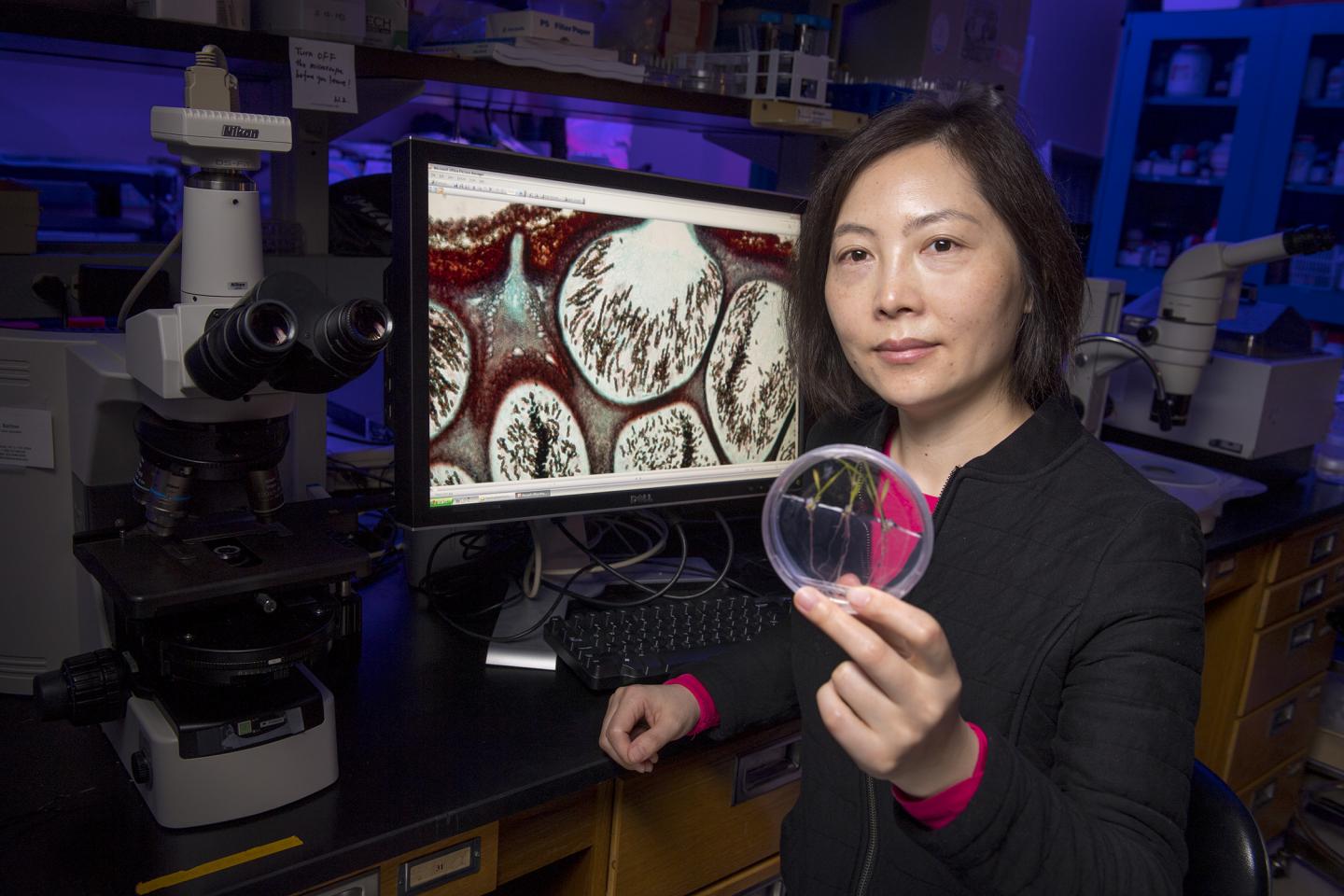
Credit: Nick Romanenko/Rutgers University
About 21 million years ago, a fungus that causes a devastating disease in rice first became harmful to the food that nourishes roughly half the world's population, according to an international study led by Rutgers University-New Brunswick scientists.
The findings may help lead to different ways to fight or prevent crop and plant diseases, such as new fungicides and more effective quarantines.
Rice blast, the staple's most damaging fungal disease, destroys enough rice to feed 60 million people annually. Related fungal pathogens (disease-causing microorganisms) also infect turfgrasses, causing summer patch and gray leaf spot that damage lawns and golf courses in New Jersey and elsewhere every summer. And now a new fungal disease found in wheat in Brazil has spread to other South American countries.
Results from the study published online in Scientific Reports may lead to better plant protection and enhanced national quarantine policies, said Ning Zhang, study lead author and associate professor in the Department of Plant Biology and the Department of Biochemistry and Microbiology in the School of Environmental and Biological Sciences.
"The rice blast fungus has gotten a lot of attention in the past several decades but related species of fungi draw little attention, largely because they're not as severe or not harmful," Zhang said. "But they're all genetically related and the relatives of severe pathogens have been little-studied. You have to know your relatives to have a holistic understanding of how the rice blast pathogen became strong and others did not."
The study is the outcome of a 2016 international symposium at Rutgers-New Brunswick hosted by Zhang and Debashish Bhattacharya, study senior author and distinguished professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Microbiology. The National Science Foundation, Rutgers Center for Turfgrass Science, and School of Environmental and Biological Sciences funded the symposium by researchers from the U.S., France and South Korea.
The scientists studied Magnaporthales, an order of about 200 species of fungi, and some of the new members were discovered in the New Jersey Pine Barrens. About half of them are important plant pathogens like the rice blast fungus – ranked the top fungal pathogen out of hundreds of thousands. After the first sign of infection, a rice field may be destroyed within days, Zhang said.
To get a holistic understanding of how the rice blast fungus evolved, scientists genetically sequenced 21 related species that are less harmful or nonpathogenic. They found that proteins (called secretomes) that fungi secrete are especially abundant in important pathogens like the rice blast fungus.
Based on previous research, the proteins perhaps became more abundant over time, allowing the fungi to infect crops, Zhang said. The researchers identified a list of genes that are abundant in pathogens but less so in nonpathogens, so the abundant genes might promote pathogens that can infect crops. The results will allow scientists to look into the mechanism behind the infection process.
"With climate change, I think the rice blast problem can only get worse because this is a summer disease in warm climates where rice is grown," Zhang said, adding that wheat, turfgrass and other important plants may also be affected.
###
Media Contact
Todd Bates
[email protected]
848-932-0550
@RutgersU
http://www.rutgers.edu
Original Source
https://news.rutgers.edu/study-could-spawn-better-ways-combat-crop-killing-fungus/20180424#.Wt9XxG4vy71 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24301-6