Credit: Kanazawa University
Precious metals come in limited supply but are in high demand. They are mainly sourced through mining, but the possibility of recycling them from metallurgical waste leachates (waters that have passed through the treated materials during mineral processing and thus contain some of the compounds present in the minerals) is attracting growing attention. To this end, compact and portable instruments to perform the analysis of wastewaters in on-field rapid analysis are highly desirable to improve the efficiency of the recovery of precious metals.
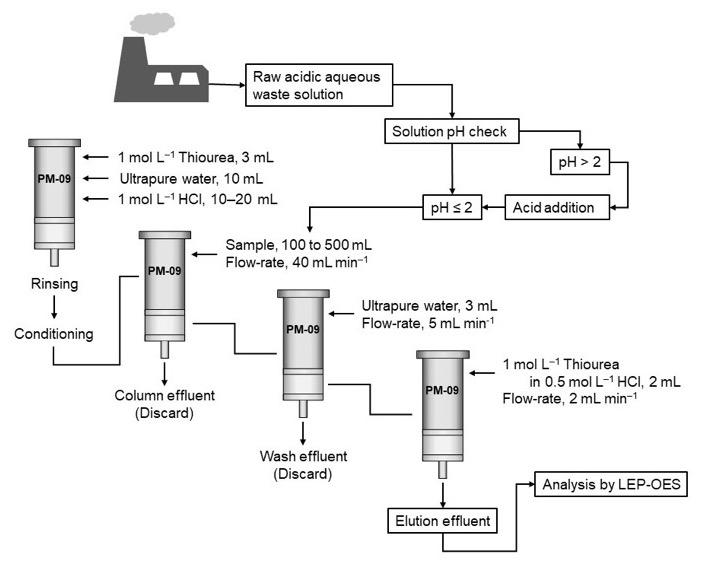
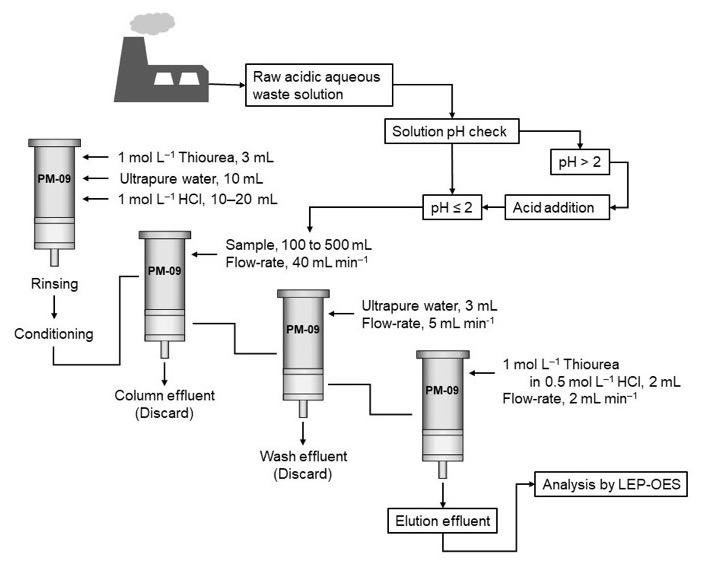
Liquid-electrode plasma-optical emission spectrometry (LEP-OES) has emerged as a tool to implement on-site analysis of elements in aqueous matrices, as it is portable and much less costly than traditional methods. However, when the concentration of noble metals is very low, as is the case for precious metals in waste spills, the sensitivity of the technique become insufficient to produce accurate analysis — one of the problems is that in metallurgical waste leachates there are several ions that interfere with the analysis. In this case, analyte separation and enrichment steps (that is, steps that remove other substances and increase the concentration of the analyte to make detection easier) have to be included in the analysis of the samples for accurate detection of the precious metals.
This is what Suman Barua, Ismail M.M. Rahman, Hiroshi Hasegawa and colleagues from Kanazawa University and Fukushima University did, reporting the first application of LEP-OES in combination with a solid-phase extraction (SPE) system (which is used as the pre-treatment step to eliminate the competing ions and to enrich the noble metals) for the rapid on-site simultaneous analysis of the precious metals gold, palladium and platinum. The SPE parameters were optimized to maximize retention and recovery of the precious metals; the LEP-OES parameters to maximize the emission peaks for the individual elements. The method was tested both on certified reference material for wastewater and on real aqueous waste samples, from which more than 95% of the precious metals were recovered. The high-precision on-site measurements could be performed in less than 15 minutes, opening the way to practical analysis of the precious metal content of wastewaters.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
81-762-645-076
http://www.kanazawa-u.ac.jp/e/index.html
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.132