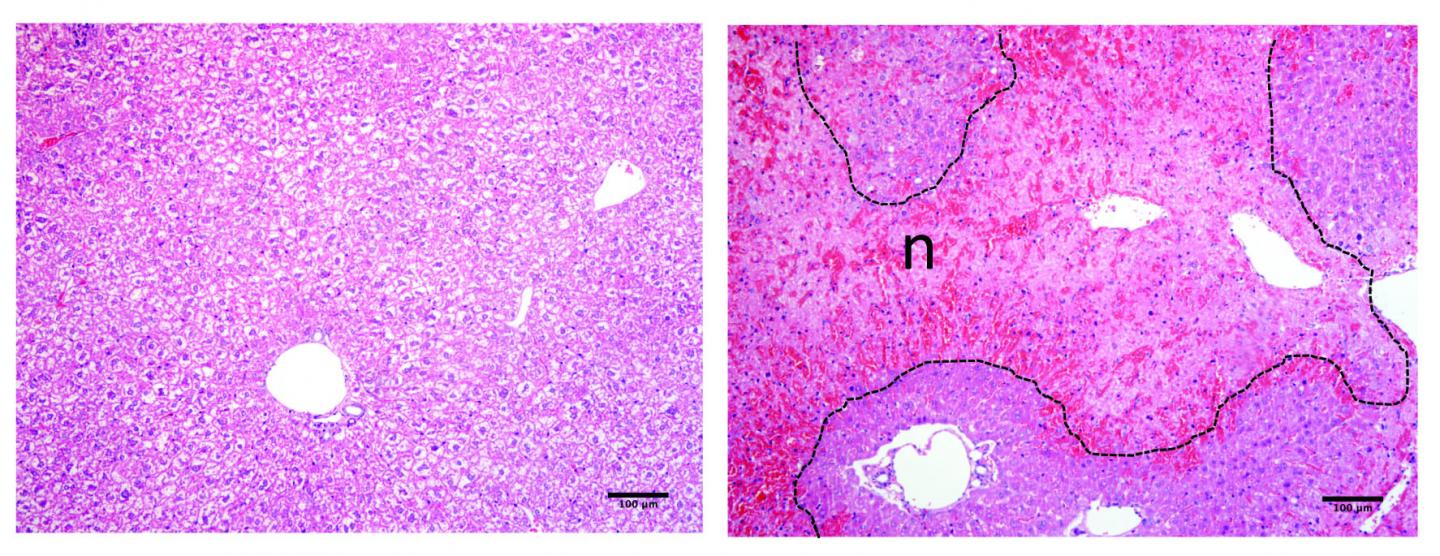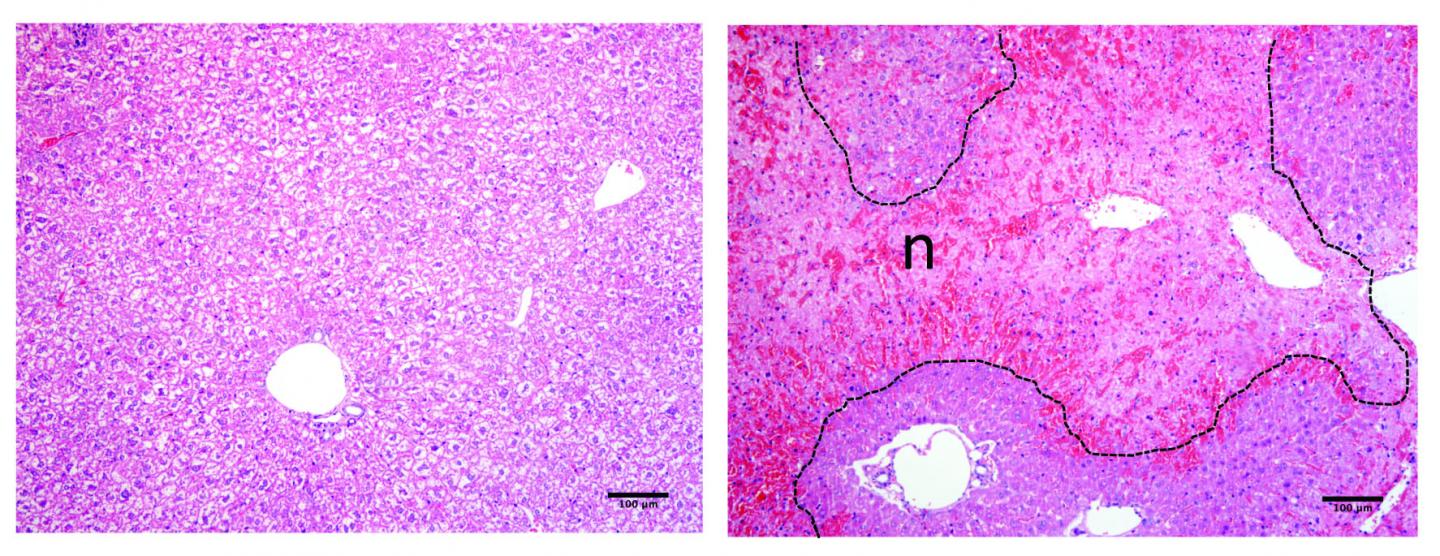
Credit: Nádia Duarte, IGC.
A new study from researchers of CEDOC-NOVA Medical School|Faculdade de Ciências Médicas and Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência, led by Maria Paula Macedo and Carlos Penha-Gonçalves, respectively, published in Hepatology Communications, showed that a molecule CD26/DPP-4 is involved in the regeneration of acute liver wounds and is a promising biomarker for hepatic disease.
It is known that DPP-4 regulates insulin secretion upon food intake. The regulation of the levels of "sugar in the blood" in type-2 diabetics is performed by therapeutic inhibition of enzymatic activity of the molecule CD26/DPP-4. This approach has earned clinical relevance. Moreover, apart from its role in the control of the amount of sugar present in blood, the molecule DPP4 appears to be related with inflammatory reactions in various pathological processes.
In this study, the researchers explored the role of CD26/DPP-4 during injury of the hepatic tissue leading to evident reduction of the main liver immune cell population (Kupffer cells). It was shown that the blood levels of CD26/DPP-4 enzymatic activity are augmented when this population of liver immune cells is diminished, both in acute and chronic mouse models of liver injury. Inversely, the levels of blood enzymatic activity decreased during recovery of these cells. The authors observed that specific deletion of such immune liver cell population in absence of liver tissue damage also lead to significant increase in CD26/DPP4 blood enzymatic activity. Thus, these results show the close relation between functional changes in Kupffer cells associated with hepatic diseases and the molecule CD26/DPP-4.
The relation between the liver immune cells and the enzymatic activity of CD26/DPP-4 in the blood, exhibited in this study, suggests that the level/amount of the enzymatic activity of the molecule CD26/DPP-4 in the blood might be used as a biomarker. Moreover, it can become a valuable biochemical parameter for the evaluation of hepatic lesion or disorder since so far can this evaluation can only be performed using invasive techniques.
###
This study was supported by the institutions mentioned above, FCT (Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia), SPD (Sociedade Portuguesa de Diabetes) and the European Commission.
Media Contact
Ana Mena
[email protected]
351-214-407-959
@IGCiencia
http://www.igc.gulbenkian.pt
Original Source
http://www.igc.gulbenkian.pt/pages/article.php/A=431___collection=pressReleases___year=2018 http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1225