Credit: Photo Credit: Janice Haney Carr
A study, published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, describes a new treatment pathway for antibiotic resistant bacteria and infectious diseases with benefits for patients and health care providers.
Researchers from the University of Birmingham and Newcastle University found that the unusual approach of removing antibodies from the blood stream reduced the effects of chronic infections, the requirement for days spent in hospital and the use of antibiotics.
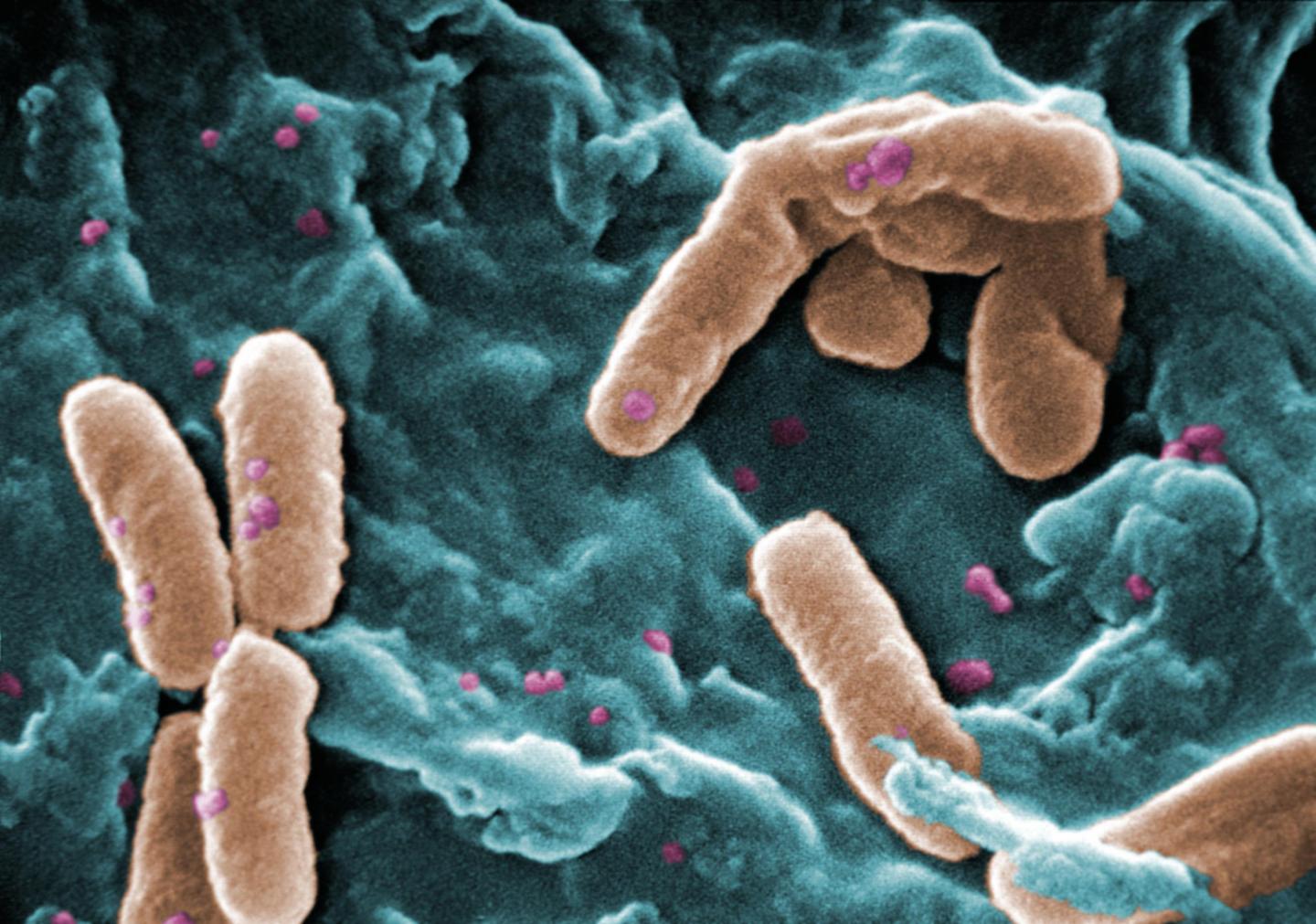
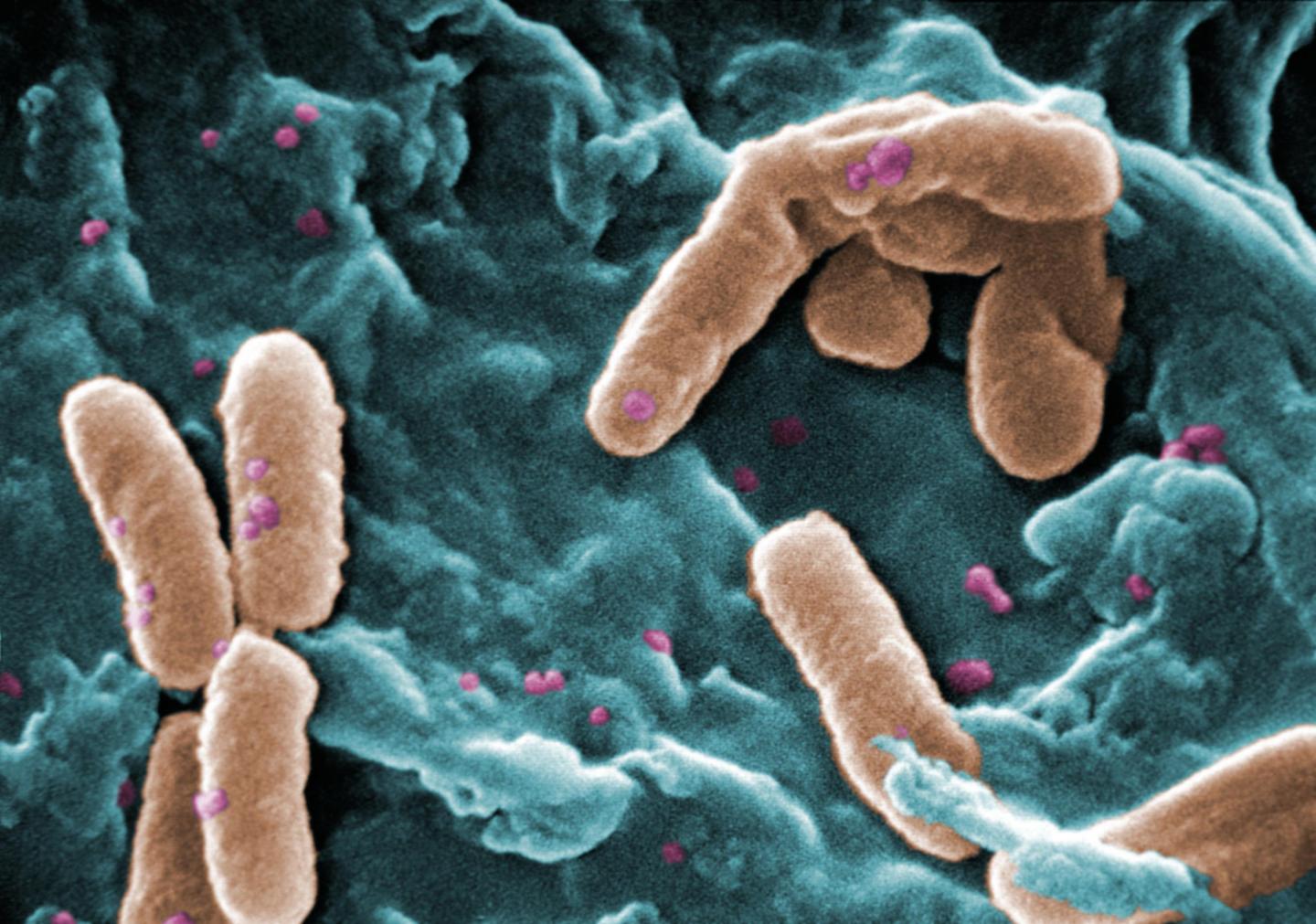
In this study, the team identified two patients with bronchiectasis who suffered with chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections that were resistant to many antibiotics; a 64-year-old male, diagnosed with bronchiectasis aged fifteen, and a 69-year-old female who had bronchiectasis from childhood.
Bronchiectasis is a disease that leads to permanent enlargement of the airways in the lung and affects over 300,000 patients in the UK. Symptoms are debilitating for patients, and typically include a chronic cough, shortness of breath, coughing up blood, and chest pain. Bronchiectasis often affects patients beyond the age at which lung transplantation is possible.
Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections commonly occur in patients suffering from bronchiectasis. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common bacterium that can cause disease and is known as a multidrug resistant pathogen, recognised for its advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms and association with serious illnesses.
The patients volunteered to be part of an explorative treatment that built on previous findings from the research group in 2014.
Professor Ian Henderson, Director of the Institute of Microbiology and Infection at the University of Birmingham, explained:
"These patients had an excess of a particular antibody in the bloodstream. In contrast to the protective effect normally associated with antibody, in these patients the antibody stopped the immune system killing the Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium and this worsened the patients' lung disease. Perhaps counter-intuitively, we decided to remove this antibody from the bloodstream and the outcomes were wholly positive."
Dr Tony De Soyza, Bronchiectasis service lead, Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals Trust and Senior Lecturer at Newcastle University, explained:
"We needed a brand new way of tackling this problem. Working with kidney and immunology experts, we used a process known as plasmapheresis that is somewhat like kidney dialysis. The plasmapheresis involved the removal, treatment, and return of blood plasma from circulation, and was done 5 times in a week in order to remove antibody from the patients. We then replaced antibodies with those from blood donations. This treatment restored the ability for the patients' blood to kill their infecting Pseudomonas."
Both patients reported a rapid improvement in health and wellbeing, greater independence and improved mobility compared to any point in the previous two years.
Professor Henderson added: "This shows that we can improve patient wellbeing significantly, by reducing the need for treatment and the numbers of days spent in hospital, which will also help to reduce the reliance on antibiotics. The next step is to do longer term studies to investigate whether an earlier intervention, with slightly less aggressive therapies, could help prevent disease progression in patients."
This is the first description of antibody-dependent enhancement of bacterial disease. It may be widely applicable to other bacterial infections and offers hope for the treatment of some antibiotic resistant infections.
###
Contact:
For interview requests or a copy of the full paper, contact Liz Bell, Communications Manager for Science and Technology, University of Birmingham, on +44 (0)121 414 2772.
For out of hours media enquiries please call: +44 (0) 7789 921 165.
Media Contact
Liz Bell
[email protected]
44-012-141-42772
@unibirmingham
http://www.bham.ac.uk