Credit: University of Tsukuba
Tsukuba, Japan – Genes encode proteins and proteins dictate cell function. Therefore, the thousands of genes expressed in a cell determine what that cell can do. Among the multiple elements that are involved in the precise regulation of gene expression are enhancers, which are short region of DNA that can be bound by proteins (activators) to increase the likelihood of transcription of a particular gene.
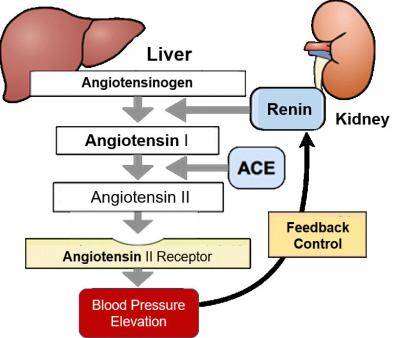
One notable regulatory cascade that involves enhancers is the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) that plays a major role in blood pressure regulation and electrolyte homeostasis. Because increased expression of the protein renin leads to a rise in blood pressure, its transcription must be finely regulated.
While upregulation of the gene renin in the promoter and enhancer elements is relatively well established, the mechanisms controlling its feedback transcriptional suppression are poorly understood. This knowledge gap prompted a team of researchers from the University of Tsukuba to delve deeper into understanding this important regulatory cascade.
"We deleted either 5? or 3? regions of the endogenous mouse renin (mRen) in mice, and placed the animals in a hypertensive environment. While the mRen gene bearing the 3? deletion was appropriately downregulated, the one bearing the 5? deletion (-5E) lost hypertension responsiveness," explains Aki Ushiki, lead author of the study, which was recently reported in Molecular and Cellular Biology. "This means the -5E region is essential for the basal expression of the mRen gene."
Based on their findings, they proposed the -5E element functions as an enhancer under normal conditions and is involved in full activation of mRen gene transcription. Conversely, in the hypertensive state, the enhancer activity somehow becomes attenuated by the hormone angiotensin signaling, which leads to suppression of mRen gene transcription.
"Understanding of this enhancer-mediated transcriptional modulatory mechanism for mRen gene has a broad impact on not only the RAS field but also enhancer biology in general," corresponding author Keiji Tanimoto says. "Also, as the mRen enhancer core sequence is fairly conserved in humans, our findings shed light on the unexplored distal regulatory region of renin genes and provide a novel mechanistic insight into renin gene regulation."
###
Media Contact
Masataka Watanabe
[email protected]
029-853-2039
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00566-17