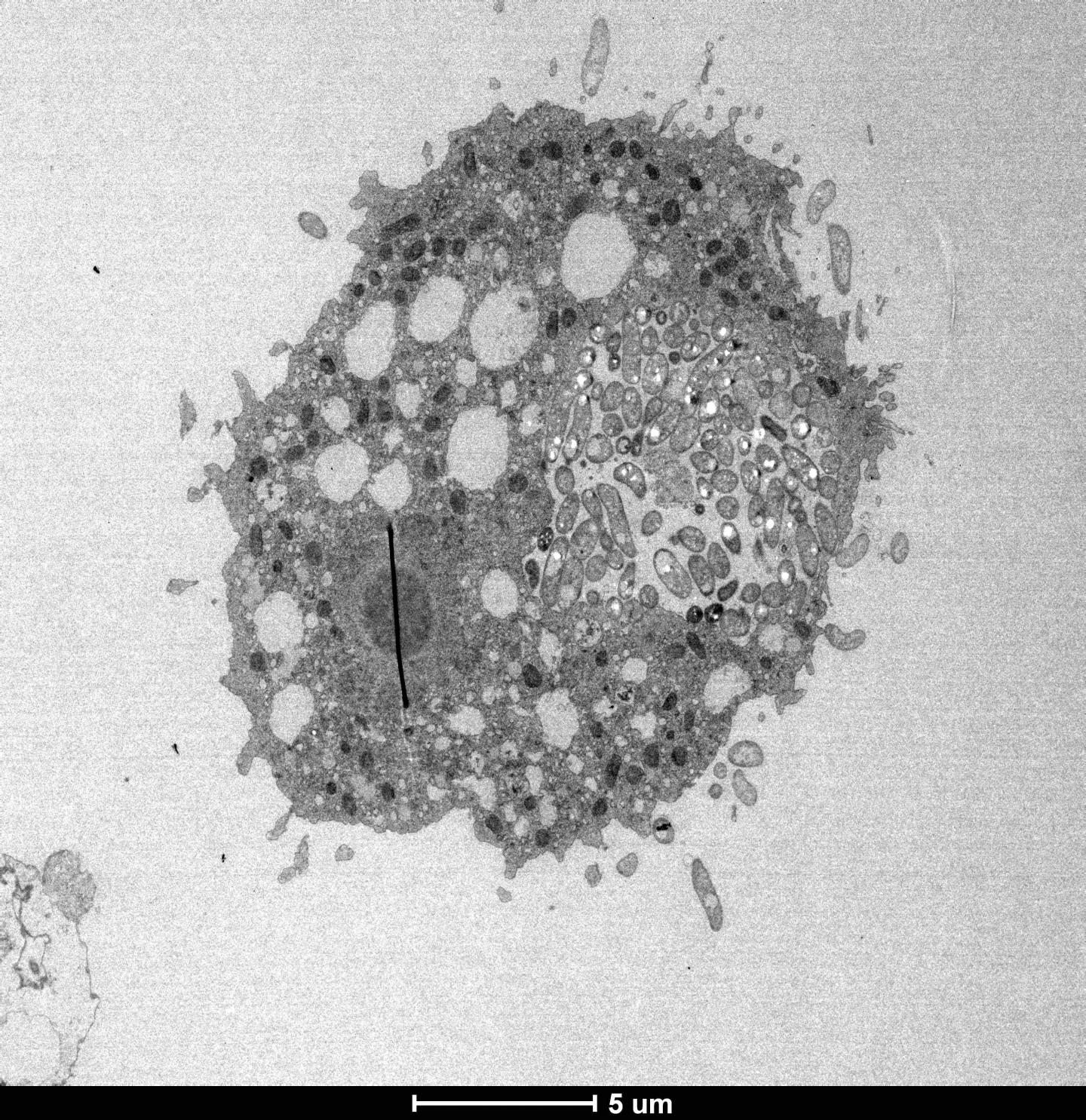
Credit: Blokesch lab and BioEM facility (EPFL)
The cholera-causing bacterium, Vibrio cholerae, is commonly found in aquatic environments, such as oceans, ponds, and rivers. There, the bacterium has evolved formidable skills to ensure its survival, growth, and occasional transmission to humans, especially in endemic areas of the globe.
One of the ways the pathogen defends itself against predatory aquatic amoebas involves "hitchhiking" them and hiding inside the amoeba. Once there, the bacterium resists digestion and establishes a replication niche within the host's osmoregulatory organelle. This organelle is essential for the amoeba to balance its internal water pressure with the pressure exerted by the environment.
In a new study, the group of Melanie Blokesch at EPFL in collaboration with the BioEM facility headed by Graham Knott has deciphered the molecular mechanisms that V. cholerae uses to colonize aquatic amoebas. The researchers demonstrated that the pathogen uses specific features that allow it to maintain its intra-amoebal replication niche and to ultimately escape from the succumbed host. Several of these features, including extracellular enzymes and motility, are considered minor virulence factors as they also play a role in human disease.
The study suggests that the aquatic milieu provides a training ground for V. cholerae and that adaptation towards amoebal predators might have contributed to V. cholerae's emergence as a major human pathogen.
"We are quite excited about these new data, as they support the hypothesis that predation pressure can select for specific features that might have dual roles – in the environment and within infected humans," says Blokesch. She also highlights that continuous funding by the ERC (StG & CoG) has been crucial for this project, "as studying the environmental lifestyle of the pathogen is a bit outside the mainstream research on pathogenesis".
###
Reference
Charles Van der Henst, Audrey Sophie Vanhove, Natália Carolina Drebes Dörr, Sandrine Stutzmann, Candice Stoudmann, Stéphanie Clerc, Tiziana Scrignari, Catherine Maclachlan, Graham Knott, Melanie Blokesch. Molecular insights into Vibrio cholerae's intra-amoebal host-pathogen interactions. Nature Communications 27 August 2018. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05976-x
Media Contact
Nik Papageorgiou
[email protected]
41-216-932-105
@EPFL_en
http://www.epfl.ch/index.en.html
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05976-x