is to identify new pathways for interventions that promote urban mental health, using a complexity science approach.
Article details
Adam Finnemann, Karoline Huth, Denny Borsboom, Sacha Epskamp & Han van der Maas, 2024, ‘The urban desirability paradox: U.K. urban-rural differences in well-being, social satisfaction, and economic satisfaction’, in: Science Advances, 10, doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adn1636
Contact details
Email: [email protected], phone +31 651896886.
Journal
Science Advances
DOI
10.1126/sciadv.adn1636
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
‘The urban desirability paradox: U.K. urban-rural differences in well-being, social satisfaction, and economic satisfaction
Article Publication Date
19-Jul-2024




