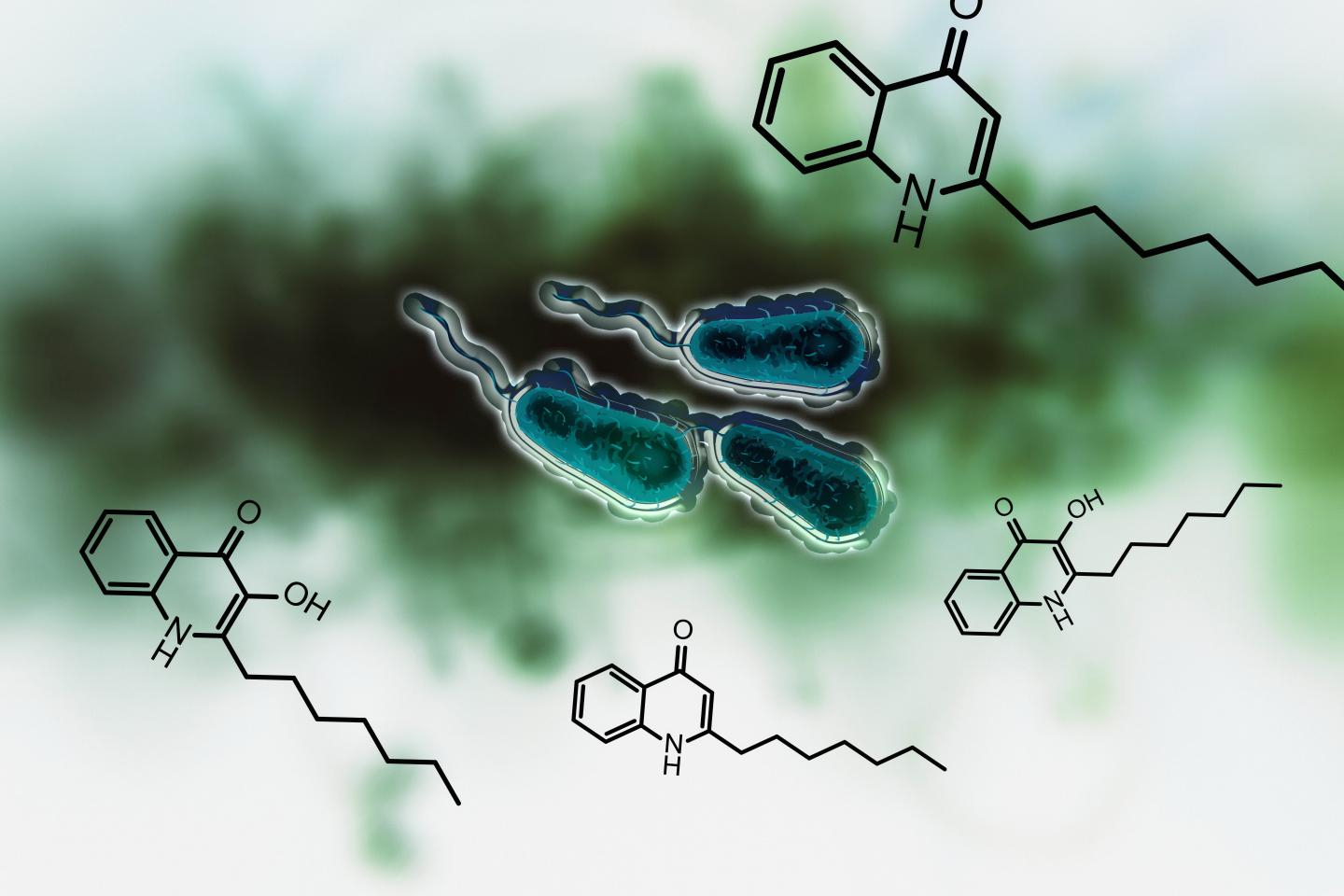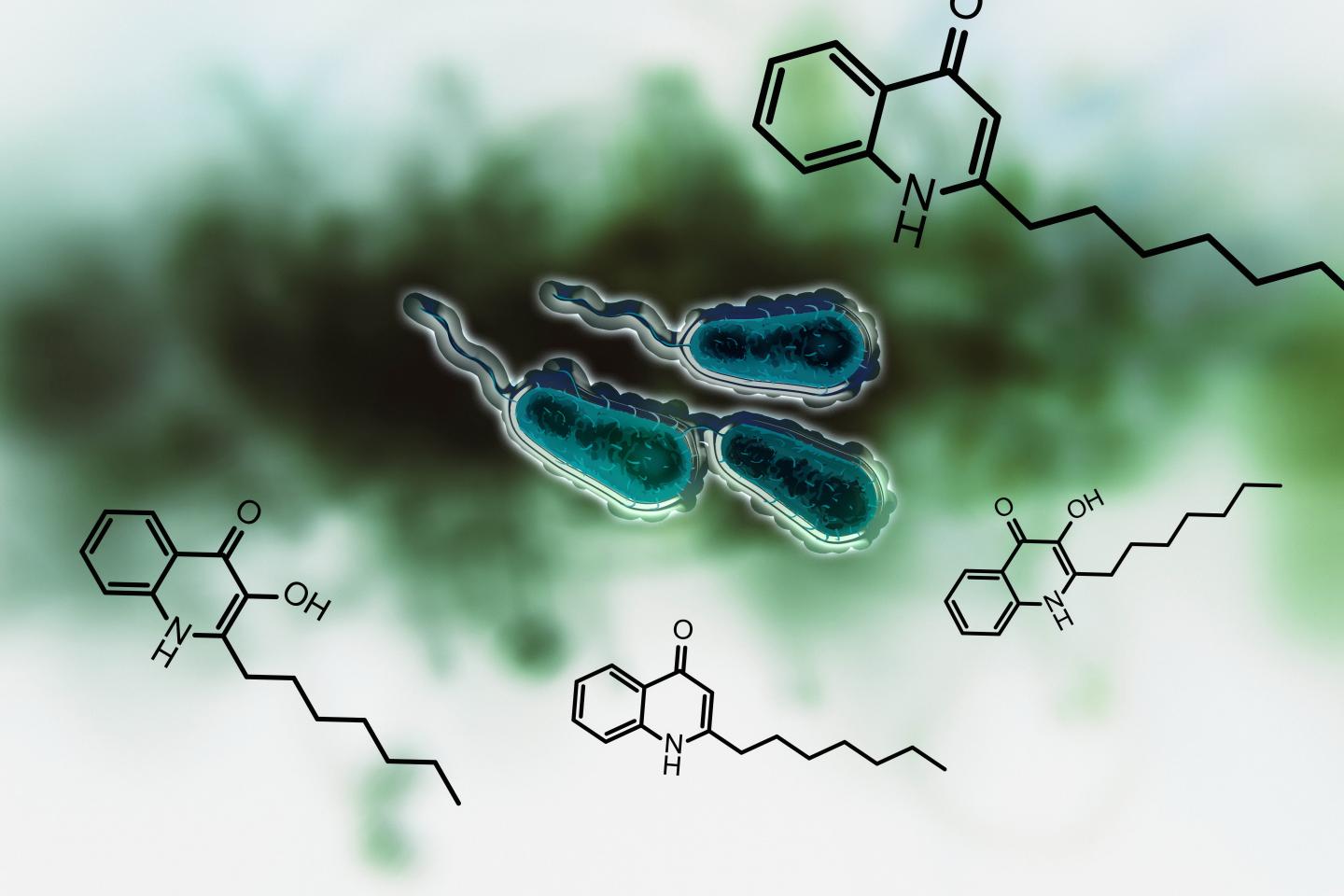
Credit: AG Böttcher
The World Health Organization (WHO) considers Pseudomonas aeruginosa a germ requiring urgent action to prevent and control its spread. The bacteria can cause a variety of diseases from chronic lung infections to sepsis. As a result of its increasing resistance to many antibiotics, such infections are often life-threatening. Instead of trying to develop a new antibiotic to combat Pseudomonas aeruginosa, chemist Dr Thomas Böttcher and his team in Konstanz have focused their research efforts on inhibiting virulence factors in the germ. These include toxins and other agents which benefit the infection process. To this aim, the research team developed a technique which is able to measure the inhibition of enzymes directly in a living cell. The method is described in the current issue of the renowned Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
Thomas Böttcher and Konstanz-based doctoral researcher Michaela Prothiwa concentrated their efforts on a specific metabolic pathway in the bacteria which is responsible for the biosynthesis of signals called quinolones. Pseudomonas aeruginosa uses these signals to coordinate the production of virulence factors. Quinolones hereby act as quorum sensing signals: The bacteria use these molecules to quantify their cell number or population density, much like the method used to determine a majority vote. If the quinolones signal that their number and density is large enough, then the bacteria begin to produce virulence factors. These are responsible for the infectious properties of the bacteria.
The aim of the Konstanz research team is to shut down this quinolone-based communication. The enzyme PqsD plays a central role in the biosynthesis of quinolones. The researchers were able to develop a molecule that can be used to inhibit the enzyme and thus to prevent the bacteria from producing quinolones that help the bacteria to determine their population density. Inhibition of the signal renders them unable to produce toxins and virulence factors. "We are disrupting the communication between the microorganisms", says Thomas Böttcher.
For this purpose, his team of chemists at the University of Konstanz developed a new method of searching for enzyme inhibitors. Until now, enzyme inhibitors had typically been developed in cell-free systems and had often proved ineffective in living cells. A novel strategy using chemical probes now makes it possible to measure the inhibition of an enzyme directly in a living cell. Libraries of chemical compounds can now be tested to discover inhibitors for specific metabolic pathways in bacteria. The strategy is not limited to the enzyme PqsD only. In the future, it will also be used for the specific development of inhibitors that target other bacterial metabolic pathways.
Another publication from Thomas Böttcher's research team appears in Chemistry – A European Journal and focuses on virulence factors and a drug considered an "essential medicine" by the WHO. This research aims to understand why some enzymes in bacteria produce small siderophores made of either two or three building blocks.
The metabolites produced by cyclization of two building blocks include virulence factors for diseases affecting fish and insects, while a larger compound consisting of three building blocks is in one of the most important drugs used worldwide. This drug is utilized during blood transfusions or to treat diseases caused by excess iron in the bloodstream. Along with doctoral researcher Sina Rütschlin, Thomas Böttcher developed a new model to explain how these siderophores are produced with either two or three building blocks. The future goal is to be able to customize enzymes optimized for the production of these chemical agents.
###
Key facts:
* Original publication: Michaela Prothiwa, Felix Englmaier, and Thomas Böttcher: Competitive Live-Cell Profiling Strategy for Discovering Inhibitors of the Quinolone Biosynthesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140 (43). https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.8b07629
* Inhibiting the infectious properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, one of the most commonly found germs in health care facilities worldwide, by disrupting the biosynthesis of a bacterial signal
* A new technique for measuring enzyme inhibition in living cells provides the basis for developing new customized inhibitors
* Funding provided by the Emmy Noether Programme and the Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung (Carl Zeiss Foundation)
Original publication:
Sina Rütschlin and Thomas Böttcher: Dissecting the mechanism of oligomerization and macrocyclization reactions of NRPS independent siderophore synthetases. Chem. Eur. J., 2018, 24. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201803494
* Research on why some enzymes in a bacteria produce siderophores made of two building blocks and other enzymes produce siderophores made of three building blocks.
* The metabolites produced by cyclization of two building blocks include virulence factors for diseases affecting fish and insects, while structures consisting of three building blocks are in one of the most important drugs used worldwide.
* Funding provided by the Emmy Noether Programme and the Konstanz Research School Chemical Biology (KoRS-CB).
Note to editors:
You can download a photo here:
https://cms.uni-konstanz.de/fileadmin/pi/fileserver/2018/Bilder/Strategische_Kommunikationsst%C3%B6rung.jpg
Caption: Schematic representation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Copyright: AG Böttcher
Contact
University of Konstanz
Communications and Marketing
Phone: + 49 7531 88-3603
E-Mail: [email protected]
Media Contact
Julia Wandt
[email protected]
https://cms.uni-konstanz.de/en/university-of-konst
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b07629