Credit: KAIST
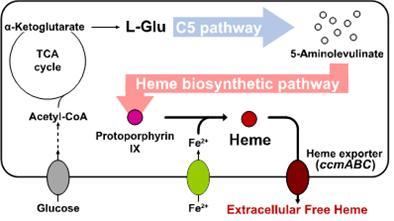
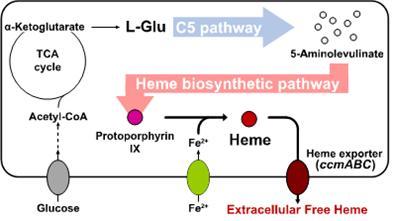
Researchers of KAIST have defined a novel strategy for the secretory production of free haem using engineered Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains. They utilized the C5 pathway, the optimized downstream pathways, and the haem exporter to construct a recombinant micro-organism producing extracellular haem using fed-batch fermentation. This is the first report to extracellularly produce haem using engineered E. coli.
This strategy will expedite the efficient production of free haem to serve as a bioavailable iron-supplying agent and an important prosthetic group of multiple hemoproteins for medical uses. This study, led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, was published in Nature Catalysis on Aug. 28.
Haem, an organometallic compound complexed with a ferrous ion, is an essential molecule delivering oxygen in the blood of many animals. It is also a key component of electron transport chains responsible for the respiration of aerobic organisms including diverse bacteria. It is now being widely applied as a bioavailable iron-supplying agent in the healthcare and dietary supplement industries. The demand for haem and the need for the efficient production of this compound continue to grow.
Many previous researchers have attempted to produce free haem using engineered E. coli. However, none of the studies was successful in producing free haem extracellularly, requiring an additional step to extract the accumulated haem from cells for subsequent uses. The secretion of haem in the form of haem peptides or proteins also requires an extraction step to isolate the free haem from the secreted products. Thus, the secretory production of free haem is an important task for the economical production of haem that is suitable for human consumption.
Although some researchers could produce intracellular haem using recombinant E. coli strains, its final titer was extremely low, resulting from the use of sub-optimal metabolic pathways. Furthermore, the addition of the precursors L-glycine and succinate was deemed undesirable for massive industrial production. Thus, it is necessary to construct an optimized haem biosynthetic pathway to enable the efficient production of haem and examine the consequent secretion of free haem.
To address this issue, the KAIST team used multiple strategies to produce extracellular free haem by enhancing its biosynthesis in E. coli. First, the capacities of the C4 and C5 pathways to produce aminolevulinate (ALA) without feeding precursors were examined. After confirming the superior performance of the C5 pathway over the C4 pathway, the metabolic genes of the C5 pathway and downstream pathways for haem biosynthesis were overexpressed. Then, the metabolic pathways were optimized by adjusting the expression levels of the relevant genes and disrupting the putative haem degradation enzyme encoded by the yfeX gene.
Consequently, the resulting engineered strain secreted a significant amount of haem to the medium. Subsequent optimization of the cultivation conditions and the supplementation of nitrogen sources further increased both the titer of the total free haem and the amount of free haem secreted to the medium. Finally, the overexpression of the ccmABC genes encoding the haem exporter further enhanced the production and secretion of haem, producing the highest titer of haem both intracellularly and extracellularly from glucose.
Professor Lee said, "The eco-friendly and sustainable chemical industry is a key global agenda every nation faces. We are conducting research to bio-synthesize high concentrations, high yields, and high productivity in natural products. This novel technology will serve as an opportunity to advance the biochemical industry moving forward."
###
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NR2012M1A2A2026557) from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Further Contact: Dr. Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea ([email protected], +82-42-350-3930)
Media Contact
Younghye Cho
[email protected]
82-423-502-294
@KAISTPR
http://www.kaist.ac.kr
Original Source
https://www.kaist.ac.kr/_prog/_board/?code=ed_news&mode=V&no=84721&upr_ntt_no=84721&site_dvs_cd=en&menu_dvs_cd=0601 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41929-018-0126-1