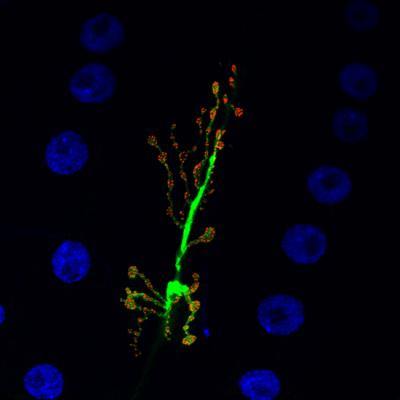
Credit: University of Leicester
Researchers from the University of Leicester have shed new light on how neurons in the brain communicate with one another. This could potentially help in our understanding of how and why a range of neurodegenerative diseases occur.
The team, led by Dr Joern Steinert from the MRC Toxicology Unit at the University of Leicester, has found that the important molecule present in the whole animal kingdom — including the human body — called nitric oxide, plays a vital role in regulating the functions of neurons not only periphery but also in the brain, helping to decipher the 'mosaic' of knowledge about how our brain communicates.
Nitric oxide is a signalling molecule involved in many physiological and pathological processes which helps in dilating blood vessels, raising blood supply and lowering blood pressure.
The new research, which is funded by the Medical Research Council and published in the journal PLOS Biology, has found that nitric oxide also regulates the functions of neurons via a modulation of a signalling step at a synapse – the point where two neurons connect and neurotransmitters are released.
This regulation changes the position of the protein — called complexin — within a synapse and regulates the amount of the neurotransmitter which is released.
"We showed for the first time that this complexin protein can be regulated or modified so that it is now able to adjust the function of a synapse and eventually the neuron," says Dr Steinert. "This would have bigger impacts on the global function of the brain which has to be constantly regulated and adjusted to changes in demand. Implications are also related to neurological disease, in which this exact signalling might go wrong and leaves the neuron unable to function.
"This research can also help to better understand neurological conditions, such as seen in many neurodegenerative diseases. If the pathways which we characterised go wrong, it can easily disrupt whole brain function and leading to neuronal death."
The team investigated the neural pathway in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. They predominately detected changes in neuronal function — or the electrical firing of a single neuron.
The researchers then used genetic methods to express certain proteins of interest at in specific neurons, using various methods to visualise proteins and molecules within neurons in order to detect changes in their position and function within a neuron.
###
The paper, titled 'Nitric oxide-mediated post-translational modifications control neurotransmitter release by modulating complexin farnesylation and enhancing its clamping ability' is published in the journal PLOS Biology and is available here: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.2003611
Image of neuronal synapse is available here: https://www.dropbox.com/sh/pypnwulm8ze5h8l/AABpiTfUbsLzxF_2aGVJsMuqa?dl=0
Media Contact
Dr Joern Steinert
[email protected]
@UoLNewsCentre
http://www.leicester.ac.uk
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2003611