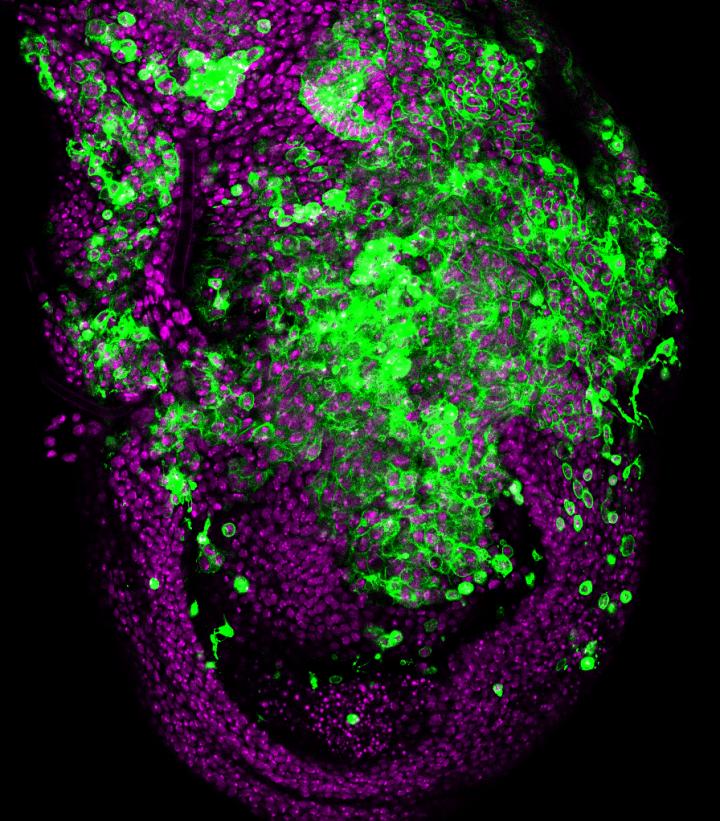
Credit: Lara Barrio, IRB Barcelona
Metastatic tumours are characterised by a high degree of chromosomal instability–that is to say a constant change in the number and structure of chromosomes they hold. In spite of this observation, it is unknown whether chromosomal instability contributes to the metastatic process. A study at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) using Drosophila melanogaster has demonstrated that chromosomal instability itself can induce invasive behaviour in epithelial cells and has identified the underlying molecular mechanisms involved.
To perform this study, the team directed by ICREA researcher Marco Milán generated a fruit fly model with chromosomal instability. "The cells started to actively invade adjacent tissues," explains Marco Milán, group leader of the Growth Control and Development lab at IRB Barcelona and head of the study.
The aim was to study whether chromosomal instability itself has the capacity to stimulate invasive behaviour in epithelial cells. The results published in Developmental Cell indicate that indeed this is the case and they describe a series of molecular and cell mechanisms that favour cell migration and invasion of other tissues. In particular, the researchers have demonstrated that invasive cells use the actin cytoskeleton and activate the ERK and JNK signalling pathways to trigger a pro-invasive transcriptional programme executed by the oncogene Fos and repressed by the tumour suppressor Capicua.
"These findings are relevant in the context of cancer because they highlight the causal relationship between aneuploid genes and cell invasion and they identify the molecular elements involved in the process," say Najate Benhra and Lara Barrio, first authors of the study and postdoctoral researchers at IRB Barcelona. Milán adds, "the results increase our understanding of the effects of chromosomal instability on the metastatic potential of solid human tumours and identify molecular targets for the development of future treatments".
###
This research has been funded by the Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities.
Reference article: Najate Benhra, Lara Barrio, Mariana Muzzopappa, and Marco Milán
Chromosomal instability induces cellular invasion in epithelial tissues
Developmental Cell (2018) doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2018.08.021
Marco Milán laboratory: https://www.irbbarcelona.org/en/profile/marco-milan
Media Contact
Sònia Armengou
[email protected]
34-934-037-255
http://www.irbbarcelona.org
Original Source
https://www.irbbarcelona.org/en/news/a-study-using-drosophila-sheds-light-on-the-metastatic-behaviour-of-human-tumours http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2018.08.021