A team led by researchers from Tianjin University (P.R. China) has solved the structure of the Zika virus helicase, which is a key target for antiviral development. The research is published in Springer’s journal Protein & Cell.
The Zika virus can cause microcephaly and other severe birth defects. However, as there are currently no effective vaccines or therapies available to contain ZIKV infection, ZIKV remains a significant challenge to public health.
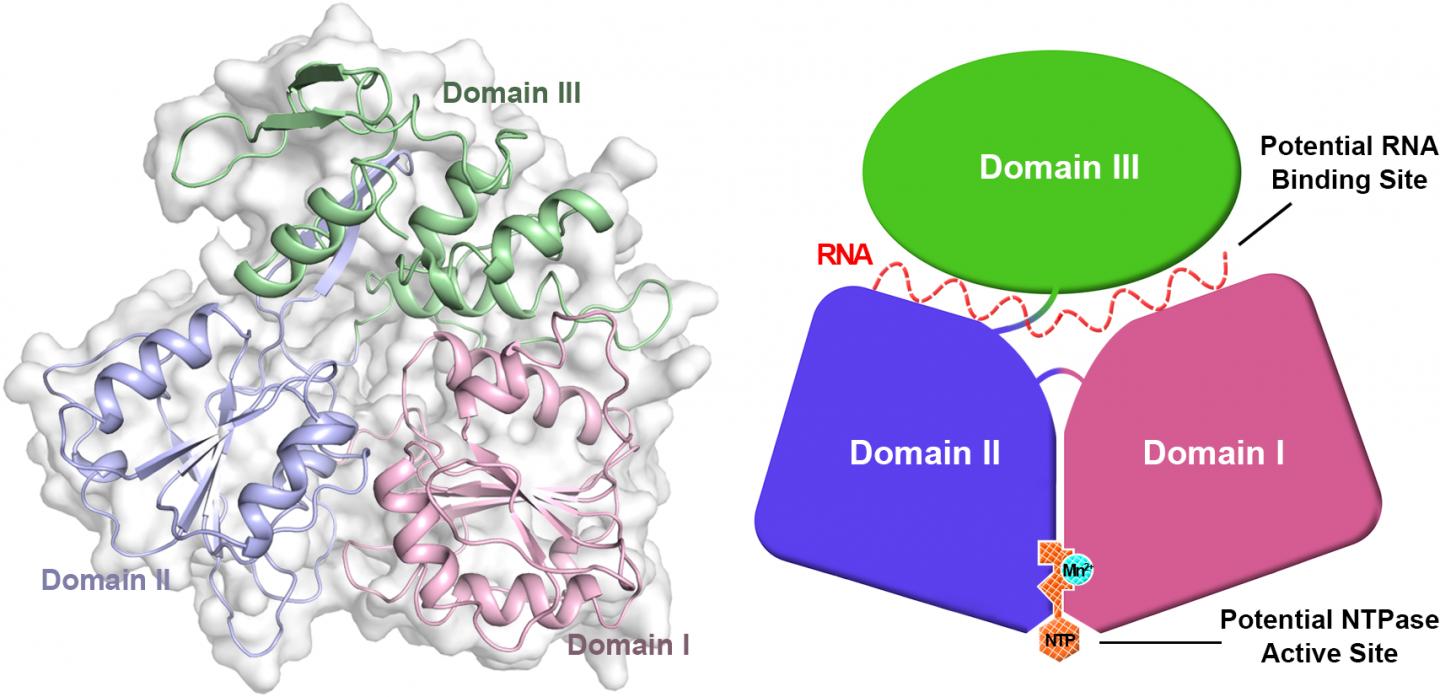
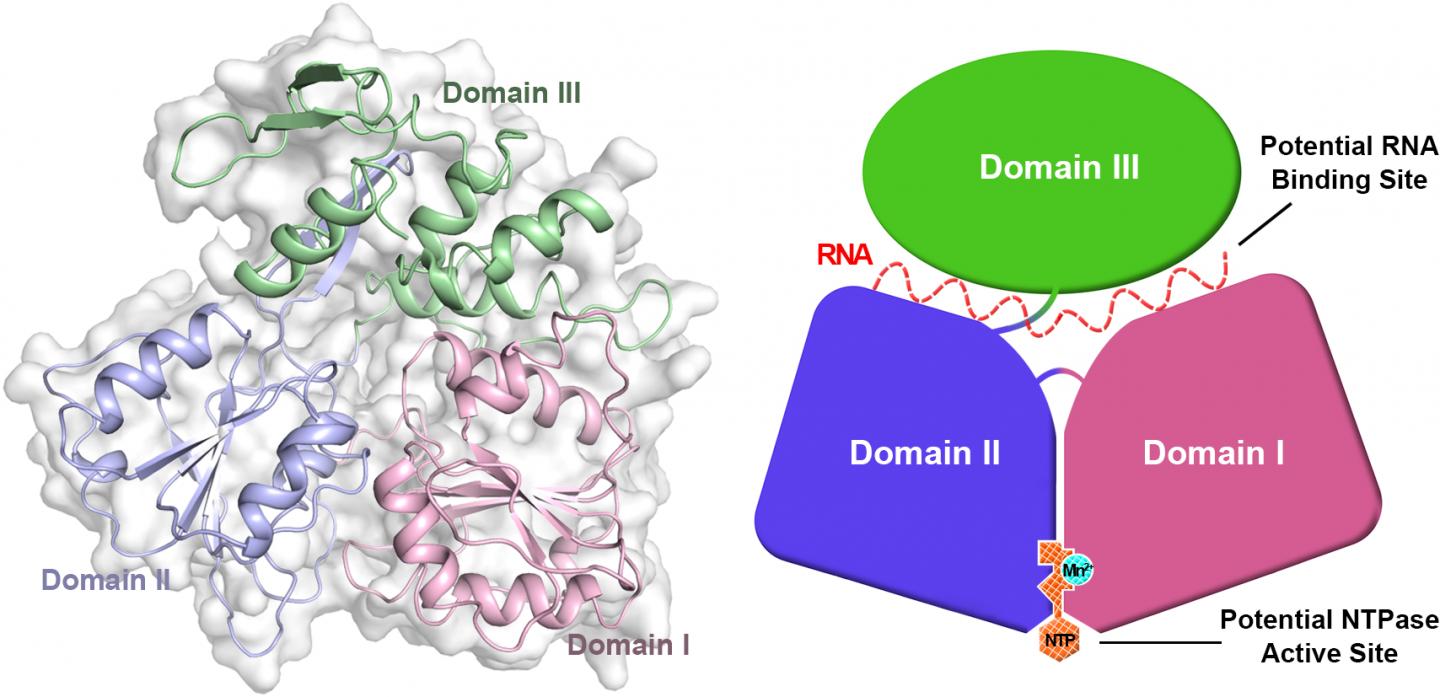
All viruses seem to need a helicase for replication. The Zika virus helicase is a motor enzyme which can convert energy from nucleoside triphosphate to unwind double stranded nucleic acids. This is an essential step for viral replication. By targeting Zika virus helicase with small-molecule inhibitors, it might be possible to stop viral replication and prevent disease. The scientists have successfully obtained an image at 1.8 angstroms of this viral enzyme. An angstrom is one ten-billionth (10-10) of a meter. This high-resolution image of the Zika virus key enzyme will help scientists develop drugs to treat the Zika virus disease.
###
Reference: Hongliang Tian, et al. (2016). The crystal structure of Zika virus helicase: basis for antiviral drug design. Protein & Cell. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13238-016-0275-4
Media Contact
Joan Robinson
[email protected]
49-622-148-78130
@SpringerNature
http://www.springer.com
The post Researchers solve the structure of the Zika virus helicase appeared first on Scienmag.