Credit: Bastian Braeuning / TUM
Pore-forming toxins are common bacterial poisons. They attack organisms by introducing holes in cell membranes. A team of scientists at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now unraveled the mechanism of action for one of these toxins. The findings could help combat associated diseases and advance crop protection.
Pore-forming toxins are bacterial poisons that destroy cells by creating holes in the cell membranes. Many bacterial pathogens produce such toxins, including, for example, some strains of the intestinal bacterium Escherichia coli as well as Yersinia enterolitica, a pathogen related to the plague. They attack all kinds of organisms with the help of their toxins – from plants to insects, and even humans.
Scientists all over the world are trying to understand how these toxins produce the fatal openings in cell membranes in hope of one day inhibiting the pathogenic, pore-forming poisons.
After several years of research, an interdisciplinary team from the Technical University of Munich managed to elucidate the mode of action of a toxin subspecies in which two components interact to develop the deadly effect.
Two partners with lethal impact
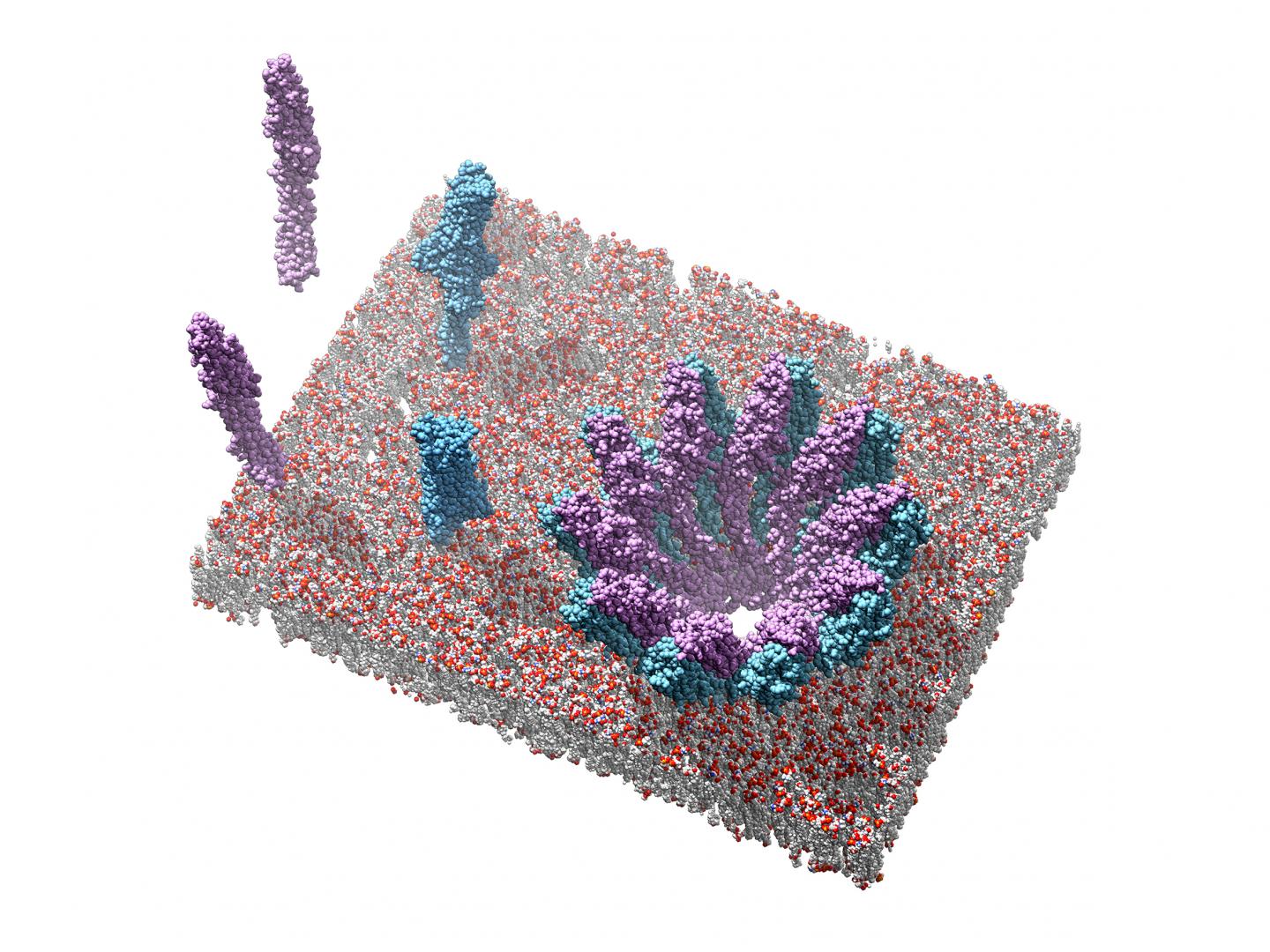
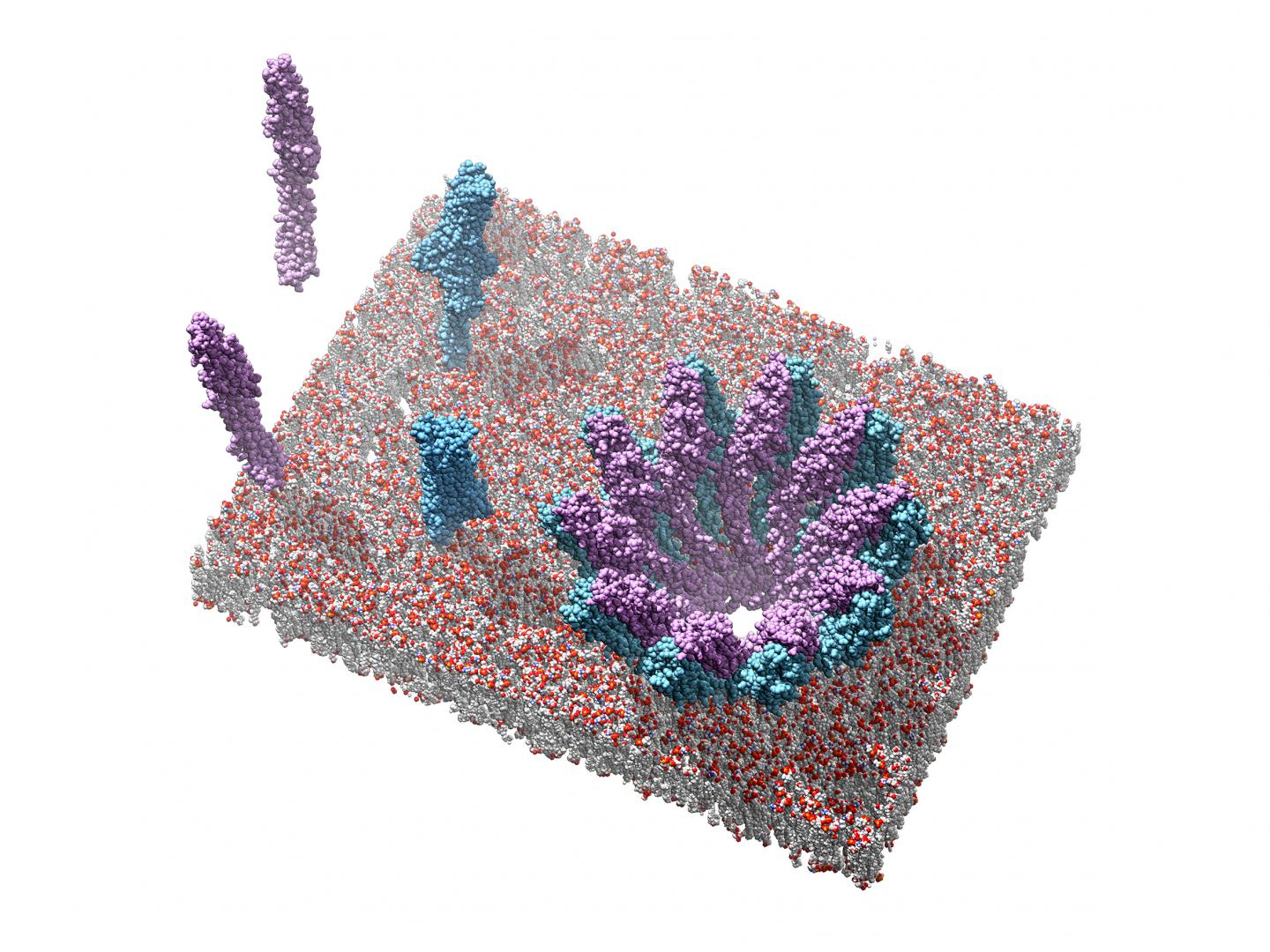
Combining crystallographic and cryo-electron microscopy methods, Bastian Bräuning and Professor Michael Groll from the Department of Biochemistry, in collaboration with Eva Bertosin and Professor Hendrik Dietz from the Department of Experimental Biophysics, managed to shed light upon the precise molecular structures of the soluble individual components, as well as the pore complex.
"We determined that only one of the two components is able to bind to the membrane. In a second step it recruits the other component and the base domains of two proteins together form the basic pore unit," explains Bastian Bräuning. "This is a new kind of mechanism from which we can obtain much useful insight."
The structure of the resulting hole in the cell membrane resembles a crown, whose teeth comprise 40 subunits of the two interacting partners.
One mechanism – a myriad of potential applications
The team of researchers led by Bräuning and Groll investigated the interaction of the two partner proteins in form of toxins from Yersinia enterolitica and Photorhabdus luminescens. The latter is a symbiotic bacterium in nematodes that attack insects and might prove useful for the development of novel insecticides.
These new insights put the development of substances that inhibit the interaction of two toxin components, and therefore prevent the formation of pores into the realm of the conceivable.
"Our combination of crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy was key to understanding the necessity of the two-component construction of the toxin from a biochemical perspective," explains Professor Michael Groll. "This insight will also help us understand more complex variants in the future, for example those in which three components work together."
###
The work is the result of close a cooperation between the professors of Biochemistry and Biophysics at the Technical University of Munich. Both working groups are part of the Cluster of Excellence Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CIPSM). The results were validated by the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry and Bioanalytics at the Institute of Pharmacy of the Martin-Luther University Halle-Wittenberg. The X-ray structure data were collected at the synchrotron light source of the Paul Scherrer Institute (Villigen, Switzerland).
Publication:
Bastian Bräuning, Eva Bertosin, Florian Praetorius, Christian Ihling, Alexandra Schatt, Agnes Adler, Klaus Richter, Andrea Sinz, Hendrik Dietz and Michael Groll
Structure and mechanism of the two-component α-helical pore-forming toxin YaxAB
Nature Communications, vol. 9, 1806 (2018) – DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04139-2
Media Contact
Dr. Andreas Battenberg
[email protected]
49-892-891-0510
@TU_Muenchen
http://www.tum.de
Original Source
https://www.tum.de/nc/en/about-tum/news/press-releases/detail/article/34629/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04139-2