Credit: Associate Professor Mikako Fujita
With the successful suppression of the AIDS virus (HIV) through medication, the focus turns toward its eradication. Researchers from Kumamoto University in Japan have developed a new compound that is key to the destruction of HIV. When the compound is introduced into infected cells, viral budding (release) is suppressed thereby confining it within the host cells. The cells then die naturally through apoptosis (cell death). This treatment is believed to lead to the complete recovery from AIDS in the near future.
In recent years, multi-drug therapy has made it possible to suppress HIV multiplication in the body when taken properly. This method, however, cannot remove the virus particles of the latent HIV reservoir–non-replicating virus particles that remain dormant in the cells of the body. As soon as drug administration is stopped, the viral load will again increase in the body. Removal of the viral reservoir is currently the top goal in AIDS research.
The "kick and kill" approach, which was developed several years ago, is a strategy for killing reservoir cells. This technique uses a drug that targets the reservoir cells and activates the virus which then allows the immune system to find these cell using the activated virus as a landmark. Although this approach was clinically tested, there is still the problem of not being able to efficiently deactivate the virus after successful activation.
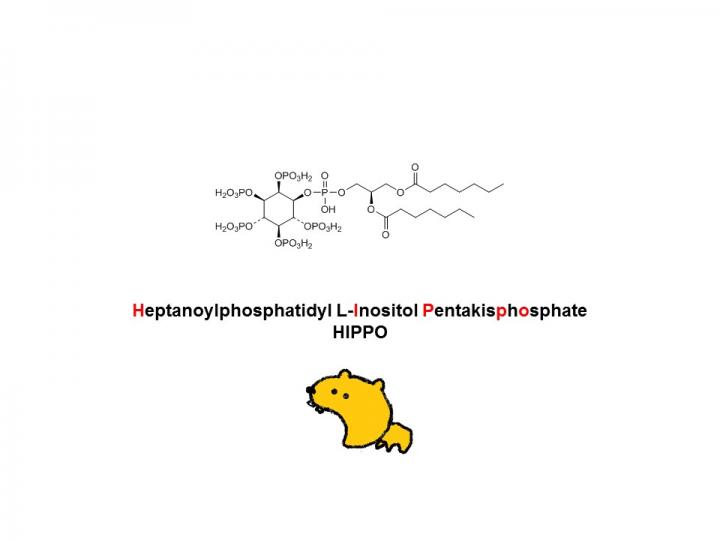
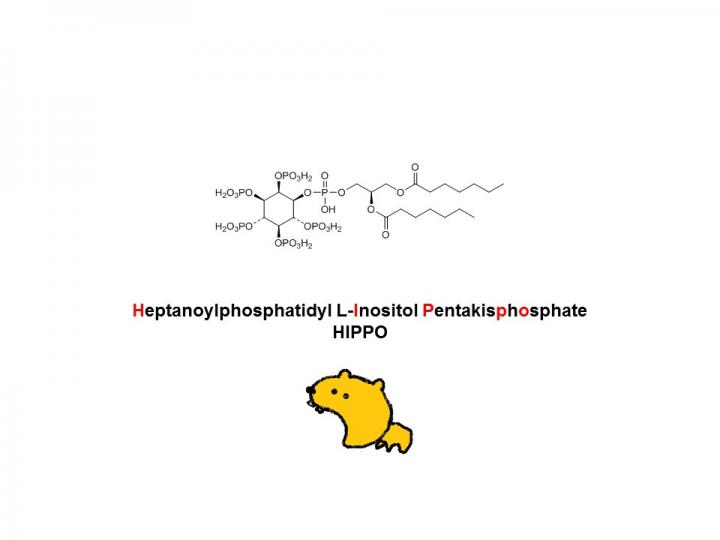
Researchers at Kumamoto University developed a new approach that they call "Lock-in and apoptosis." First, they synthesized the compound L-HIPPO, which binds strongly to the HIV protein Pr55Gag and suppresses viral budding. When L-HIPPO was added to virus-infected cells via a carrier called α-CDE, the virus became confined within the cell and the cell would die through natural apoptosis.
"Unfortunately, this approach is not immediately available for people infected with HIV," said Associate Professor Mikako Fujita of Kumamoto University, one of the leaders of the study. "First, we have to improve upon the drugs that activate the virus and combine them with L-HIPPO to efficiently target the viral reservoir. This would be a big step towards a complete recovery from HIV. We believe that our research will help to completely eradicate AIDS."
###
This finding was posted online in the Scientific Reports on 21 August 2017.
[Resource] Tateishi, H.; Monde, K.; Anraku, K.; Koga, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Ciftci, H. I.; DeMirci, H.; Higashi, T.; Motoyama, K.; Arima, H.; Otsuka, M. & Fujita, M., A clue to unprecedented strategy to HIV eradication: textquotedblleftLock-in and apoptosistextquotedblright, Scientific Reports, Springer Nature, 2017, 7.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-09129-w
Media Contact
J. Sanderson, N. Fukuda
[email protected]
http://ewww.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/en/news/
Original Source
http://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-09129-w http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09129-w