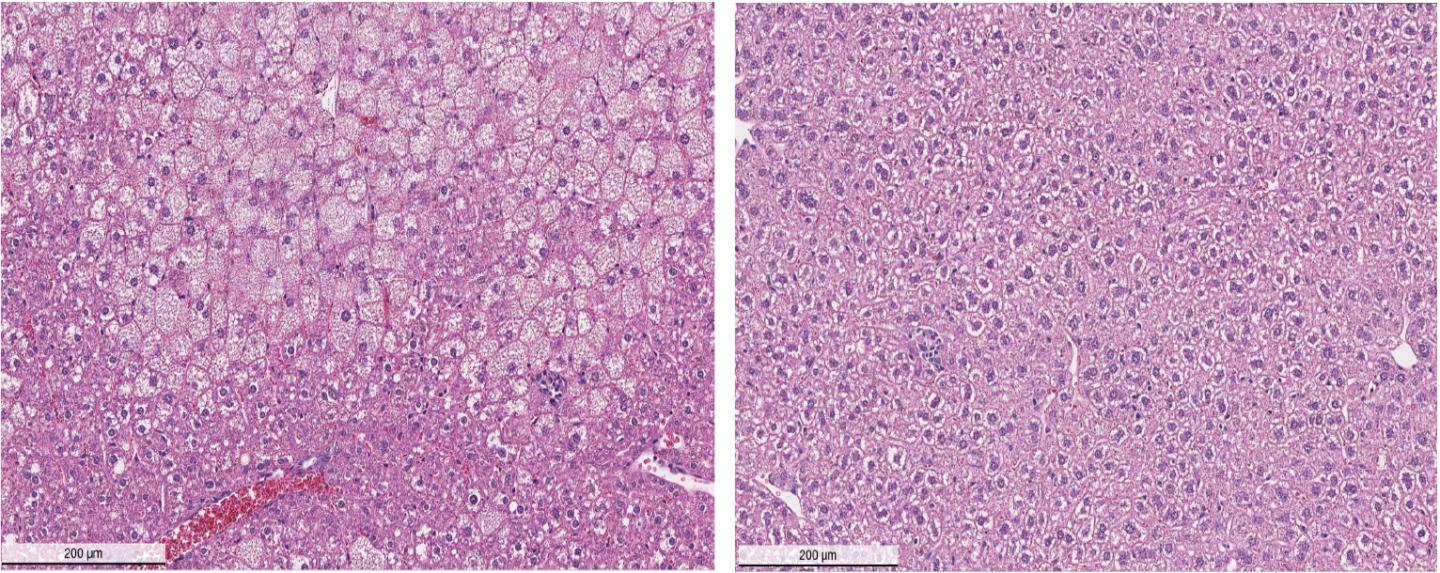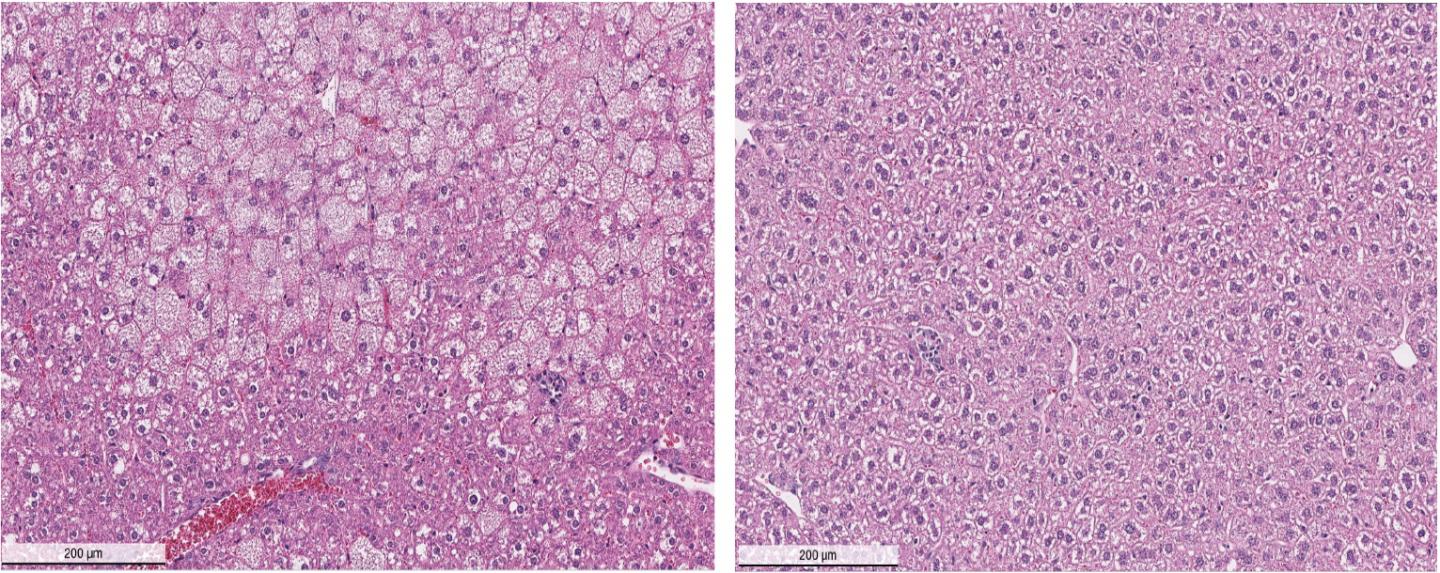
Credit: Tonks Lab, CSHL
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL), working in collaboration with DepYmed Inc., a CSHL spinout company, today report that they have conducted promising preclinical experiments on a compound that could be used to treat Wilson's disease and possibly other disorders — including certain types of cancer — in which levels of copper in the body are elevated, causing or contributing to pathology.
Wilson's disease, affecting 1 in 30,000 people, is a severe inherited disorder that leads to profound liver and neurological damage. It is caused by mutations in a gene called ATP7B that encodes an enzyme critical in the excretion of excess copper from cells and organs.
Copper, like many other metals, is obtained mainly through the diet. Although essential in bodily function, it can be toxic when it accumulates. Normally, amounts of copper are precisely regulated both at the cellular level and in the body as a whole. In Wilson's patients, abnormal copper buildup begins in the liver, the organ that collects the metal from the gut and distributes it to other tissues via the bloodstream.
Copper toxicity can lead to liver enlargement, hepatitis, cirrhosis and even liver failure, necessitating a transplant. As the disease progresses, it can also affect the brain, with symptoms that include speech defects, cognitive impairment, psychiatric disorders, tremors, dystonia and Parkinsonian symptoms. Although Wilson's disease can't be controlled by switching to a low-copper diet, it is often manageable with drugs when treated early.
"Unfortunately, Wilson's disease may be hard to diagnose because its early symptoms are shared by other ailments, and so it is often not treated promptly" says CSHL Professor Nicholas Tonks, who, with Navasona Krishnan, Ph.D., formerly of his lab, led the research. "Moreover, currently used treatments, involving 'de-coppering' agents, have side effects and lately have become very expensive."
The team's new research confirms that DPM-1001, a small molecule, robustly reduces copper levels in cells grown in culture that were sampled from Wilson's disease patients, as well as systemically in a mouse model of Wilson's disease. It acts as a chelator – a compound that interacts with a metal to facilitate its natural removal.
The team showed that DPM-1001 is orally available — it could be taken as a pill — and is "exquisitely specific" for copper. Current de-coppering agents tend to affect levels of other metals in addition to copper – an undesirable feature in a drug for an illness like Wilson's. Such drugs would likely be taken for extended times, and the binding of metals other than copper may contribute to unwanted side effects.
In a mouse model of Wilson's disease, DPM-1001 ameliorated associated liver complications including enlarged cell size, irregular shape and arrangement in liver tissue. This was accompanied by dramatic lowering of tissue copper levels and reduced disease symptoms.
"It is our hope that this compound may represent the basis for an improved approach to Wilson's Disease," Tonks said. Optimization work on the compound continues in his lab in collaboration with DepYmed Inc.
###
Funding: National Institutes of Health; CSHL Cancer Center Support Grant; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory-Northwell Alliance; Gladowsky Breast Cancer Foundation; Don Monti Memorial Research Foundation; Irving Hansen Foundation; Estate of Thomas C. Nelson; Robertson Research Fund. Drs. Tonks and Krishnan serve on the Scientific Advisory Board of DepYmed, Inc., an early-stage drug discovery company that was spun out of CSHL. DepYmed, Inc., provided the experimental compounds used in this study.
Citation: Krishnan, N et al, "DPM-1001 decreased copper levels and ameliorated deficits in a mouse model of Wilson's disease" is published June 26, 2018 in Genes & Development.
About Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Founded in 1890, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory has shaped contemporary biomedical research and education with programs in cancer, neuroscience, plant biology and quantitative biology. Home to eight Nobel Prize winners, the private, not-for-profit Laboratory employs 1,100 people including 600 scientists, students and technicians. The Meetings & Courses Program annually hosts more than 12,000 scientists. The Laboratory's education arm also includes an academic publishing house, a graduate school and the DNA Learning Center with programs for middle and high school students and teachers. For more information, visit http://www.cshl.edu
Media Contact
Peter Tarr
[email protected]
516-367-5055
@genomeresearch
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory – Advancing the frontiers of biology through education and research