Light-to-heat conversion has been intensively investigated due to the potential applications including photothermal therapy and solar energy harvesting. Light-to-heat conversion efficiency (LHCE) is the most important figure of merit for evaluating photothermal materials, such as organic molecules, carbon-based materials and nanocrystals. Based on the heat balance equation, a few methodologies have been successfully developed to measure LHCE of colloidal nanocrystal solution. Although, these methods have been further improved by other researchers, the accuracy is still on debate due to overestimation of the mass term of measurement system as well as the imprecision fitting of heat dissipation coefficient. In addition, most of the reported methodologies are limited to colloidal solutions.
Credit: by Kai GU and Haizheng ZHONG
Light-to-heat conversion has been intensively investigated due to the potential applications including photothermal therapy and solar energy harvesting. Light-to-heat conversion efficiency (LHCE) is the most important figure of merit for evaluating photothermal materials, such as organic molecules, carbon-based materials and nanocrystals. Based on the heat balance equation, a few methodologies have been successfully developed to measure LHCE of colloidal nanocrystal solution. Although, these methods have been further improved by other researchers, the accuracy is still on debate due to overestimation of the mass term of measurement system as well as the imprecision fitting of heat dissipation coefficient. In addition, most of the reported methodologies are limited to colloidal solutions.
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, Kai GU and Haizheng ZHONG from Beijing Institute of Technology have developed a general methodology to measure the LHCE of solid materials. They proposed a photothermal and electrothermal equivalence (PEE) method that simulates the laser heating process with electric heating process. In electrothermal measurement, the heat dissipation coefficient of the sample can be derived under a known electric power by performing a linear fitting at thermal equilibrium. In photothermal measurement, the maximum temperature change of the sample is monitored under laser heating to calculate the LHCE. The versatility of the PEE method was investigated for various organic and inorganic photothermal materials, including Au nanorods, graphene and PbSe nanocrystals, etc. Furthermore, they discussed the error and reliability of the PEE method and deviations from assumptions to demonstrate the advantages of the PEE method.
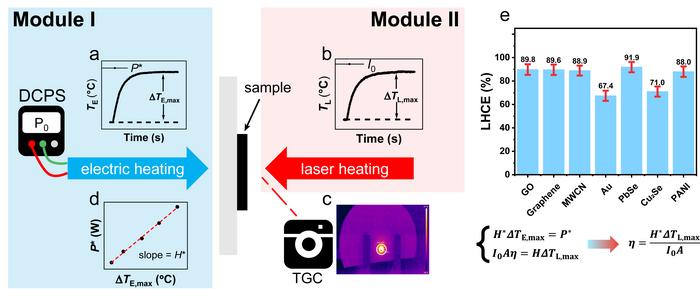
The PEE method consists of two steps: electrothermal measurement (Module I) and photothermal measurement (Module II), as shown in Fig.1. Electrothermal measurement was accomplished by determining the temperature increase of the sample on a resistor using a thermographic camera (TGC). Similarly, photothermal measurement was accomplished by determining temperature increase of the sample under laser heating. By plotting the curve of temperature evolution versus time (Fig. 1a and 1b), the maximum temperature change can be obtained by monitoring the average temperature using TGC (Fig. 1c). Heat dissipation coefficient of the sample can be derived by linearly fitting the plots of the maximum temperature change and the input power of electric heating (Fig. 1d). With the considerations of light absorbance and heat dissipation coefficient, the LHCE of the sample can be derived from the equation in Fig. 1 using heat balance equation. To demonstrate the applicability of the PEE method, we measured the LHCE of Au nanorods, PbSe nanocrystals, Cu2Se nanocrystals, multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCN), graphene oxide (GO), graphene and polyaniline (PANI), as shown in Fig.1e. Details of the error and assumption analysis can be found in the paper.
In summary, we have developed a robust and reliable method to measure the LHCE of solid materials, which have potential to promote the fundamental research of advanced photothermal materials.
Journal
Light Science & Applications
DOI
10.1038/s41377-023-01167-6




