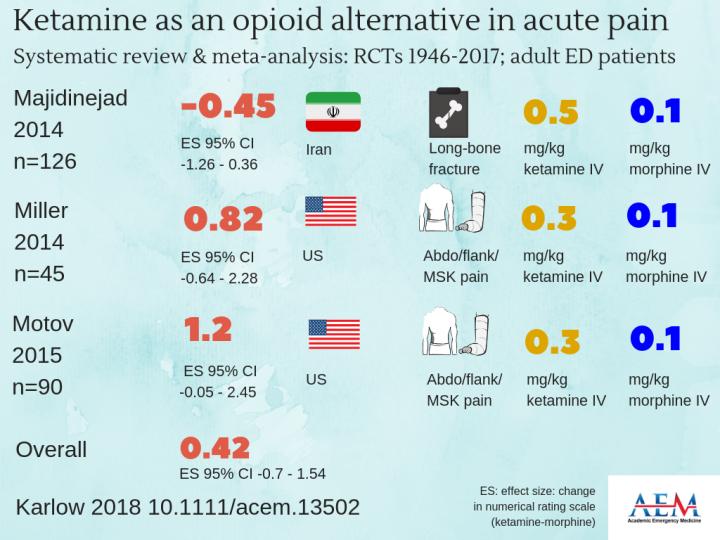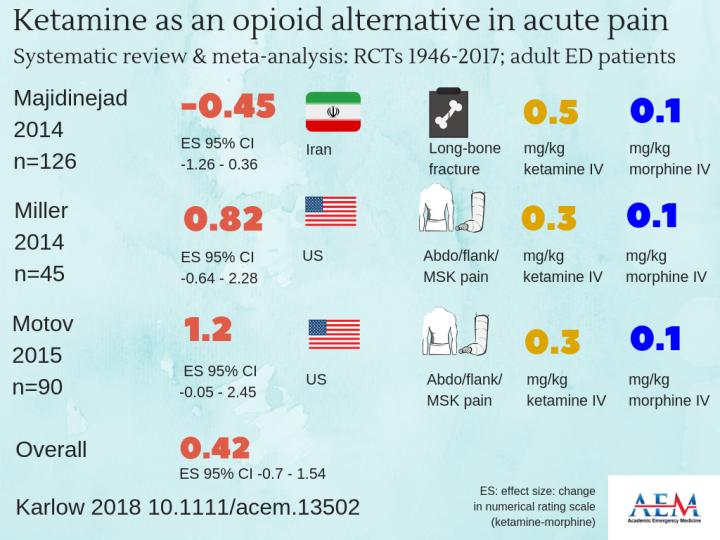
Credit: KIRSTY CHALLEN, B.SC., MBCHB, MRES, PH.D., LANCASHIRE TEACHING HOSPITALS, UNITED KINGDOM.
DES PLAINES, IL — Intravenous, low-dose ketamine (LDK) is as effective as intravenous morphine in the control of acute pain in adults in the emergency department (ED). That is the finding of a study to be published in the October 2018 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM). The results indicate that ketamine can be considered as an alternative to opioids for ED short-term pain control.
The lead author of the study is Nicholas Karlow, MPHS, a medical student at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri. The findings of the study are discussed in the featured episode of SGEM Hop (Skeptics Guide to EM Hot Off the Press).
The systematic review and meta-analysis by Karlow, et al. maintains that there is a role for opioids in the treatment of pain in the ED, but suggest that as physicians continue to face pressure to reduce opioid use, it is important to establish that alternatives such as ketamine are comparable in providing patients with appropriate analgesia in a similar time frame.
The study further suggests that for patients with opioid use disorders or substance use disorders that require a potent analgesic in the emergency department, ketamine may be a favorable option compared to an opioid.
Moving forward, the authors suggest that observational studies assessing adverse events should use similar outcome measures and time frames, and that researchers should explore patient and physician satisfaction with ketamine analgesia and side effects compared to other opioid alternatives for acute pain.
"Karlow and colleagues provide persuasive evidence that emergency physicians can reasonably expect sub-dissociative ketamine to be as effective as morphine for patients with acute abdominal or musculoskeletal pain. Minor ketamine adverse effects will likely prevent this therapy from becoming routinely first line, but low dose ketamine represents a good alternative choice for selected patients," commented Steven M. Green, MD, professor of emergency medicine and residency director at Loma Linda University, California.
Dr. Green's principal research interest has been on procedural sedation and analgesia, with numerous studies of ketamine dating back to 1990 and more recent works relating to sedation's optimal practice, politics, and future. He is a deputy editor at Annals of Emergency Medicine journal.
###
About Academic Emergency Medicine
Academic Emergency Medicine, the monthly journal of Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, features the best in peer-reviewed, cutting-edge original research relevant to the practice and investigation of emergency care. The above study is published open access and can be downloaded by following the DOI link: https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.13502. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Stacey Roseen at [email protected].
About the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine
SAEM is a 501(c)(3) not-for-profit organization dedicated to the improvement of care of the acutely ill and injured patient by leading the advancement of academic emergency medicine through education and research, advocacy, and professional development. To learn more, visit saem.org.
Media Contact
Stacey Roseen
[email protected]
708-606-7120
@SAEMonline
http://saem.org
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/acem.13502