Credit: Osaka University
Osaka – Chronic inflammatory disorders, including autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, involve the action of various inflammatory molecules (cytokines) produced by cells of the immune system. One such cytokine, IL-17, is produced by Th17 cells, which are white blood cells that provide host defense against pathogens, as well as mediating inflammatory reactions. Although Th17 cells are lead players in autoimmune disease, the way in which they control other inflammatory cells had been unclear.
Now, an international team of researchers led by Osaka University has used a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis to investigate how Th17 cells interact with other cells at the site of inflammation and influence cytokine production. They reported their findings in the journal Immunity.
Several inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6 and TNFα, cause joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. The disease progresses through the interaction of T cells of the immune system with specialized cells in the joint lining (synovium), which promotes the destruction of bone and cartilage. The recent development of new anti-rheumatic drugs such as TNF and IL-6 inhibitors has dramatically improved the quality of life of many patients with rheumatoid arthritis, but treatment for 30% of these patients remains a challenge. Therefore, novel therapies are eagerly awaited.
The inflammatory cytokine GM-CSF activates cells involved in innate and adaptive immune systems, which represent non-specific defense mechanisms and specific learned responses to foreign substances, respectively. GM-CSF particularly triggers scavenger white blood cells (macrophages) and immune cell messengers known as dendritic cells.
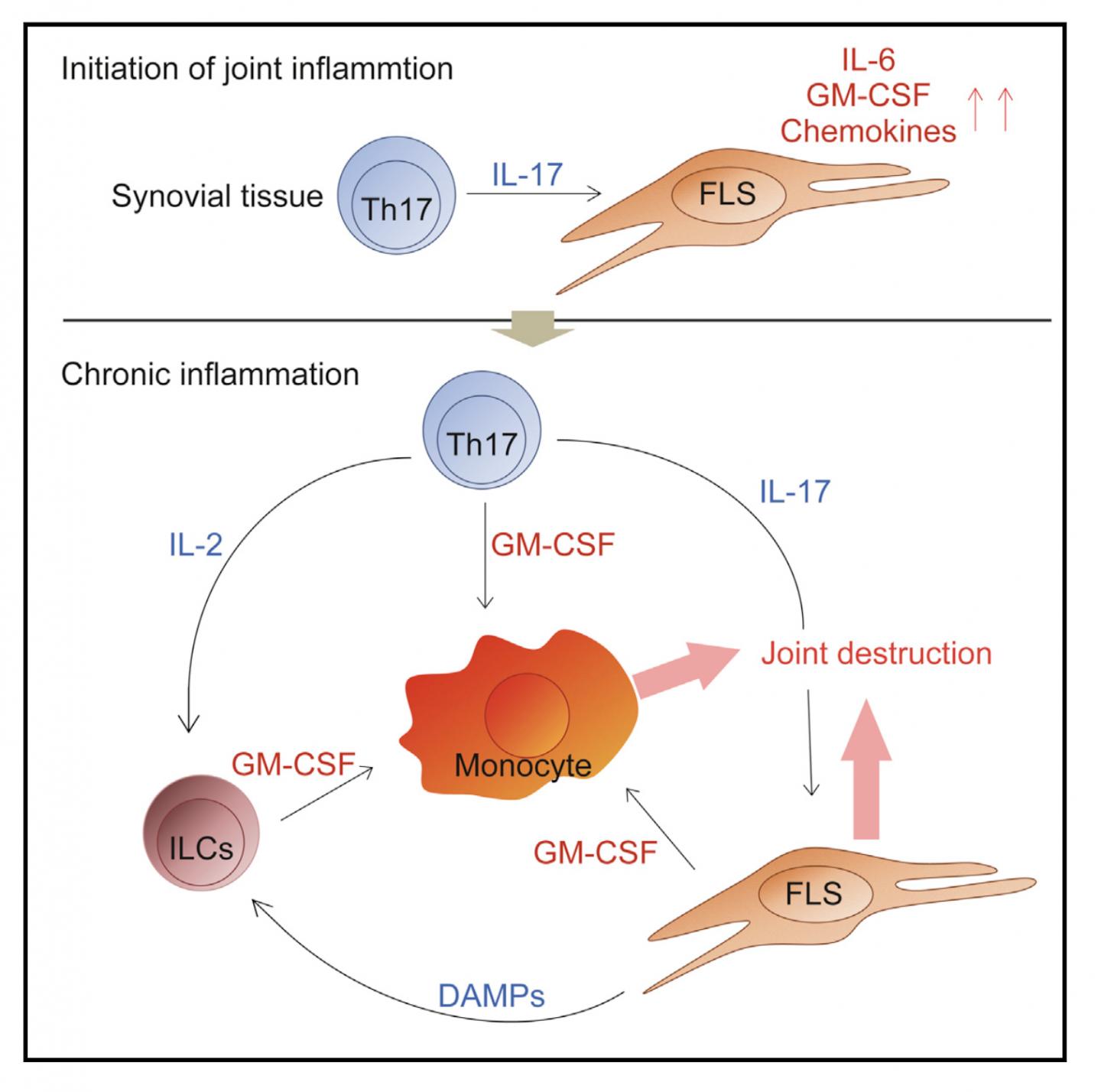
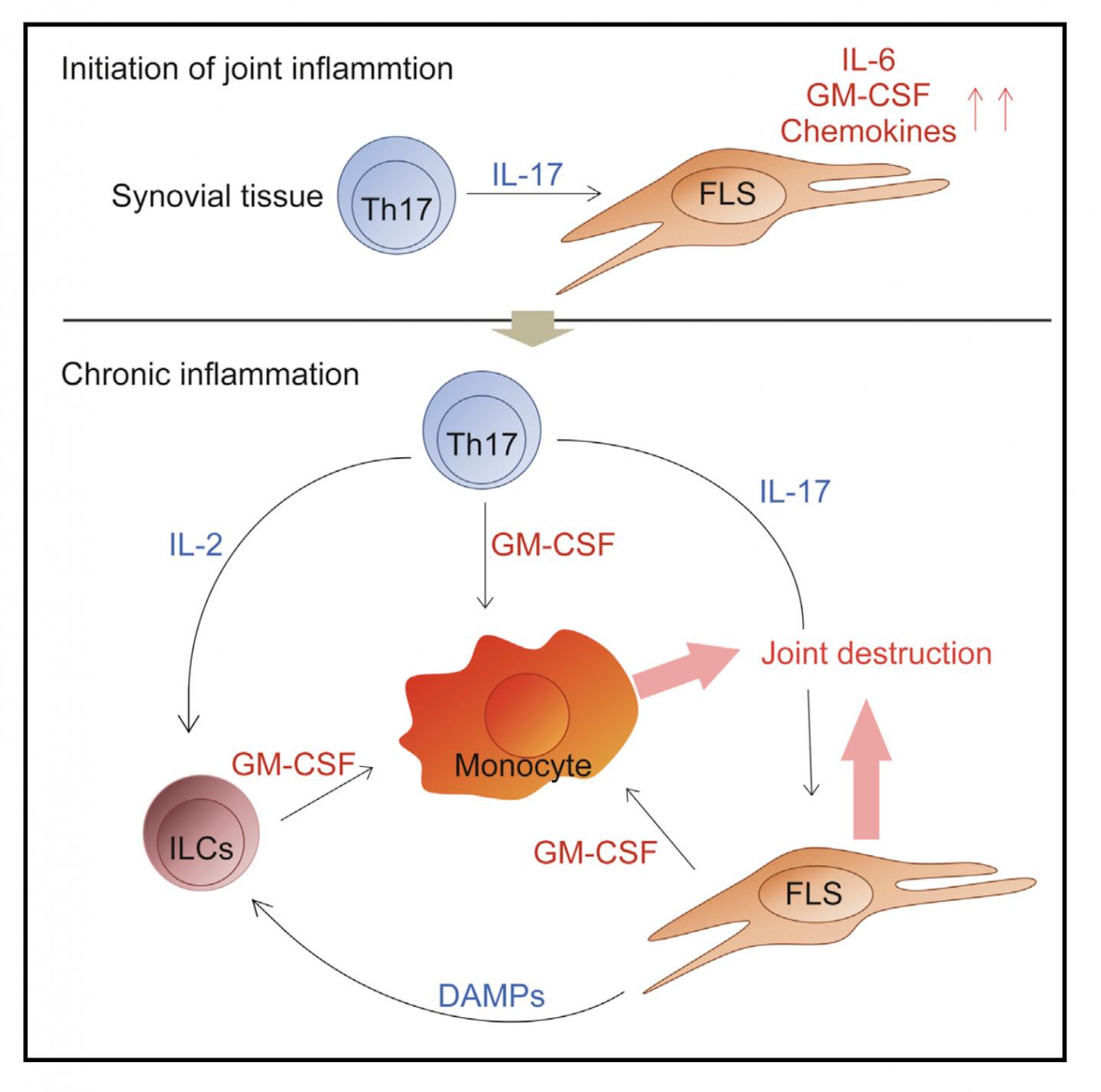
The team found that GM-CSF was crucial for the development of arthritis in the mouse model. "GM-CSF produced both by stromal cells of the connective tissue and T cells contributed to joint inflammation in the mice, but only stromal cell-derived GM-CSF was needed to initiate arthritis," study first author Keiji Hirota explains. "We also showed that stromal cells secreted GM-CSF in response to stimulation by IL-17 from inflammatory Th17 cells."
GM-CSF was also found to be secreted by a group of innate immune cells, which expanded in number within inflamed joints in response to IL-17 production by Th17 cells and other inflammatory cytokines. This contributed to the maintenance and development of rheumatoid arthritis in the mice.
"Our findings outline an inflammatory network controlled by autoimmune Th17 cells and involving stromal cells and innate immune cells, which leads to the onset and development of autoimmune arthritis," corresponding author Shimon Sakaguchi says. "By selectively removing GM-CSF-producing cells from the mouse synovium, we significantly reduced the severity of arthritis. This suggests the usefulness of developing such a novel immunotherapeutic approach that targets the cellular network to reduce chronic joint inflammation."
###
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan's most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university's ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum.
Website: http://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en/top
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
@osaka_univ_e
http://www.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
Original Source
http://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en/research/2018/20180523_1 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.009