Researchers have developed a way to create photonic time crystals and shown that these bizarre, artificial materials amplify the light that shines on them. These findings, described in a paper in Science Advances, could lead to more efficient and robust wireless communications and significantly improved lasers.
Credit: Xuchen Wang / Aalto University
Researchers have developed a way to create photonic time crystals and shown that these bizarre, artificial materials amplify the light that shines on them. These findings, described in a paper in Science Advances, could lead to more efficient and robust wireless communications and significantly improved lasers.
Time crystals were first conceived by Nobel laureate Frank Wilczek in 2012. Mundane, familiar crystals have a structural pattern that repeats in space, but in a time crystal, the pattern repeats in time instead. While some physicists were initially sceptical that time crystals could exist, recent experiments have succeeding in creating them. Last year, researchers at Aalto University’s Low Temperature Laboratory created paired time crystals that could be useful for quantum devices.
Now, another team has made photonic time crystals, which are time-based versions of optical materials. The researchers created photonic time crystals that operate at microwave frequencies, and they showed that the crystals can amplify electromagnetic waves. This ability has potential applications in various technologies, including wireless communication, integrated circuits, and lasers.
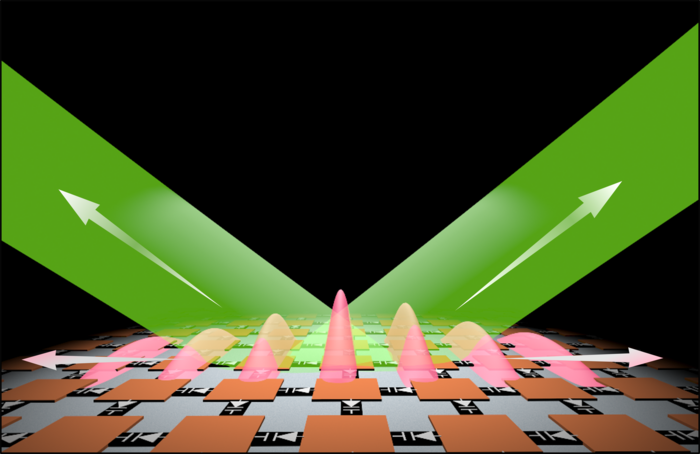
So far, research on photonic time crystals has focused on bulk materials – that is, three-dimensional structures. This has proven enormously challenging, and the experiments haven’t gotten past model systems with no practical applications. So the team, which included researchers from Aalto University, the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), and Stanford University, tried a new approach: building a two-dimensional photonic time crystal, known as a metasurface.
‘We found that reducing the dimensionality from a 3D to a 2D structure made the implementation significantly easier, which made it possible to realise photonic time crystals in reality,’ says Xuchen Wang, the study’s lead author, who was a doctoral student at Aalto and is currently at KIT.
The new approach enabled the team to fabricate a photonic time crystal and experimentally verify the theoretical predictions about its behaviour. ‘We demonstrated for the first time that photonic time crystals can amplify incident light with high gain,’ says Wang.
‘In a photonic time crystal, the photons are arranged in a pattern that repeats over time. This means that the photons in the crystal are synchronized and coherent, which can lead to constructive interference and amplification of the light,’ explains Wang. The periodic arrangement of the photons means they can also interact in ways that boost the amplification.
Two-dimensional photonic time crystals have a range of potential applications. By amplifying electromagnetic waves, they could make wireless transmitters and receivers more powerful or more efficient. Wang points out that coating surfaces with 2D photonic time crystals could also help with signal decay, which is a significant problem in wireless transmission. Photonic time crystals could also simplify laser designs by removing the need for bulk mirrors that are typically used in laser cavities.
Another application emerges from the finding that 2D photonic time crystals don’t just amplify electromagnetic waves that hit them in free space but also waves travelling along the surface. Surface waves are used for communication between electronic components in integrated circuits. ‘When a surface wave propagates, it suffers from material losses, and the signal strength is reduced. With 2D photonic time crystals integrated into the system, the surface wave can be amplified, and communication efficiency enhanced,’ says Wang.
Journal
Science Advances
DOI
10.1126/sciadv.adg7541
Article Title
Metasurface-Based Realization of Photonic Time Crystals
Article Publication Date
5-Apr-2023




