Credit: KAIST
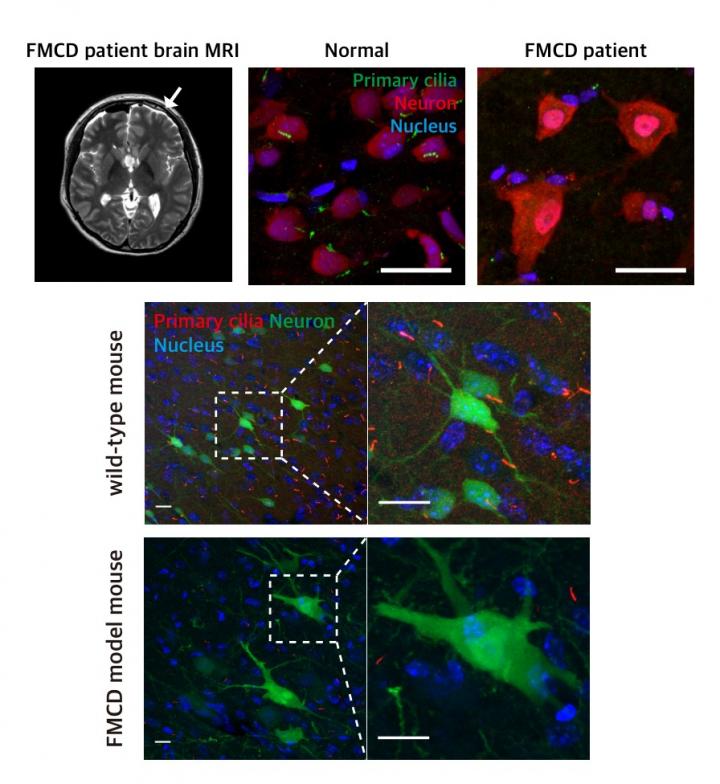
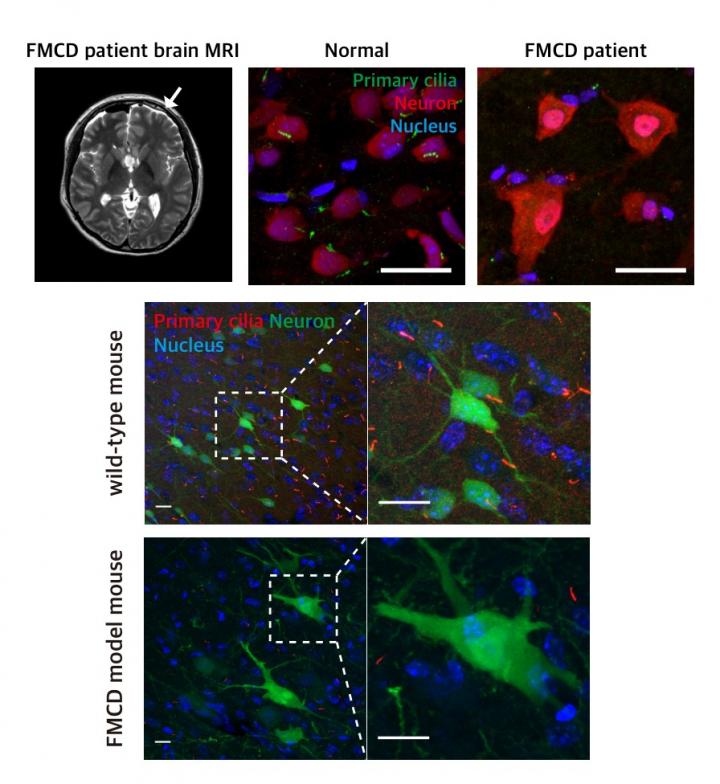
Focal malformations of cortical development (FMCDs) are a heterogeneous group of brain cortical abnormalities. These conditions are the most common causes of medically refractory epilepsy in children and are highly associated with intellectual disability, developmental delay, and autism-spectrum disorders. Despite a broad spectrum of cortical abnormalities in FMCDs, the defective migration of neuronal cells is considered a key pathological hallmark.
A Korean research team led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has recently investigated the molecular mechanism of defective neuronal migration in FMCDs. Their research results were published online in Neuron on June 21, 2018.
The research team previously demonstrated that brain-only mutations in the mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) gene causes focal cortical dysplasia, one major form of FMCDs leading to intractable epilepsy in children. However, the molecular mechanisms by which brain-only mutations in MTOR lead to cortical dyslamination and defective neuronal migration in FMCDs remain unclear.
To study the molecular mechanism of brain cortical dyslamination, the research team utilized patients' brain tissues and modeled the MTOR mutation-carrying cell and animal models recapitulating the pathogenesis and symptoms of FMCD patients. By performing comprehensive molecular genetic experiments, they found that the formation of primary cilia, one of cellular organelles, was disrupted in MTOR mutation-carrying neurons and demonstrated that this ciliary disruption was a cause of cortical dyslamination in FMCDs.
MTOR mutations prevented degradation of the OFD1 protein, one of the negative regulators of ciliary formation. As a result, the OFD1 protein was abnormally accumulated in MTOR mutation-carrying neurons, causing focal cortical dyslamination. By suppressing the expression of the OFD1 protein, the research team was able to rescue the defective formation of primary cilia, leading to the restoration of cortical dyslamination and defective neuronal migration considerably.
Based on these results, the research team is carrying out further research to develop novel therapeutics for patients with FMCDs caused by brain-only mutations.
###
This work was supported by grants from the Suh Kyungbae Foundation and Citizens United for Research in Epilepsy.
The research paper is titled "Brain Somatic Mutations in MTOR Disrupt Neuronal Ciliogenesis, Leading to Focal Cortical Dyslamination." (Digital Object Identifier #: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.05.039)
Media Contact
Younghye Cho
[email protected]
82-423-502-294
@KAISTPR
http://www.kaist.ac.kr
Original Source
http://www.kaist.ac.kr/_prog/_board/?mode=V&no=82690&code=ed_news&site_dvs_cd=en&menu_dvs_cd=0601&list_typ=B&skey=&sval=&smonth=&site_dvs=&GotoPage= http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.05.039