Credit: Petr Popov et al./Current Opinion in Structural Biology
Scientists from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT), the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech), and the University of Southern California (USC) have developed a new computational method for the design of thermally stable G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) that are of great help in creating new drugs. The method has already proved useful in obtaining the structures of several principal human receptors. An overview of the new method was published in the prestigious science journal Current Opinion on Structural Biology.
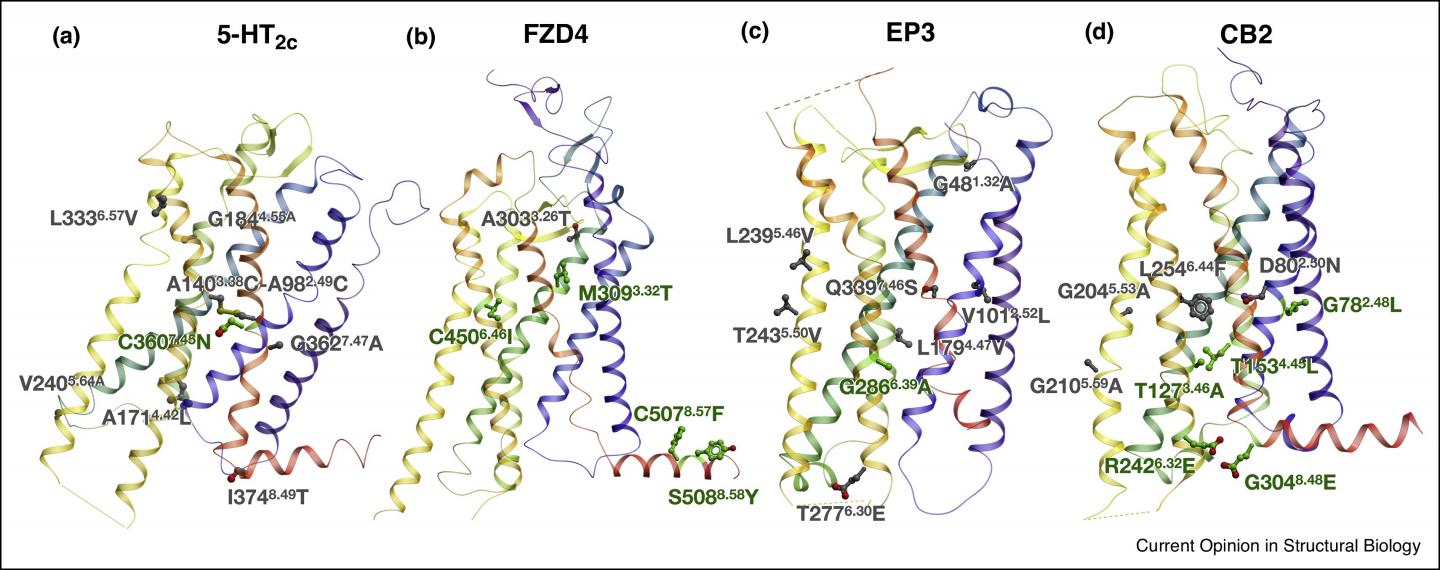
Receptors are molecules that capture and transmit signals and play a key role in the human body regulation. GPCRs are among the best-known human protein families involved in vision, olfaction, immune response, and brain processes, making them an important drug target. For a receptor to serve as a target, the researchers need to understand its structure in great detail, just as a locksmith needs to know the lock’s inner structure to make a key that fits. Studying a receptor that becomes unstable when detached from the cell membrane is a much more challenging task, which is largely facilitated by the computational methods that help to accurately predict the receptor’s soft spots and the changes that will make it more stable.
“The structural studies of GPCRs are of high scientific and applied value, since these proteins are the target for 30 to 40 percent of drugs. Our method relies on several approaches, including machine learning, molecular modeling, and bioinformatics, that are tailored specifically to GPCRs. These approaches are complementary, which enables effectively predicting the smallest possible changes that can enhance the receptor’s stability and make it easier to obtain its molecular structure,” explains professor Petr Popov of MIPT’s Laboratory of Structural Biology of G Protein-Coupled Receptors and the Skoltech Center for Computational and Data-Intensive Science and Engineering.
The new method developed at MIPT, Skoltech, and USC allowed researchers to obtain the structures of four important human receptors, including the cannabinoid receptor involved in brain signal transmission and pain perception, and the prostaglandin receptor implicated in inflammatory processes in the human body. The results of the study were published in the top international science journals Cell and Nature Chemical Biology.
###
Media Contact
Varvara Bogomolova
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




