Tokyo, Japan – A retrovirus known as human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is known to cause a number of diseases, including inflammatory diseases of the eye. Recently, researchers in Japan have investigated an antibody treatment for inflammatory eye disease in ocular cells infected with HTLV-1.
Credit: Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, TMDU
Tokyo, Japan – A retrovirus known as human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is known to cause a number of diseases, including inflammatory diseases of the eye. Recently, researchers in Japan have investigated an antibody treatment for inflammatory eye disease in ocular cells infected with HTLV-1.
In a new study published in Frontiers in Immunology, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) evaluated the safety of an anti-VEGF drug, Aflibercept, in a cell culture model exposed to HTLV-1. HTLV-1 infection can cause such diseases as adult T-cell leukemia and HTLV-1 uveitis, an inflammatory eye condition.
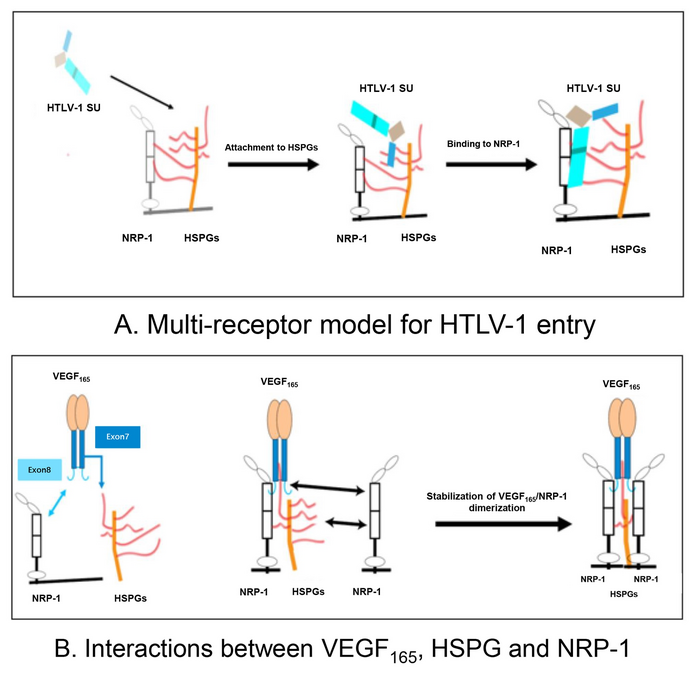
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a protein involved in the formation of new blood vessels. VEGF is known to play a role in eye diseases including age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy, and treatment with anti-VEGF antibodies, which block the action of VEGF, has been shown to ameliorate the effects of these diseases. HTLV-1 has previously been shown to mimic VEGF. It has also been shown that VEGF is a selective competitor of HTLV-1 entry (Fig 1). However, the safety of intraocular anti-VEGF antibody treatment has not been evaluated in the context of HTLV-1 infection. Therefore, the research team from TMDU set out to analyze the safety of treatment with Aflibercept in a co-culture model of human retinal epithelial (RPE) cells and HTLV-1–infected T-cells.
“We treated the co-cultured cells with the anti-VEGF drug Aflibercept and analyzed the expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, which are released during the body’s immune response,” says lead author of the study Yuan Zong.
The researchers also evaluated the pro-viral load, or the amount of virus present in the cells, as well as the proliferation of the cultured cells. The production of cytokines and chemokines was not affected by the use of anti-VEGF treatment.
“Additionally, our results showed that the anti-VEGF treatment did not increase the pro-viral load or proliferation of the RPE cells,” says senior author Kyoko Ohno-Matsui.
“Treatment with the anti-VEGF drug did not appear to exacerbate inflammation in the eye related to HTLV-1 infection,” says corresponding author Koju Kamoi.
The research team’s findings provide preliminary evidence that anti-VEGF drugs do not exacerbate HTLV-1–related inflammation and so may be safe for intraocular use in people with HTLV-1. This study, conducted using a cell culture model, paves the way for further evaluation of anti-VEGF therapy use in patients with HTLV-1 in animal or human models to confirm the efficacy of this treatment strategy.
###
The article, “Safety of intraocular anti-VEGF antibody treatment under in vitro HTLV-1 infection,” was published in Frontiers in Immunology at DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1089286.
Journal
Frontiers in Immunology
DOI
10.3389/fimmu.2022.1089286
Article Title
Safety of intraocular anti-VEGF antibody treatment under in vitro HTLV-1 infection




