Physical properties (stability, solubility, etc.), critical to the performance of pharmaceutical and functional materials, are known to strongly depend on the solid-state form and environmental factors, such as temperature and relative humidity. Recognising that late appearing, more stable forms can lead to disappearing polymorphs and potentially market withdrawal of a life-saving medicine, the pharmaceutical industry has heavily invested in solid form screening platforms.
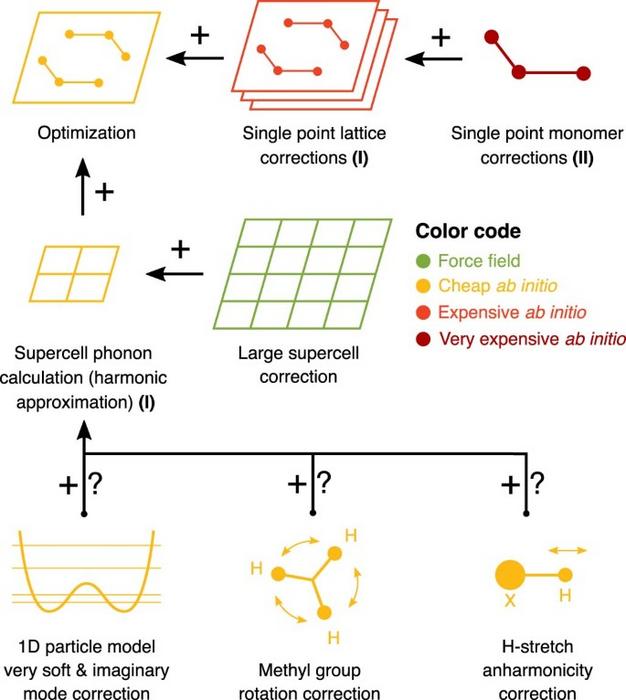
Credit: Firaha, D., Liu, Y.M., van de Streek, J. et al.
Physical properties (stability, solubility, etc.), critical to the performance of pharmaceutical and functional materials, are known to strongly depend on the solid-state form and environmental factors, such as temperature and relative humidity. Recognising that late appearing, more stable forms can lead to disappearing polymorphs and potentially market withdrawal of a life-saving medicine, the pharmaceutical industry has heavily invested in solid form screening platforms.
Quantitatively measuring the free energy differences between crystalline forms is no small challenge. Metastable crystal forms can be difficult to prepare in pure form and they are frequently susceptible to converting to more stable forms. Thus, having the ability to computationally model free energies means that the risks posed by physical instability can be understood and mitigated for all systems, including those that are experimentally intractable. The lack of reliable experimental benchmark data has been a major bottleneck in developing computational methods for accurately predicting solid-solid free energy differences. Reports in the literature are sparse and much of the experimental data on free energy determinations for molecules of pharmaceutical interest is simply not in the public domain.
To overcome this challenge, experts in academia and industry have compiled the first ever reliable experimental benchmark of solid-solid free energy differences for chemically diverse, industrially relevant systems. They then predicted these free energy differences using several methods pioneered by the group of Prof. Alexandre Tkatchenko within the Department of Physics and Materials Science at the University of Luxembourg, and further improved by Dr. Marcus Neumann and his team of researchers at Avant-garde Materials Simulation. Without using any empirical input, these calculations leveraging high performance computing (HPC) were able to predict and explain data from seven pharmaceutical companies with surprising accuracy. The potential future implications of this work are manifold, and this latest development is just one of many potential application of quantum mechanical calculations in the pharmaceutical industry.
“I am thrilled to see how computational methods developed in my academic group have been quickly adopted to reliably predict the energetics of drug crystal forms in the pharmaceutical industry in a matter of years, breaking the traditional barrier between research and industrial innovation”, remarks Prof. Tkatchenko.
“We owe a fair part of our success to the visionaries among our customers who have enabled us to create an industrial working environment with an academic touch that promotes creativity based on core values such as honesty, integrity, perseverance, team-spirit and genuine care for people and the environment”, points out Dr Marcus Neuman, founder and CEO of AMS.
“Building links between fundamental science, high performance computing, and major industry players in order to make a lasting impact for the future of health is no small feat”, said Prof. Jens Kreisel, Rector of the University of Luxembourg. “We take very seriously our mission of nurturing an ecosystem where researchers can drive societal change for good.”
Journal
Nature
DOI
10.1038/s41586-023-06587-3
Article Title
Predicting crystal form stability under real-world conditions
Article Publication Date
8-Nov-2023




