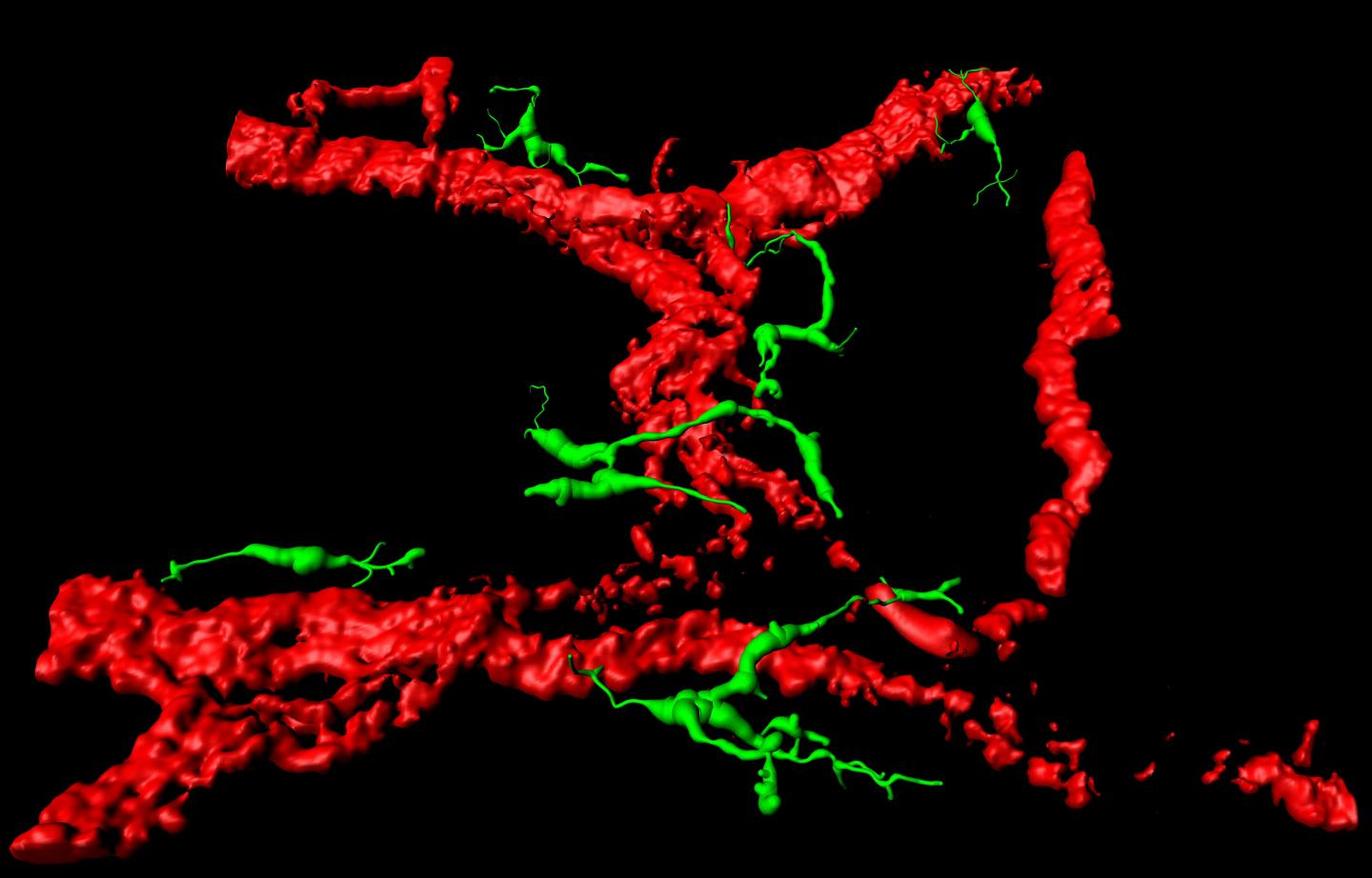
Credit: © TARGID – KU Leuven
Macrophages are specialised immune cells that destroy bacteria and other harmful organisms. KU Leuven scientists, Belgium, have come to the surprising conclusion that some macrophages in the intestines of mice can survive for quite some time. Most importantly, these long-lived macrophages are vital for the survival of the nerve cells of the gastrointestinal tract. This sheds new light on neurodegenerative conditions of the intestine, but also of the brain.
In the immune system macrophages play the role of PacMan: they are white blood cells that clean up foreign substances by engulfing them. Apart from this, macrophages themselves provide vital growth factors and support for different tissues in the body, allowing them to function and develop properly. As such, these specialised immune cells are soldier and nourisher at the same time. Their proper functioning is immensely important in the intestine, as they have to differentiate between harmful bacteria, harmless bacteria and nutritional components.
Scientists assumed that macrophages in the intestine are short-lived and live for about three weeks at most in both mice and humans before being replaced by new cells. A KU Leuven study now shows that this is not entirely true, explains Professor Guy Boeckxstaens. "We've discovered that a small part of the macrophages in mice is long-lived. We marked certain macrophages and found that they still functioned after at least eight months. They can be found in very specific places in the intestine, particularly in close contact with nerve cells and blood vessels."
What is more, the small group of long-lived macrophages play a very important role in the gastrointestinal tract, adds PhD student Sebastiaan De Schepper. "If the long-lived macrophages don't do their job properly, already after a few days the mice suffer from digestive problems. This leads to constipation or even the complete degeneration of the nervous system in the stomach and intestine." The discovery that long-lived macrophages do indeed exist in the intestine and that they are crucial for the normal functioning of the intestine is, therefore, immensely important.
These new insights offer promising opportunities for further research, concludes Boeckxstaens: "Next, we want to study the role of long-lived macrophages in human diseases where nerve cells of the intestine are affected, for instance in obese and diabetic patients with abnormal gastro-intestinal function. Moreover, the results can also be meaningful for brain research. In the brain, we have microglia, similar long-lived macrophages that play an important role in neurological conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Scientists currently believe that nerve cells in these patients die off because microglia do not provide sufficient care. Maybe one day research of the intestine can offer us a better understanding of these brain conditions."
###
About KU Leuven
KU Leuven is Europe's most innovative university in the latest Reuters ranking. Located in Belgium, it is dedicated to research, education, and service to society. KU Leuven is a founding member of the League of European Research Universities (LERU) and has a strong European and international orientation. Its scientists conduct basic and applied research in a comprehensive range of disciplines. The university welcomes more than 50,000 students from over 140 countries. The KU Leuven Doctoral Schools train approximately 4,500 PhD students. http://www.kuleuven.be/english
Media Contact
Guy Boeckxstaens
[email protected]
32-473-678-009
@LeuvenU
http://www.kuleuven.be/english/news?
Original Source
https://nieuws.kuleuven.be/en/content/2018/discovery-of-long-lived-macrophages-in-the-intestine http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.07.048