Credit: Bailey Shen.
It's the part of the eye exam everyone hates: the pupil-dilating eye drops. The drops work by opening the pupil and preventing the iris from constricting in response to light and are often used for routine examination and photography of the back of the eye. The drops sting, can take up to 30 minutes to work, and cause blurry vision for several hours afterwards, often making them inconvenient for both patient and doctor.
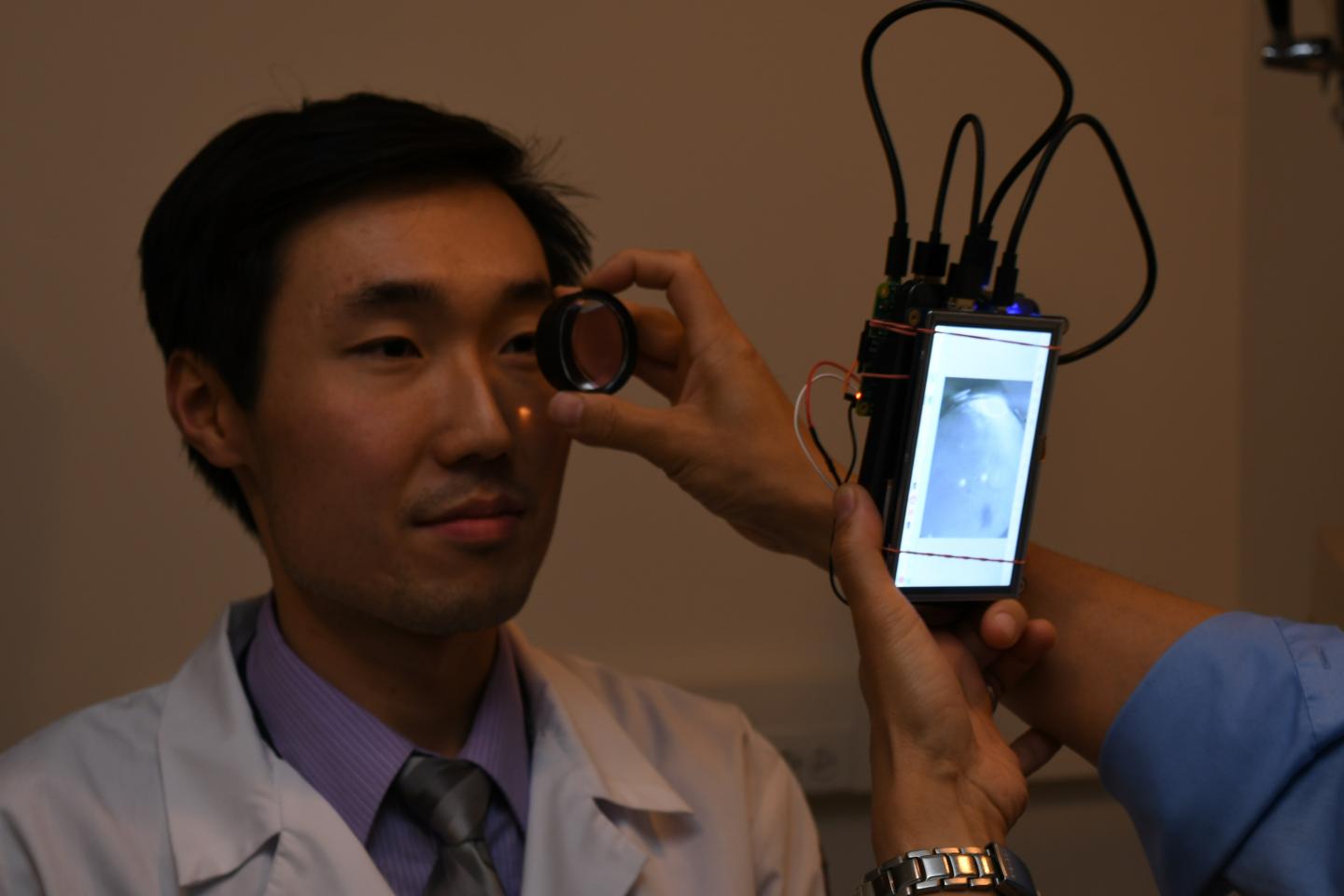
Now, researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine and Massachusetts Eye and Ear/Harvard Medical School have developed a cheap, portable camera that can photograph the retina without the need for pupil-dilating eye drops. Made out of simple parts mostly available online, the camera's total cost is about $185.
"As residents seeing patients in the hospital, there are often times when we are not allowed to dilate patients — neurosurgery patients for example," said Dr. Bailey Shen, a second-year ophthalmology resident at the UIC College of Medicine. "Also, there are times when we find something abnormal in the back of the eye, but it is not practical to wheel the patient all the way over to the outpatient eye clinic just for a photograph."
The prototype camera can be carried in your pocket, Shen said, and can take pictures of the back of the eye without eye drops. The pictures can be shared with other doctors, or attached to the patient's medical record.
The camera is based on the Raspberry Pi 2 computer, a low-cost, single-board computer designed to teach children how to build and program computers. The board hooks up to a small, cheap infrared camera, and a dual infrared- and white-light-emitting diode. A handful of other components – a lens, a small display screen and several cables – make up the rest of the camera.
The camera works by first emitting infrared light, which the iris – the muscle that controls the opening of the pupil – does not react to. Most retina cameras use white light, which is why pupil-dilating eye drops are needed.
The infrared light is used to focus the camera on the retina, which can take a few seconds. Once focused, a quick flash of white light is delivered as the picture is taken. Cameras exist that use this same infrared/white light technique, but they are bulky and often cost thousands of dollars.
Shen's camera photos show the retina and its blood supply as well as the portion of the optic nerve that leads into the retina. It can reveal health issues that include diabetes, glaucoma and elevated pressure around the brain.
Shen and his co-author, Dr. Shizuo Mukai, associate professor of ophthalmology at Harvard Medical School and a retina surgeon at Massachusetts Eye and Ear, describe their camera and provide a shopping list of parts, instructions for assembly, and the code needed to program the camera in the Journal of Ophthalmology.
"This is an open-source device that is cheap and easy to build," said Mukai. "We expect that others who build our camera will add their own improvements and innovations."
"The device is currently just a prototype, but it shows that it is possible to build a cheap camera capable of taking quality pictures of the retina without dilating eye drops, " Shen said. "It would be cool someday if this device or something similar was carried around in the white-coat pockets of every ophthalmology resident and used by physicians outside of ophthalmology as well."
###
This work was supported in part by gifts to the Mukai Fund of Massachusetts Eye and Ear.
Media Contact
Sharon Parmet
[email protected]
312-413-2695
@uicnews
http://www.uic.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag