A new method for shaping matter into complex shapes, with the use of ‘twisted’ light, has been demonstrated in research at the University of Strathclyde.
Credit: University of Strathclyde
A new method for shaping matter into complex shapes, with the use of ‘twisted’ light, has been demonstrated in research at the University of Strathclyde.
When atoms are cooled to temperatures close to absolute zero (-273 degrees C), they stop behaving like particles and start to behave like waves.
Atoms in this condition, which are known as Bose–Einstein condensates (BECs), are useful for purposes such as realisation of atom lasers, slow light, quantum simulations for understanding the complex behaviour of materials like superconductors and superfluids, and the precision measurement technique of atom interferometry.
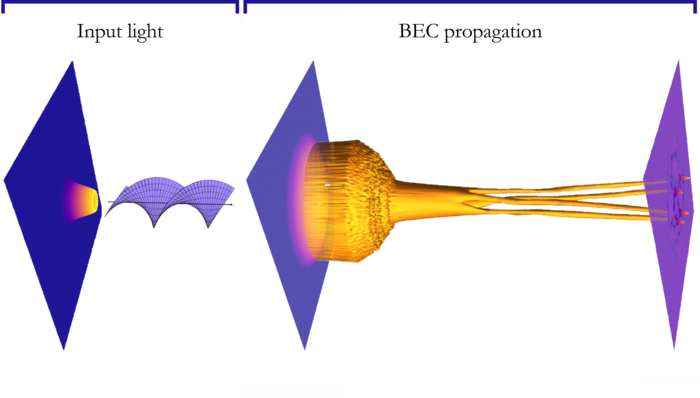
The Strathclyde study has shown that when twisted light is shone on to a moving BEC, it breaks into clusters of BEC droplets that move following the light’s features, with the number of droplets equal to twice the number of light twists. Altering the properties of the light beam can change both the number of BEC droplets and the way that they move.
The research has been published in Physical Review Letters.
Grant Henderson, a PhD student in Strathclyde’s Department of Physics, is lead author on the paper. He said: “By shining a laser beam on to a BEC, we can influence how it behaves. When the laser beam is ‘twisted,’ it has a helical phase profile and carries orbital angular momentum (OAM). Laser beams with OAM can trap and rotate microscopic particles, behaving like an optical spanner.
“This method of shining twisted light through ultracold atoms opens a new and simple way of sculpting matter into unconventional and complex shapes. It has the potential for the design of novel quantum devices such as atomtronic circuits and ultra-sensitive detectors.”
Journal
Physical Review Letters
DOI
10.1103/PhysRevLett.129.073902
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Control of Light-Atom Solitons and Atomic Transport by Optical Vortex Beams Propagating through a Bose-Einstein Condensate
Article Publication Date
12-Aug-2022




