Credit: David J. McGee, Xiao-Hong Lu and Elizabeth A. Disbrow
Amsterdam, NL, September 24, 2018 – While human genetic mutations are involved in a small number of Parkinson's disease (PD) cases, the vast majority of cases are of unknown environmental causes, prompting enormous interest in identifying environmental risk factors involved. The link between Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) and gastric ulcers has been known for several decades, but new evidence suggests that this harmful bacterium may play a role in PD as well. A new review in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease summarizes the current literature regarding the link between H. pylori and PD and explores the possible mechanisms behind the association.
In a comprehensive review of prior studies, investigators uncovered four key findings:
- People with PD are 1.5-3-fold more likely to be infected with H. pylori than people without PD.
- H. pylori-infected PD patients display worse motor functions than H. pylori-negative PD patients.
- Eradication of H. pylori improved motor function in PD patients over PD patients whose H. pylori was not eradicated.
- Eradication of H. pylori improved levodopa absorption in PD patients compared to PD patients whose H. pylori was not eradicated.
"This is an in-depth and comprehensive review that summarizes all the major papers in the medical literature on Parkinson's disease and H. pylori, the common stomach bacterium that causes gastritis, ulcers and stomach cancer," explained lead investigator David J. McGee, PhD, Associate Professor, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, LSU Health Sciences Center-Shreveport, Shreveport, LA, USA. "Our conclusion is that there is a strong enough link between the H. pylori and Parkinson's disease that additional studies are warranted to determine the possible causal relationship."
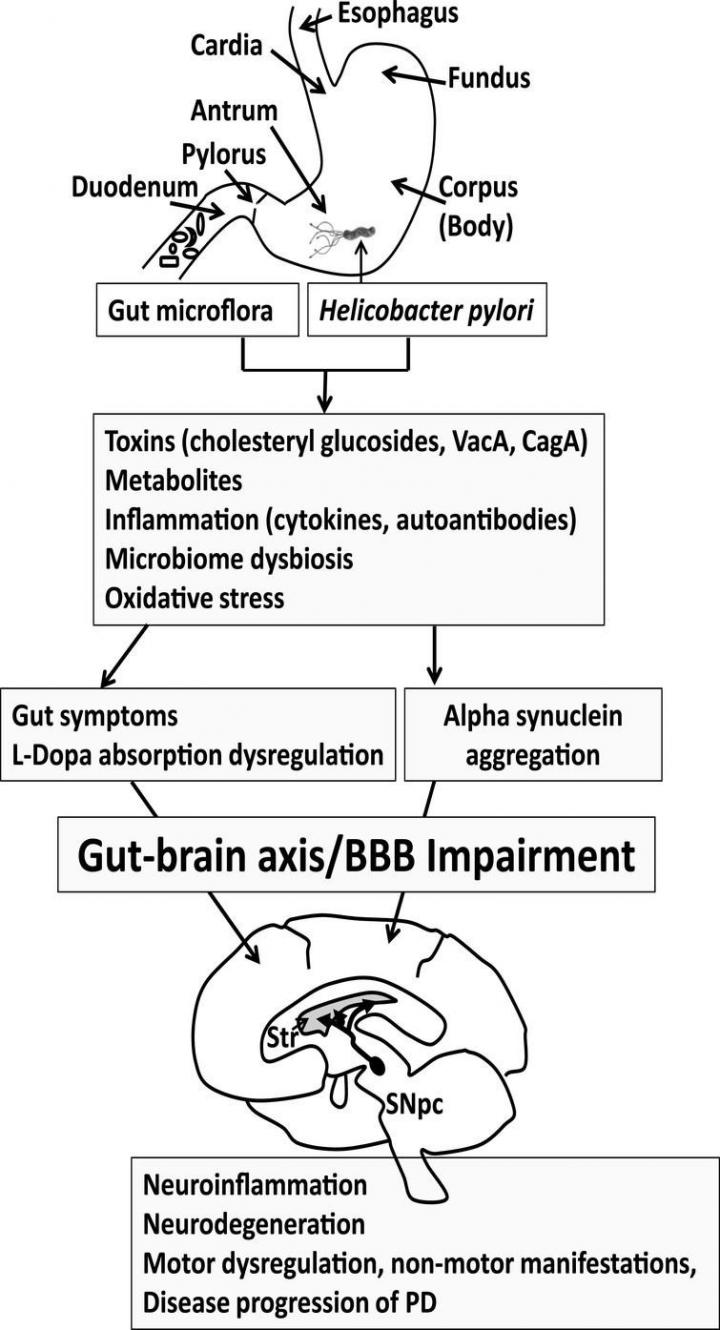
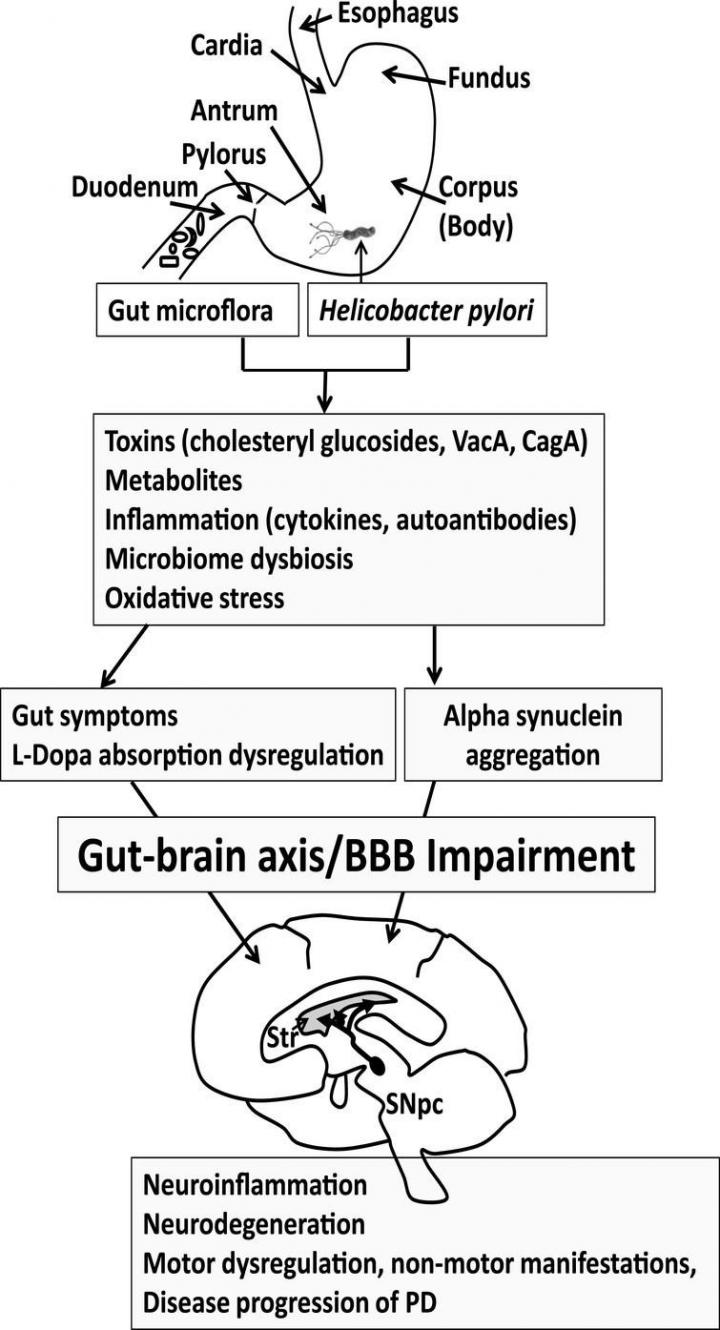
Investigators also analyzed existing studies to try and find possible testable pathways between the bacterial infection and Parkinson's to lay the groundwork for future research. They found four main possible explanations for the association:
- Bacterial toxins produced by H. pylori may damage neurons.
- The infection triggers a massive inflammatory response that causes damage to the brain.
- H. pylori may disrupt the normal gut microbial flora.
- The bacteria might interfere with the absorption properties of levodopa, the medication commonly used to treat the symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
The onset of PD is often preceded by gastrointestinal dysfunction, suggesting that the condition might originate in the gut and spread to the brain along the brain-gut axis. In the review, investigators note that this has been documented in rats.
Screening PD patients for the presence of H. pylori and subsequent treatment if positive with anti-H. pylori triple drug therapy, may contribute to improved levodopa absorption and ultimately improvement of PD symptoms, potentially leading to a longer life span in patients with PD.
"Evidence for a strong association among H. pylori chronic infection, peptic ulceration and exacerbation of PD symptoms is accumulating," concluded Dr. McGee.
"However, the hypotheses that H. pylori infection is a predisposing factor, disease progression modifier, or even a direct cause of PD remain largely unexplored. This gut pathology may be multifactorial, involving H. pylori, intestinal microflora, inflammation, misfolding of alpha-synuclein in the gut and brain, cholesterol and other metabolites, and potential neurotoxins from bacteria or dietary sources. Eradication of H. pylori or return of the gut microflora to the proper balance in PD patients may ameliorate gut symptoms, L-dopa malabsorption, and motor dysfunction."
###
Media Contact
Diana Murray
[email protected]
718-640-5678
@IOSPress_STM
http://www.iospress.com
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/JPD-181327