Credit: RUDN University
A professor from RUDN University together with his colleagues from Saratov Chernyshevsky State University and D. Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology of Russia developed a method for calculating the parameters of diffraction optical elements used in LCDs. In particular, the new technology can be used to expand the angle of view while preserving high resolution and color rendition. The results of the study were published in the Journal of The Society for Information Display.
Each pixel on a display corresponds to a group of three light sources: red, green, and blue. When the brightness of all three diodes is the same, white light is produced; and by changing the share of each respective light, one can achieve different shades of colors. Modern-day displays use liquid crystals to adjust the brightness of light sources. When energized, they turn, and their transparency changes muting some of the colors. This way, a required shade is produced. However, if one looks at a display from an angle, the images may become darker, and color rendition may be distorted. A professor from RUDN University and his colleagues developed a method of calculating the parameters of LCD bases to achieve intended qualities, for example, to expand the angle of view.
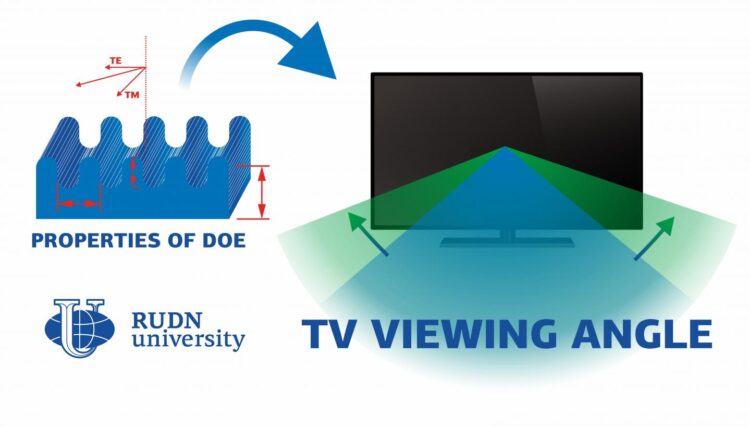
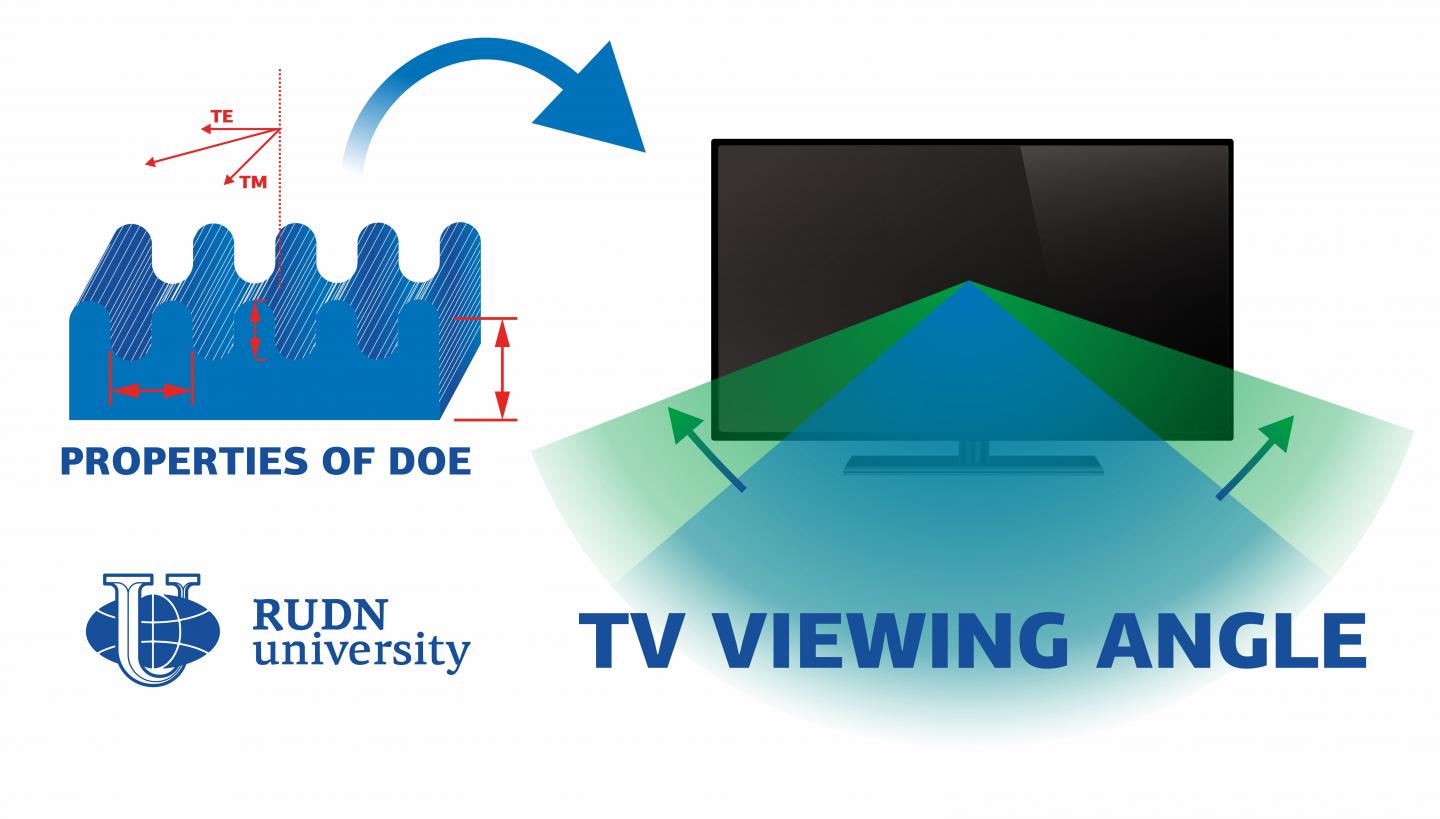
To reduce the impact of an angle of view on image quality, the light in displays undergoes additional processing. Only the beams that are oriented in a certain plane are chosen from a disorderly flux of light. To do so, diffraction optical elements are used. DOE are bases with surface microrelief. It is this relief that determines their optical properties, in particular, the intensity of light that goes through them. The researchers compared three surface reliefs and developed an algorithm for calculating their optical parameters. Previously, similar results had been obtained for crystals with positive optical anisotropy (a parameter that shows the movement of light beams inside a crystal). In his work, the professor from RUDN University studied DOE made of the so-called discotic liquid crystals (DLC) that have negative optical anisotropy.
“Our goal was to calculate diffraction in DOE with negative optical anisotropy. Such elements can be based on discotic liquid crystals. DOE of this type may be used to expand the angles of view of liquid crystal displays,” said Prof. Viktor Belyaev, a Ph.D. in Technical Sciences from the Department of Mechanics and Mechatronics of RUDN University.
The team used DOE with undulated and rectangular periodic profiles. In all elements, the period or waves or rectangular ridges was 2.52 um, and the width of cuts in the rectangular DOE amounted to either 0.63 or 1.25 um. The team chose these values because they were divisible by the wavelength of the incident light (0.63 um for red light). The height of the relief varied from 0.063 to 1.89 um. Using these parameters, the team calculated how the intensity of light depended on the ratio of the period to the height of relief in all three types of DOE. The new algorithm can be used to calculate the parameters of DOE based on specific display requirements.
“We have calculated the effect of the periodic profile of microrelief on diffraction parameters. The method suggested by our team helps calculate relief parameters to achieve the required properties of a spatially inhomogeneous anisotropic structure,” added Prof. Viktor Belyaev from RUDN University.
###
Media Contact
Valeriya Antonova
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.