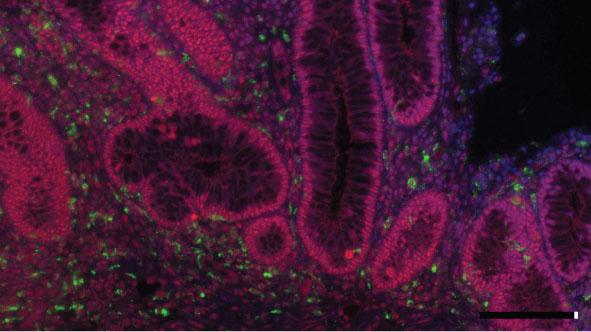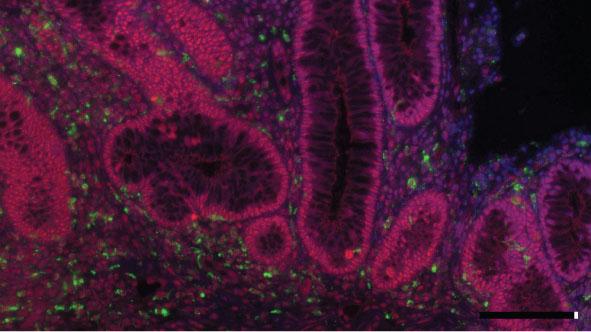
Credit: Author: Catrin Youssif, IRB Barcelona.
Scientists headed by ICREA researcher Angel R. Nebreda at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) report a new mechanism that contributes to the development of inflammation-associated colon cancer and points to new therapeutic targets. The study has been published in the journal EMBO Molecular Medicine.
More than a million people worldwide are diagnosed with colon cancer every year. Although many of these cases are spontaneous, chronic inflammation is one of the main causes underlying the development of this disease.
"Our study demonstrates that the capacity of myeloid cells to enhance tumorigenesis is determined by the protein p38. In particular, we have identified an important contribution of the hormone IGF-1, which is activated by p38 in myeloid cells", explains Nebreda, head of the Cell Sigalling and Cell Cycle lab.
The research has been done using models of acute and chronic inflammation in genetically modified mice or in mice treated with pharmacological inhibitors.
IGF-1 and inflammation
IGF-1, a hormone similar to insulin, emerges as a potential therapeutic target– preferably in combination with prior detection of inflammatory infiltration in biopsies of patients and levels of IGF-1–in intestinal diseases associated with inflammation. This finding could help to address the low success rate achieved by pharmacological inhibitors of p38 in clinical trials in patients with intestinal inflammatory disease who are predisposed to colon cancer.
"We found that p38 inhibition specifically in myeloid cells protects mice against inflammation-associated colon cancer, and this protective effect is associated with a reduced production of chemokines, which are crucial for the recruitment of cells from the immune system", explains Catrin Youssif, first author of the study and current alumnus of IRB Barcelona.
The study demonstrates that the genetic or pharmacological inhibition of IGF-1 suppresses the recruitment of inflammatory cells and reduces the burden of colon cancer tumours associated with inflammation.
"On the basis of our findings, we propose that decisions regarding therapy should take into consideration the inflammatory conditions and the levels of IGF-1 in biopsies of patients with inflammatory intestinal diseases or colitis-associated cancer," conclude the authors of the study.
###
In addition to funding from the European Research Council (ERC), the study has been supported by the "Fundació La Marató", the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness of Spain, and the "Agencia de Gestión de Ayudas Universitarias y de Investigación (AGAUR)" run by the Catalan Government.
The study has been done in collaboration with researchers at CNIO and Hospital Ramón y Cajal in Madrid, and has involved IRB Barcelona's Histopathology Facility and Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Facility, as well as Jaume Comas and Teresa Rodrigo Calduch, from the University of Barcelona.
Reference article:
Catrin Youssif, Monica Cubillos-Rojas, Mònica Comalada, Elisabeth Llonch, Cristian Perna, Nabil Djouder, Angel R Nebreda
Myeloid p38α signaling promotes intestinal IGF?1 production and inflammation?associated tumorigenesis
EMBO Molecular Medicine (2018): doi: 10.15252/emmm.201708403
Media Contact
Sònia Armengou
[email protected]
34-934-037-255
http://www.irbbarcelona.org
Original Source
https://www.irbbarcelona.org/en/news/a-study-points-to-new-therapeutic-targets-for-tumours-associated-with-chronic-inflammation http://dx.doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201708403