Credit: Division of Life Science, HKUST
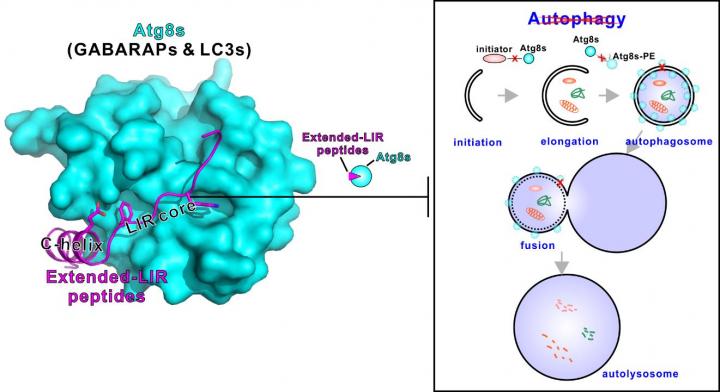
Autophagy, meaning "self-eating" in Greek, is a general metabolic mechanism adopted by nearly all the eukaryotic species, from the single cell yeast to humans. It is a process that cells degrade unnecessary components for materials recycling and energy generation to survive against stress or maintain homeostasis.
On the good side, autophagy can protect cells by eliminating harmful materials (e.g. amyloid aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases and pathogen invasions), but defects in autophagy are often related to numerous diseases, such as Alzheimer's diseases or Parkinson diseases, and in case of tumors, the autophagy pathway can be hijacked to supply enough nutrients for their massive growth. As a result, either activating or inhibiting autophagy in a precisely spatiotemporally controlled manner could be a promising treatment against various kinds of diseases.
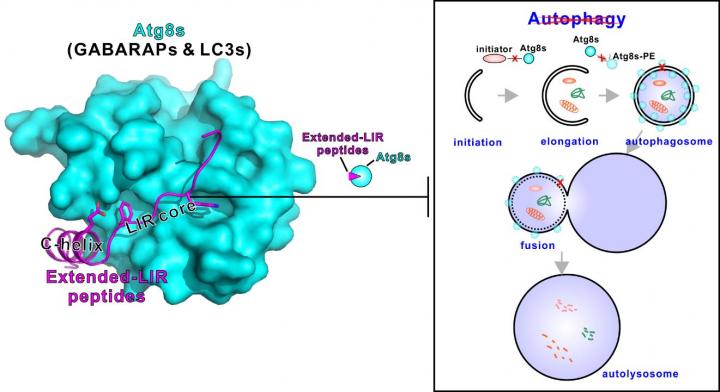
Recently, a research team led by structural biologist Prof. Mingjie Zhang from HKUST has discovered potent and specific inhibitory peptides to target the Atg8 family proteins (including LC3s and GABARAPs), central components in the autophagy pathway. These genetically encodable autophagy inhibitory peptides can be used to occlude autophagy spatiotemporally in living animals, which leads to many situations where they can be utilized in a variety of designs.
Their findings were published on Jun 4, 2018 in the journal Nature Chemical Biology (doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0082-8).
During their study on ankyrins, a long-term interest in their laboratory, the researchers first identified a GABARAP-selective inhibitory peptide naturally harbored in 270/480?kDa ankyrin-G and a super-potent pan-Atg8 inhibitory peptide from 440?kDa ankyrin-B. Based on the crystal structures they solved, they further optimized the ankyrin-G derived peptide to be a more GABARAP-selective one, "The distinct function of LC3s and GABARAPs in the autophagy pathway is still a wide-open area. At the current stage, the late function of these proteins are always masked by their early effect and/or redundancy. The peptides developed here probably will serve as a great tool to dissect the different roles of these two sub-families of Atg8 proteins in autophagy, " said Prof. Hong Zhang, one of the senior co-authors in this paper from Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Science.
The researchers also provided evidence that the peptides they developed can effectively block autophagy in cultured COS7 cells as well as living animals C. elegans at a given time and a given location. "The super strong Atg8 binding peptides are genetically encodable and can be expressed in tissue- and temporal-specific manners in living animals as we have demonstrated, and thus are far better than any of the small molecule-based drugs existing in autophagy research in cell cultures and more importantly in living animals, " Prof. Mingjie Zhang said.
"The inhibitory peptides can directly serve as leads to develop drugs for potential cancer treatments. They can also be indirectly used as a research tool to look for autophagy inducers for treating neurodegenerative diseases, " said Jianchao Li, one of the leading authors in Prof. Mingjie Zhang's laboratory.
###
The research is supported by Research Grant Council of Hong Kong and National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Media Contact
Johnny Tam
[email protected]
852-235-88556
http://www.ust.hk
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0082-8