Credit: Sudip Bhattacharyya
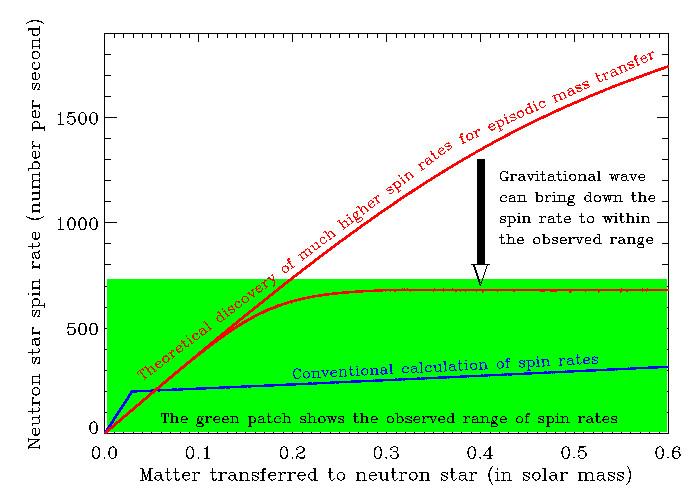
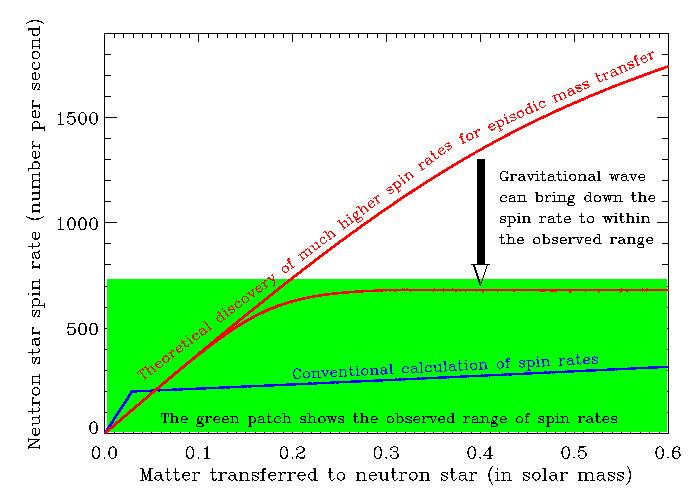
Professor Sudip Bhattacharyya of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), Mumbai, India, and Professor Deepto Chakrabarty (MIT, USA), an adjunct visiting professor at the same institute, have shown that a population of neutron stars should spin around their axes much faster than the highest observed spin rate of any neutron star. They pointed out that the observed lower spin rates are possible if these neutron stars emit gravitational waves continuously, and hence spin down.
Neutron stars are the densest observable objects in the universe, with a fistful of stellar material outweighing a mountain on Earth. While such stars are not bigger than a city, in size, they have more material than in the Sun crammed inside them. A population of these stars can increase their spin rate by the transfer of matter from a normal companion star. Infact, some of them have been observed to spin several hundred times in a second around their own axes.
In the 1970s, it was theoretically worked out how fast these neutron stars could spin, and since then this has formed the basis of studies of these stars. But the new study led by Professor Bhattacharyya has shown that for episodic mass transfer, which happens for many neutron stars, the stellar spin rate should be much higher, and the star could easily attain a spin rate more than a thousand times per second. Since no neutron star has been observed with such a high spin rate, the team has pointed out that many of these stars are likely to be slowed down by continuously emitting gravitational waves.
Gravitational waves emitted by massive objects is a prediction of Einstein's general theory of relativity, which has recently been discovered during transient phenomena of black hole mergers. But the detection of continuous gravitational waves, which could provide an opportunity to study these waves almost permanently, is still elusive. The new study of Professors Bhattacharyya and Chakrabarty provide a strong indication that many fast spinning neutron stars generate gravitational waves continuously, and careful observations should be made to detect such waves.
###
Media Contact
Sudip Bhattacharyya
[email protected]
http://www.tifr.res.in
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag