Credit: Ilya Osterman
Scientists from the Lomonosov Moscow State University in cooperation with colleagues have worked out a safe, not that expensive and highly efficient method, which allows to speed up and improve searching of new germicides. They have elaborated a system, which measures antimicrobial activity, along with determining the mode of action of a new material. The research results are published in a top-rated journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. The research has been conducted in collaboration with colleagues from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology and Gause Institute of New Antibiotics.
An antibiotic dilemma
Bacteria constantly become resistant to antibiotics, what compels mankind to search for new materials, which could solve this problem, over the last decades. The main search method is high throughput screening — namely testing of a huge number of materials from chemical libraries, as well as of new natural compounds. However, such experiments don't provide with any data regarding the mode of action. In order to improve technique efficiency it's necessary to search for ways of decreasing reagent costs, process automation and the reduction of this activity stages number.
There are already strains of a wide range, which help in identification of the activity of different antibiotic types. Combination of these strains could provide a benefit by accelerating the search process of necessary compounds and operating principle understanding. However, this requires plenty of each material testing. So, scientists face a dilemma: whether to simultaneously test many materials according to one characteristic or many characteristics of one material in order to understand, which impact it has. Both ways aren't perfect, however, Russian scientists have made an attempt to make a compromise by combination of these two approaches' advantages.
Ilya Osterman, Doctor of Chemical Sciences, a researcher of the Chemistry of Natural Compounds Department, at the Faculty of Chemistry of the Lomonosov Moscow State University, who is the research author, informs: "We've worked out an approach, which allows to in vivo determine not only the mode of action of new promising antimicrobial agents, but also their efficiency. Approach automation has allowed to analyze thousands of compounds per day".
Once Katushka appears, tryptophan stops synthesizing
The created reporter system (a term, used in molecular biology, in order to describe reporter gene or markers, inserted into an organism, which help to measure, how actively other genes work) is based on genes, which code two fluorescent proteins. One of them is a far-red protein Katushka2S, which is a marker for a termination of translation — namely, protein synthesis. Its light could be seen in case protein production terminates cause of a stop of ribosome movement along the RNA chain.
Upstream Katushka2S protein gene there was inserted a regulatory component of a tryptophan operon, which contains in its genome instructions of tryptophan amino acid biosynthesis. An operon is a functional group of genes, one part of which codes proteins, providing some work together. The other part regulates the number of these proteins, intensifying of suppressing their synthesis, when required. A tryptophan operon contains an attenuator — a genome portion, where in case of tryptophan excess, transcription stops.
Genes of tryptophan biosynthesis were replaced with a Katushka2S protein gene. The attenuator itself was also changed: namely, an alanine codon was inserted instead of a three letter codon of a tryptophan amino acid in the structure of the coded enzymes. This modified attenuator stopped reacting to tryptophan concentration, however, it became dependant on antibiotics, which disrupt protein synthesis — in their presence the amount of Katushka2S protein gets large.
Ilya Osterman shares: "At the first stage there was elaborated a gene engineering design, which included two fluorescent proteins. First protein expression depended on the presence of protein synthesis inhibitors, while expression of the second one — on the presence of DNA synthesis inhibitors. Afterwards, with the help of a hyperresponsive strain of coliform bacteria there was created a reporter, aimed at the detection of corresponding antibiotic types".
Provide DNA synthesis with red light
What was the second fluorescent protein? It turned out to be RFP – a red fluorescent protein. It's interesting that color also matters: both protein shine in the same range (of red and far-red), which is allowed to pass through human tissues quite well.
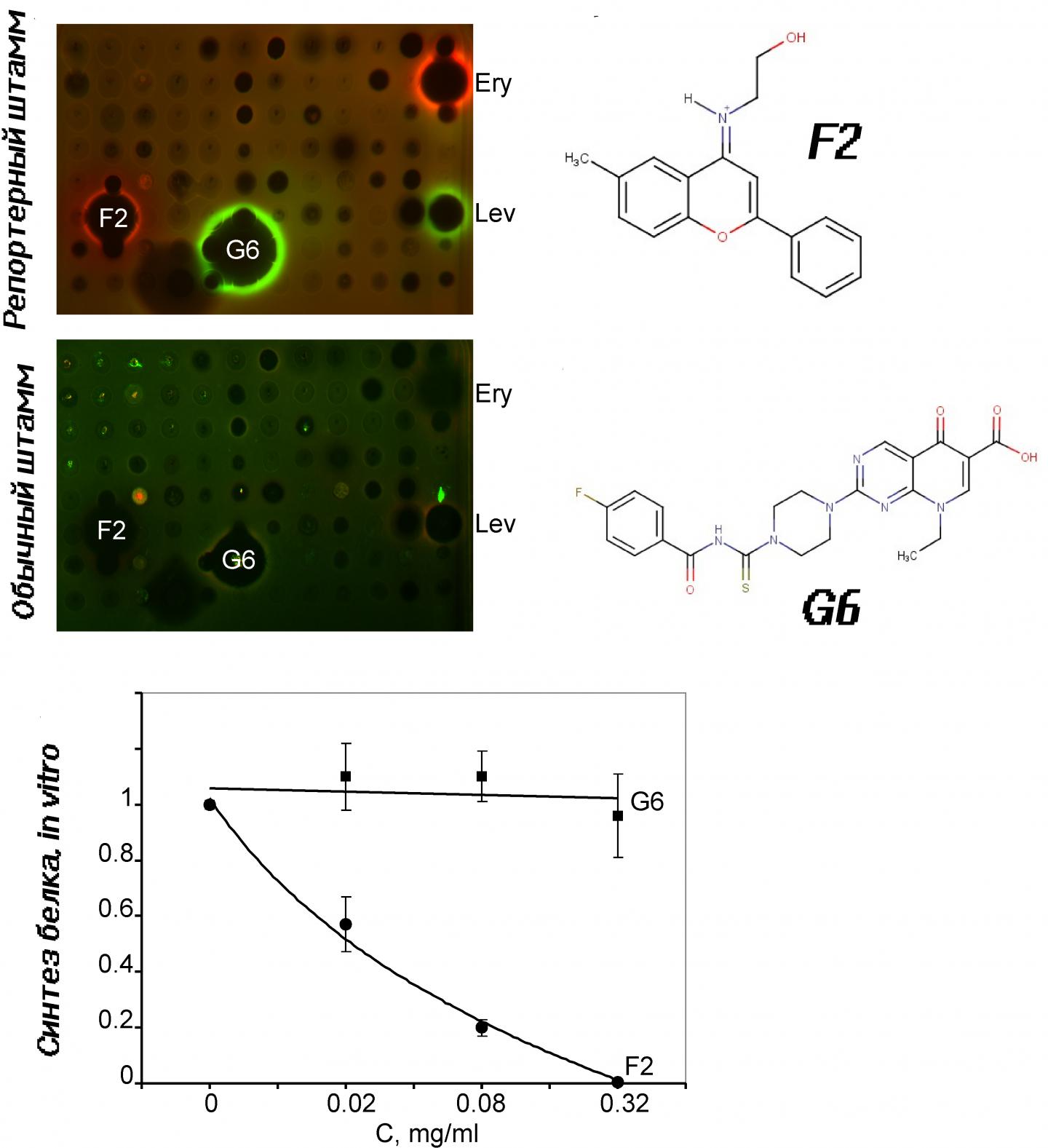
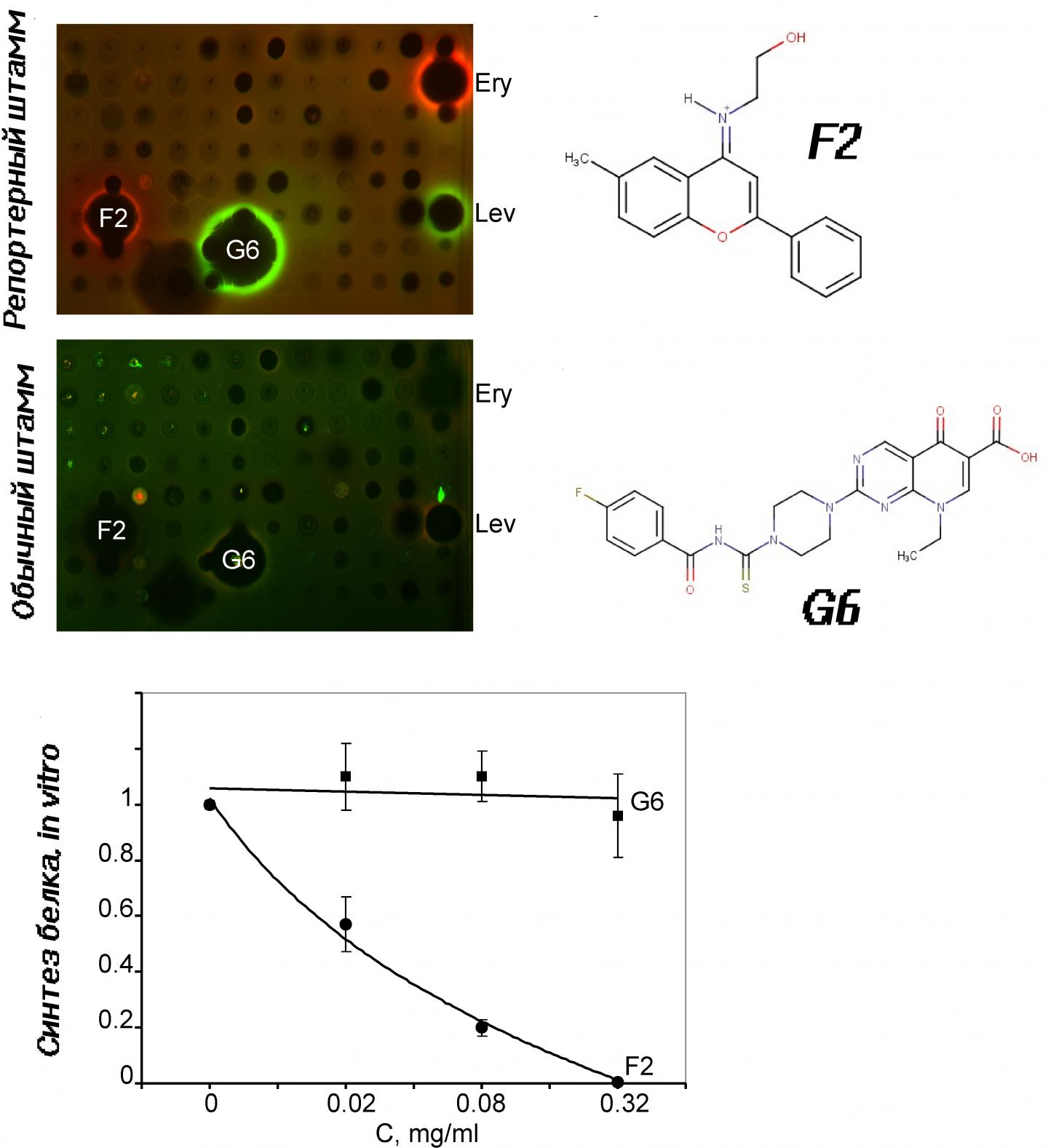
A RFP gene was inserted in such a way that it started working during SOS-response — namely, cell reaction to stress, uncomfortable conditions, which require alertness from DNA damage and repair system. According to the scientists' idea, this process should start the synthesis of a red fluorescent protein, which, like warning red light, could give a notice that there is something wrong inside a bacterium cell. The more light there is, the stronger effect an antibiotic has. How one should assemble such a reporter system? Scientists have put a RFP gen right after the sulA gen promoter, namely the area, where the main organoid of protein synthesis — a ribosome, — moving along the chain, gets learnt the sequence start, where protein is recorded. SulA gen starts at the last stages of SOS-response and suppresses cell division. So, once sulA gen starts operating, a red fluorescent protein also begins synthesizing in conjunction with it. Katushka2S operated in the same way in a tryptophan operon, it only warned with the help of red light with different wave length about a termination of protein synthesis and not DNA synthesis. This system of two reporters has already been tested on activity clarification of a new antibiotic — amicoumacin, — along with some other antibiotics. The target, which amicoumacin hits, has been unknown before.
The leading author of the research further notices: "So far, with the help of this approach we've analyzed more than 50 thousands of compounds, discovered new inhibitors of protein and DNA synthesis, which could become the basis of new germicides in the future. The process of screening will be continued".
###
Media Contact
Vladimir Koryagin
[email protected]
http://www.msu.ru
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag