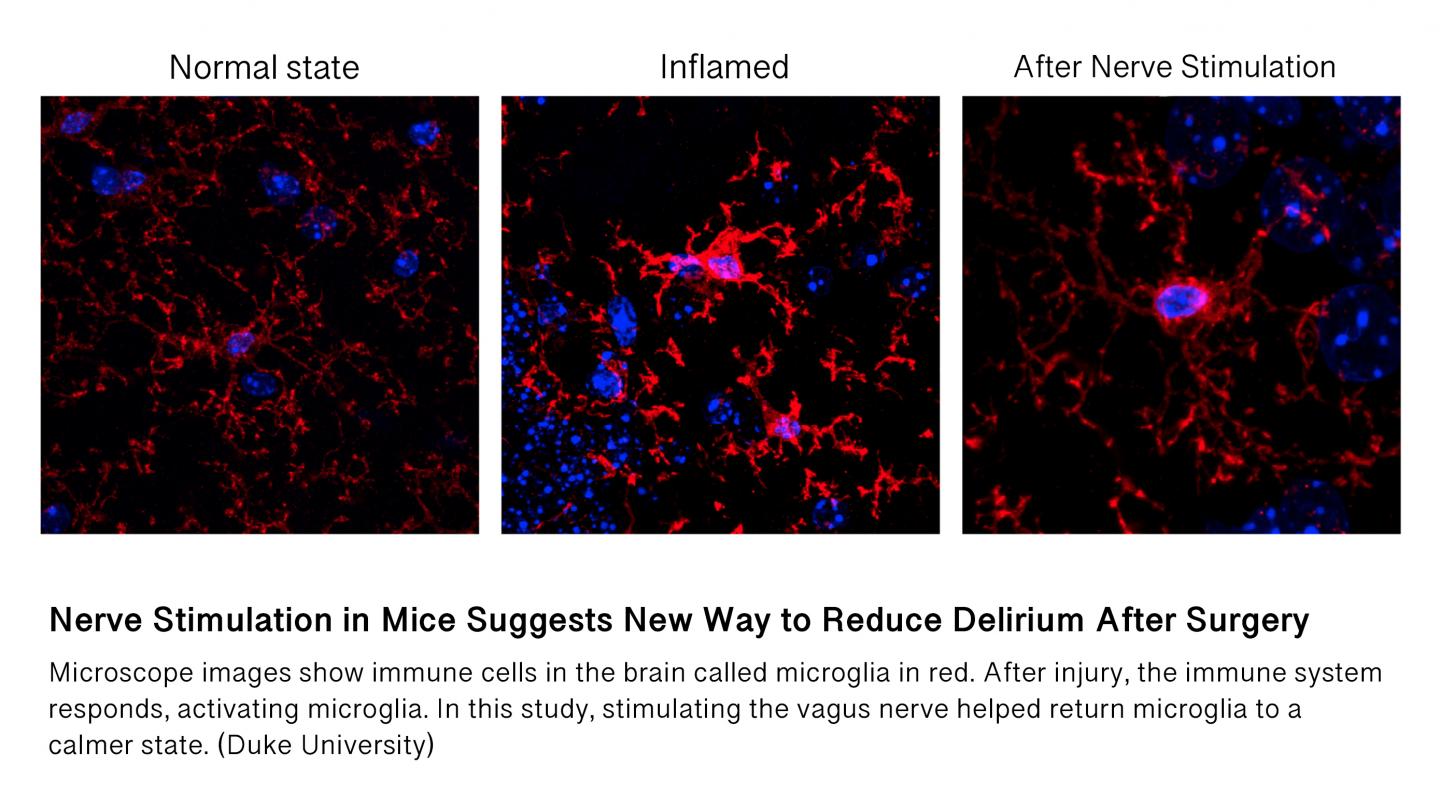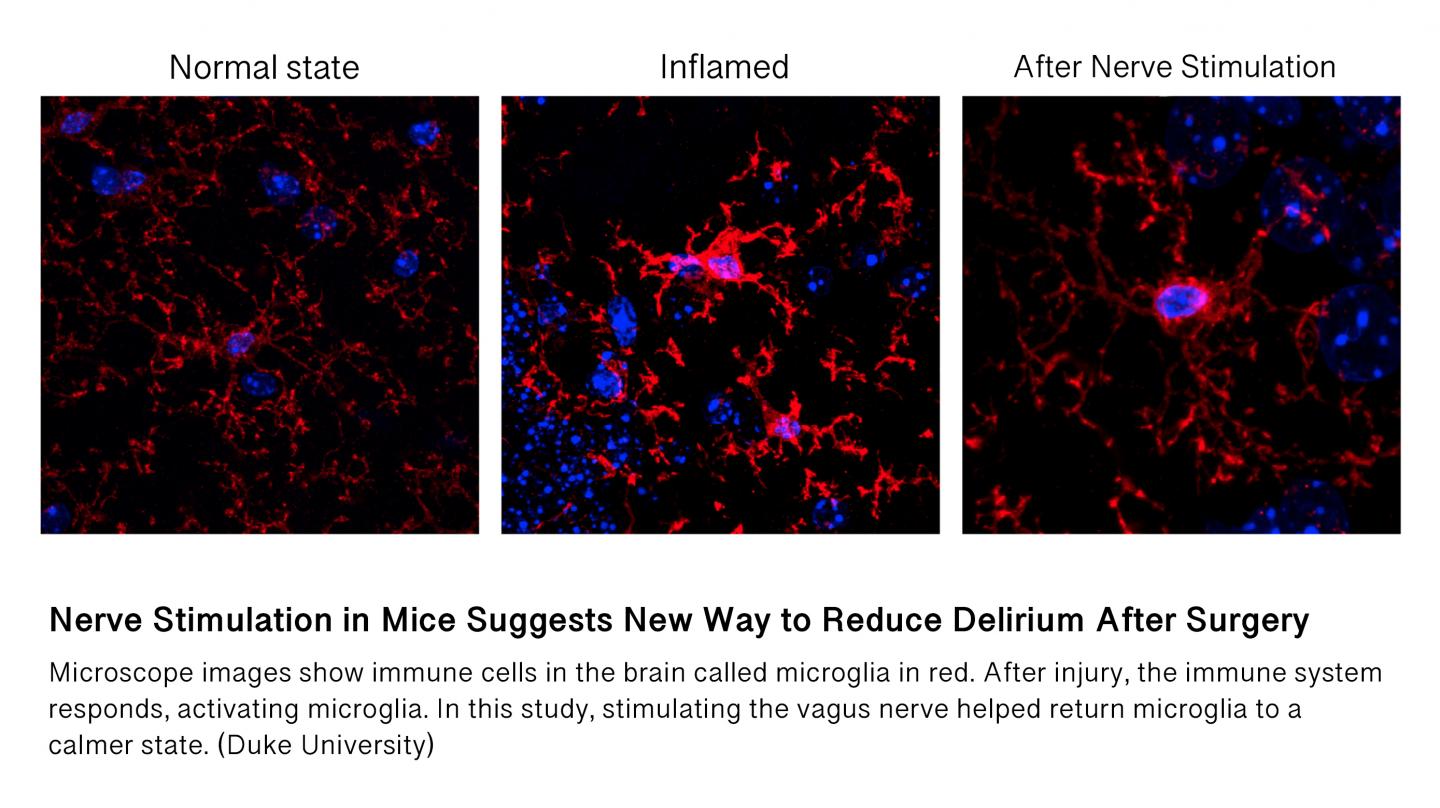
Credit: Duke University
For adults over age 65, surgical complications can dampen not only their physical health but also their mental sharpness, with more than half of high-risk cases declining into delirium.
In research published this week in the journal Brain Stimulation, Duke University scientists show in a mouse model that a current treatment for seizures can also reverse brain inflammation, such as inflammation after surgery, and the subsequent confusion or cognitive decline that results.
The therapy involves minimally invasive stimulation of the vagus nerve using small electrical pulses comparable to a cell phone's vibrations.
The scientists used a Doppler ultrasound to guide the placement of a needle that delivers the electrical pulse, avoiding nearby delicate structures such as the carotid artery. Researchers hope to refine the technique into a completely non-invasive approach to preventing cognitive decline when seniors and other at-risk patients have surgery.
"Delirium is now recognized as the most common complication in older adults after surgery," said Niccolò Terrando, Ph.D., associate professor of anesthesiology at Duke and the study's senior author. "For most patients, it lasts a few days and resolves on its own. For some, it can lead to severe complications and even contribute to long lasting cognitive deficits, like dementia."
Terrando noted that these cognitive complications have a huge impact on quality of life and can be expensive, with health care costs for delirium reaching $164 billion a year according to the American Society of Anesthesiologists.
"So far, there is no therapy for this kind of cognitive complication after surgery," Terrando said. Anti-inflammatory drugs have many side effects and work broadly, he said, and they don't adequately target the inflammation in the brain that scientists believe triggers cognitive complications.
The vagus nerve helps the brain communicate with the heart, lungs, gut and other parts of the body. Vagus nerve stimulators have been surgically implanted in epilepsy patients for more than 20 years to reduce seizures.
In recent years, U.S. doctors have also prescribed at-home, non-invasive stimulators for severe headaches. However, there is not substantial evidence that the devices are stimulating the vagus nerve and not other structures near it, said Warren M. Grill, Ph.D., professor of biomedical engineering at Duke.
For the experimental model, mice with inflammation received one nerve-stimulating treatment lasting several minutes. The researchers monitored for signs of vagus nerve activation, such as a slower heart rate and twitching of muscles around the larynx, and found improved cognitive outcomes and reduced brain inflammation after this treatment.
"This minimally invasive approach is already exceedingly benign, but in the long term it would be desirable to have an entirely non-invasive approach and we are beginning that work," Grill said.
###
In addition to Terrando and Grill, study authors include William J. Huffman, Saraswathi Subramaniyan, Ramona M. Rodriguiz, and William C. Wetsel.
The research was supported by the Duke Institute for Brain Sciences Incubator Award (2016-18), a Duke University School of Medicine voucher for studies conducted in the Mouse Behavioral and Neuroendocrine Analysis Core Facility (#1163), and by the National Institutes of Health R01AG057525 and R21AG05587701A1. The researchers disclosed no financial conflicts related to this work.
Media Contact
Samiha Khanna
[email protected]
919-419-5069
@DukeHealth
http://dukehealthnews.org
Original Source
https://corporate.dukehealth.org/news-listing/nerve-stimulation-mice-suggests-new-way-reduce-delirium-after-surgery http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2018.10.005