Credit: Shihong Yue
In a paper published in NANO, a group of researchers have developed a simple flame burning method to prepare single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) sponges on a large scale. The SWNT sponge has multifunctional properties and can be used in the fields of cleaning-up, sensing and energy storage.
How to prepare the lightweight and porous carbon nanotube (CNT) sponges with mass production and without high energy and time consumption?
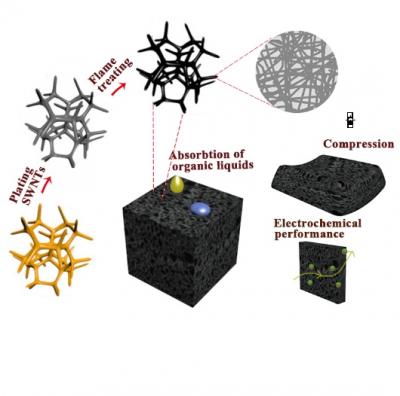
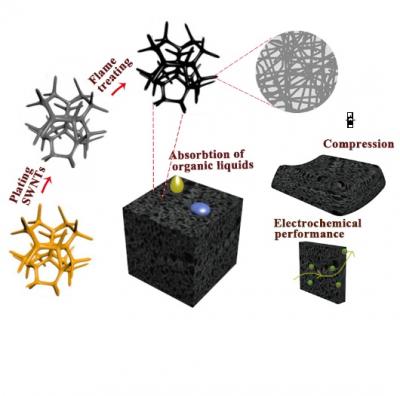
A group of researchers have discovered a method of preparing single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) sponges with a 3D elastic interconnected hollow skeleton network by burning the commercial polyurethane (PU) sponges coated with SWNTs.
The PU sponge can be removed in an ethanol flame in less than 20 s, leaving sponge-like structures. Compared with previously reported chemical vapor deposition (CVD), freeze-drying method, the flame burning method used in this work has the advantages of being density controlled, low cost and suitable for large-scale production. Additionally, the advantage of sponge shape and size controlled by pretreatment of PU templates is also the most important aspect of the method, superior to other methods.
The most significant aspect of this study is that the SWNT sponges was developed by a superfast flame burning method in less than 20 s through removing PU sponge template coated with SWNTs in an ethanol flame, which has not ever been reported. The as-synthesized SWNT sponges exhibit a series of comparable properties, including high conductivity, moderate organic liquid adsorption, good elasticity and high specific capacitance. Also, the sponges could reach an ultralow density of 0.8 mg cm?3 and keep the original geometry of PU template without distortion. The high hydrophobicity endows the SWNT sponges with admirable adsorption rate and capacity for organic solvents. The sponges could not only reach a maximum compressive stress of 11,500 Pa at 80% strain, but also bear more than 1000 compression cycles at 60% strain. Further, the porous SWNT sponges used as a flexible electrode material achieves a high specific capacitance of 126.8 F g?1 and 95% capacitive retention over 10,000 cycles.
###
This work was supported by Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Basic Research Program of Jiangsu Province) (No. BK20171409), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2014CB239701), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21173120, 51372116, 21663029).
The authors Liang Lu, Hao Tong, Fengqiao Jin, Shihong Yue, Qing Meng, Xiaogang Zhang are from Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Materials and Technology for Energy Conversion, College of Material Science and Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, People's Republic of China. Liang Lu, Hao Tong contributed equally to this work.
The corresponding authors of this study are Hao Tong and Xiaogang Zhang. [email protected], [email protected]; [email protected].
For more insight into the research described, readers are invited to access the paper on NANO.
IMAGE
Image credit: Shihong Yue
Caption:
The 3D carbon nanotube sponge prepared by superfast flame burning method.
NANO is an international peer-reviewed monthly journal for nanoscience and nanotechnology that presents forefront fundamental research and new emerging topics. It features timely scientific reports of new results and technical breakthroughs and publishes interesting review articles about recent hot issues.
About World Scientific Publishing Co.
World Scientific Publishing is a leading independent publisher of books and journals for the scholarly, research, professional and educational communities. The company publishes about 600 books annually and about 135 journals in various fields. World Scientific collaborates with prestigious organizations like the Nobel Foundation and US National Academies Press to bring high quality academic and professional content to researchers and academics worldwide. To find out more about World Scientific, please visit http://www.worldscientific.com.
For more information, contact Tay Yu Shan at [email protected].
Media Contact
Tay Yu Shan
[email protected]
@worldscientific
http://www.worldscientific.com
Original Source
https://www.worldscientific.com/page/pressroom/2018-08-23-01 http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/S1793292018500777