Credit: Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST)
A research team led by Professor Jaewon Ko and Ji Won Um from Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences identified a new principle of formation of brain synapses through synaptic binding protein complexes.
Many nerve cells that make up the brain control the function of the brain through synapses*. Although recent studies show that synaptic binding proteins play a certain role in the formation of synapses, detailed factors or processes for collectively controlling the synapses remain unknown.
The research team has been focusing on discovering related binding proteins and finding detailed mechanisms to identify the principles of formation of excitatory synapses among synapses.
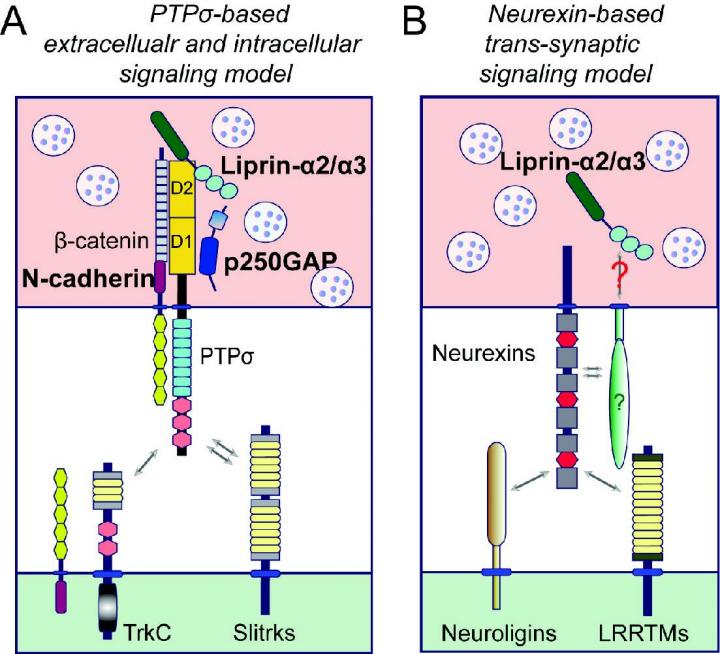
In this study, the research team found that the interaction between the PTPσ proteins and certain bone proteins among binding proteins plays a critical role in synapse formation. In particular, they have identified that the 'normal tyrosine signaling mechanism' resulting from the reaction of certain elements of the PTPσ proteins is an essential component of synapse formation.
Given the potential correlation between proteins and mental disorders such as autism, schizophrenia, and depression that recent large-scale human genetics studies have shown, the research team's experiment is expected to provide important clues to help analyze the causes of brain disorders and enable treatment through further studies of related proteins.
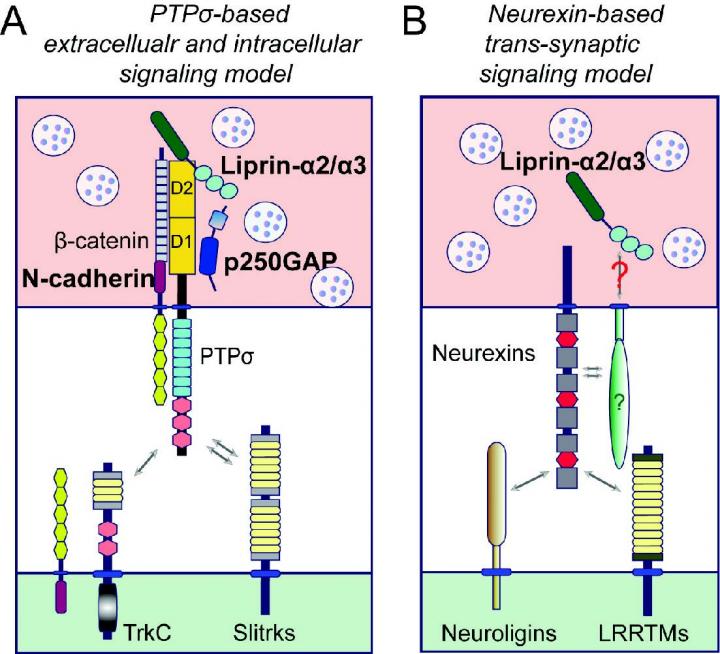
Professor Ko expressed his determination by saying, "As our recent study has reported, PTPσ proteins, along with neurexin, are considered key proteins responsible for the development of neural circuits. Our world-leading research team will conduct further studies to continue research on the development of synapses and neural circuits."
This research outcome was published on Friday June 22, 2018 in the online edition of The Journal of Neuroscience, an expert journal in the field of neuroscience; the research was conducted with support from a world-leading life science project by the Korean Health Industry Development Institute.
###
For more information, please contact:
Associate Professor Jaewon Ko
Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences
Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST)
E-mail: [email protected]
Associated Links
Research Paper in the online edition of The Journal of Neuroscience
Journal Reference
Ji Won Um, Jaewon Ko, et al., "PTPσ drives excitatory presynaptic assembly via various extracellular and intracellular mechanisms," Journal of Neuroscience June 2018.
* Synapse: The two types of synapses -excitatory and inhibitory -work in a balanced manner to promote normal brain function.
Media Contact
Dajung Kim
[email protected]
82-537-851-163
http://www.dgist.ac.kr
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0672-18.2018