Credit: HKBU
A study by Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU) has detected an extensive amount of sunscreen chemicals in seawater that could pose a risk to human health. The study, a world-first in identifying the harm caused by a combination of polluting chemicals in sunscreen, found the chemicals can cause abnormalities in and kill the offspring of zebrafish by entering the food chain. As the genetic structure of zebrafish resembles that of humans, the results imply that these contaminants could pose a risk to humans. The study also revealed that these contaminants are commonly found in the coastal waters of Hong Kong.
The team was led by Dr Kelvin Leung Sze-yin, Associate Professor of the Department of Chemistry of HKBU. The team collected seawater samples from 30 locations off the Hong Kong coast. Seven commonly used organic UV (ultra-violet) filters, the active ingredients in sunscreens, were investigated. The team also collected fish, shrimps, mussels and other wild organisms from seven local aquaculture farms around Hong Kong. The team found the presence of UV filters in concentrations ranging from 3.1 to 51.3 nanograms in each gram of the samples. The findings indicated that the UV filters that accumulated in marine life could possibly pass up the food chain to humans and affect our health.
The team collected the samples at depths of two metres in the sea, extracted the samples using the "solid phase extraction" method followed by highly sensitive instrumental analysis, a process designed to obtain reliable environmental data of UV filters.
The team simulated the real aquatic environment in a laboratory where contaminated artemia were fed to zebrafish for 47 days. The contaminated water contained three commonly used UV filters, namely benzophenone-3 (BP-3), ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate (EHMC) and octocrylene (OC).
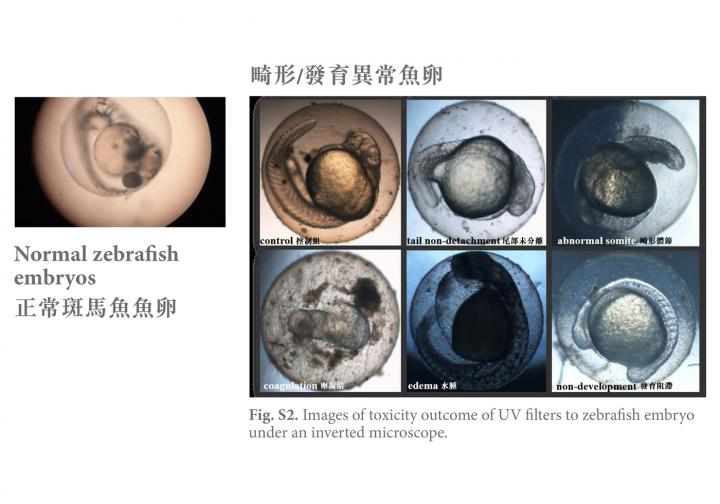
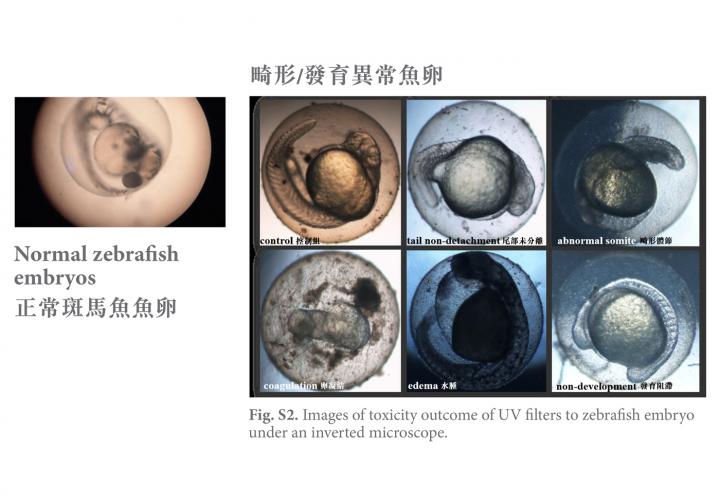
After 47 days, none of the adult zebrafish appeared to be damaged, but several of their embryos were found to have malformations or abnormalities. The embryos' 24-hour mortality rate increased dramatically, from 10 % to nearly 60%, while the 72-hour hatching rate decreased significantly, from 80% to less than 30%.
Dr Kelvin Leung said the study found that the combined presence of BP-3, EHMC and OC creates "a mixture effect" that increases their accumulation compared with the case when only one chemical is present. This increase was particularly marked in zebrafish. "Since more than 70% of the genetic structure of zebrafish resembles that of humans, the effect of these contaminants passing along the food chain to humans and the long-term impact on human fertility cannot be neglected." he added.
Dr Leung said, "UV light increases the risk of premature skin ageing, freckles and triggers skin cancer. Organic or chemical UV filters that can absorb or block UV radiation, are extensively applied in personal care products including sunscreens. Besides, UV filters are also widely found in textiles, plastics and rubber as protection against photo-degradation."
Dr Leung added, "After human use, the organic/chemical UV filters in sunscreens are discharged into the sea either directly by being washed off with sea water or indirectly through discharge of wastewater. Eventually they enter the sea, thereby posing a threat to marine organisms and the ecosystem."
Dr Leung called for regulations to cover the use of chemicals in personal care products and said more research should be done on the long-term impact of these contaminants. He recommends the usage of natural, mineral-based sunscreens, for instance, Titanium dioxide and Zinc oxide.
###
The study was published in the renowned academic scientific journal Environmental Science & Technology.
Media Contact
http://www.hkbu.edu.hk
Original Source
https://cpro.hkbu.edu.hk/en/press_release/detail/91/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02418