Credit: YU Shuhong
Nature has provided us not only the fantastic materials, but also the inspiration for the design and fabrication of high-performance biomimetic engineering materials. Woods, which have been used for thousands of years, have received considerable attention due to the low density and high strength. The unique anisotropic cellular structure endow the woods with outstanding mechanical performances. In recent decades, various materials have been produced into monolithic materials with anisotropically cellular structures, trying to duplicate the lightweight and high-strength woods. However, the reported artificial wood-like materials suffer from unsatisfactory mechanical properties. Up to now, it is still a significant challenge to fabricate the artificial wood-like materials with the lightweight and high-strength properties.
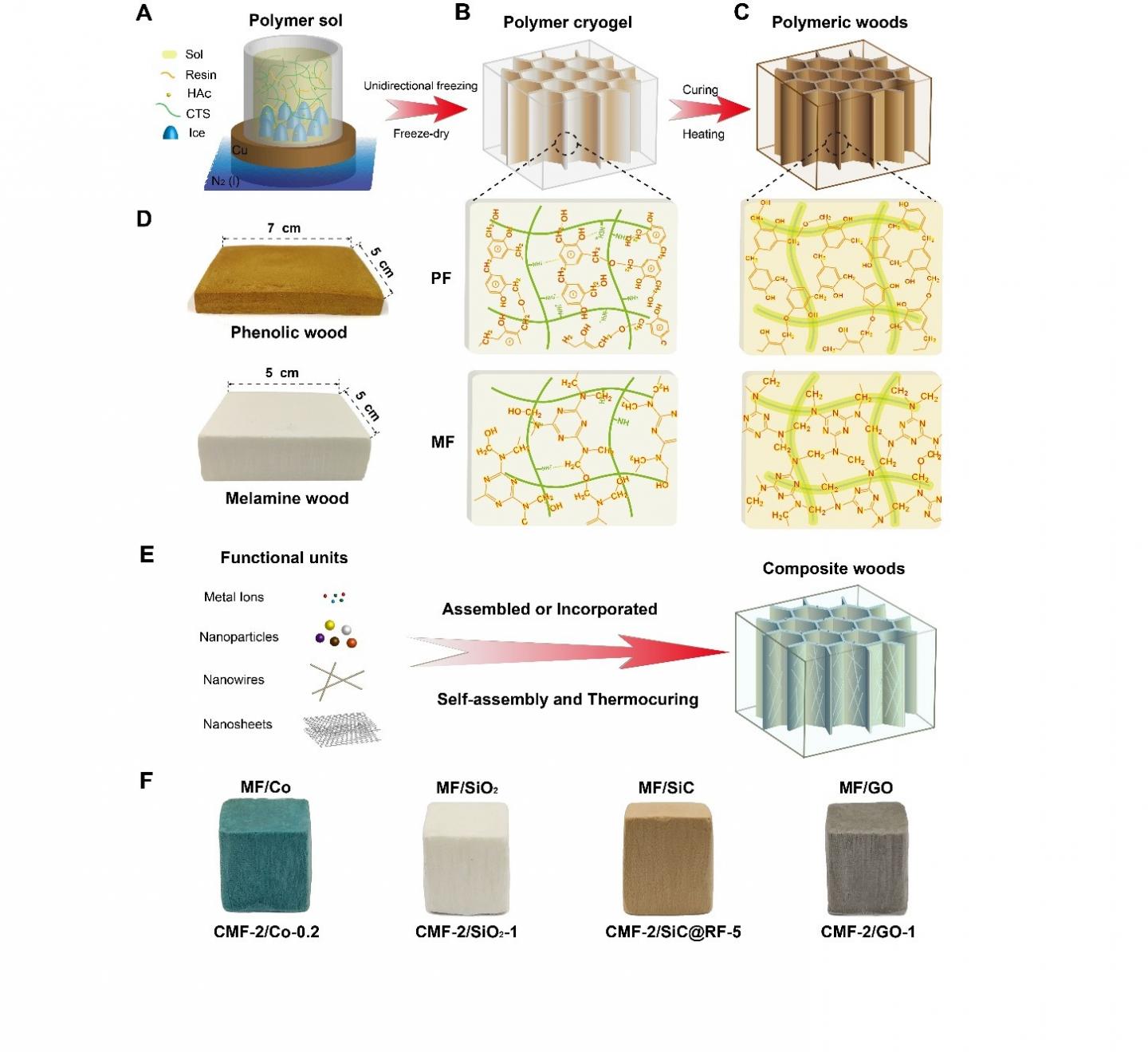
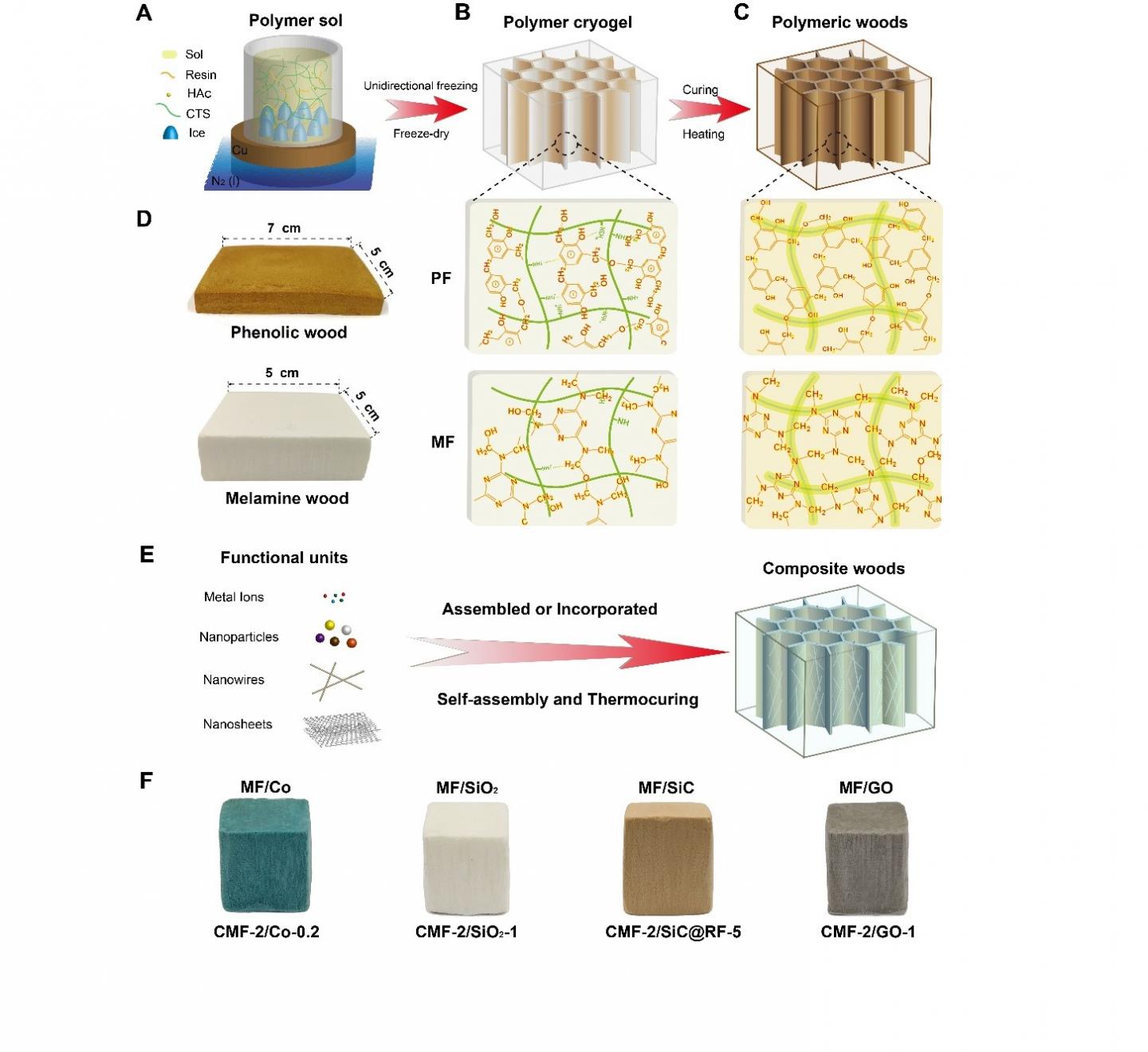
Recently, a research team led by Prof. YU Shuhong from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) demonstrate a novel strategy for large-scale fabrication of a family of bioinspired polymeric woods with similar polyphenol matrix materials, wood-like cellular microstructures, and outstanding comprehensive performance by a self-assembly and thermocuring process of traditional resins (phenolic resin and melamine resin). This work was published on Science Advances entitled as "Bioinspired polymeric woods" on August 10th (Science Advances 2018, 4, eaat7223).
The liquid thermoset resins were firstly unidirectionally frozen to prepare a "green body" with the cellular structure, followed by the subsequent thermocuring to get the artificial polymeric woods. The artificial woods bear a close resemblance to natural woods in the mesoscale cellular structures, and exhibit well controllability in the pore size and wall thickness. Benefiting from the starting aqueous solution, it also represents a green approach to prepare multifunctional artificial woods by compositing various nanomaterials, such as cellulose nanofibers and graphene oxide.
The polymeric and composite woods manifest lightweight and high-strength properties with the mechanical strength comparable to that of natural wood. In contrast with natural woods, the artificial woods exhibit better corrosion resistance to water and acid with no decrease in mechanical properties, as well as much better thermal insulation (as low as ~21 mW m?1 K?1) and fire retardancy. The artificial polymeric woods even stand out from other engineering materials such as cellular ceramic materials and aerogels in terms of specific strength and thermal insulation properties. As a kind of biomimetic engineering materials, this new family of bioinspired polymeric woods is supposed to replace the natural wood when used in harsh environments.
This novel strategy provides a new and powerful route to fabricate and engineer a wide range of high-performance biomimetic engineering composite materials with desirable multifunctionality and advantages over the traditional counterparts, which will have broad applications in many technical fields.
###
Media Contact
FAN Qiong
[email protected]
86-636-07280
http://en.ustc.edu.cn