Credit: Image courtesy of Kazuhiro Suzuki.
Researchers in Japan have discovered that the adrenergic nervous system controls when white blood cells circulate through the body, boosting the immune response by retaining T and B cells in lymph nodes at the time of day when they are most likely to encounter foreign antigens. The study, "Adrenergic control of the adaptive immune response by diurnal lymphocyte recirculation through lymph nodes," will be published online October 31 ahead of issue in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
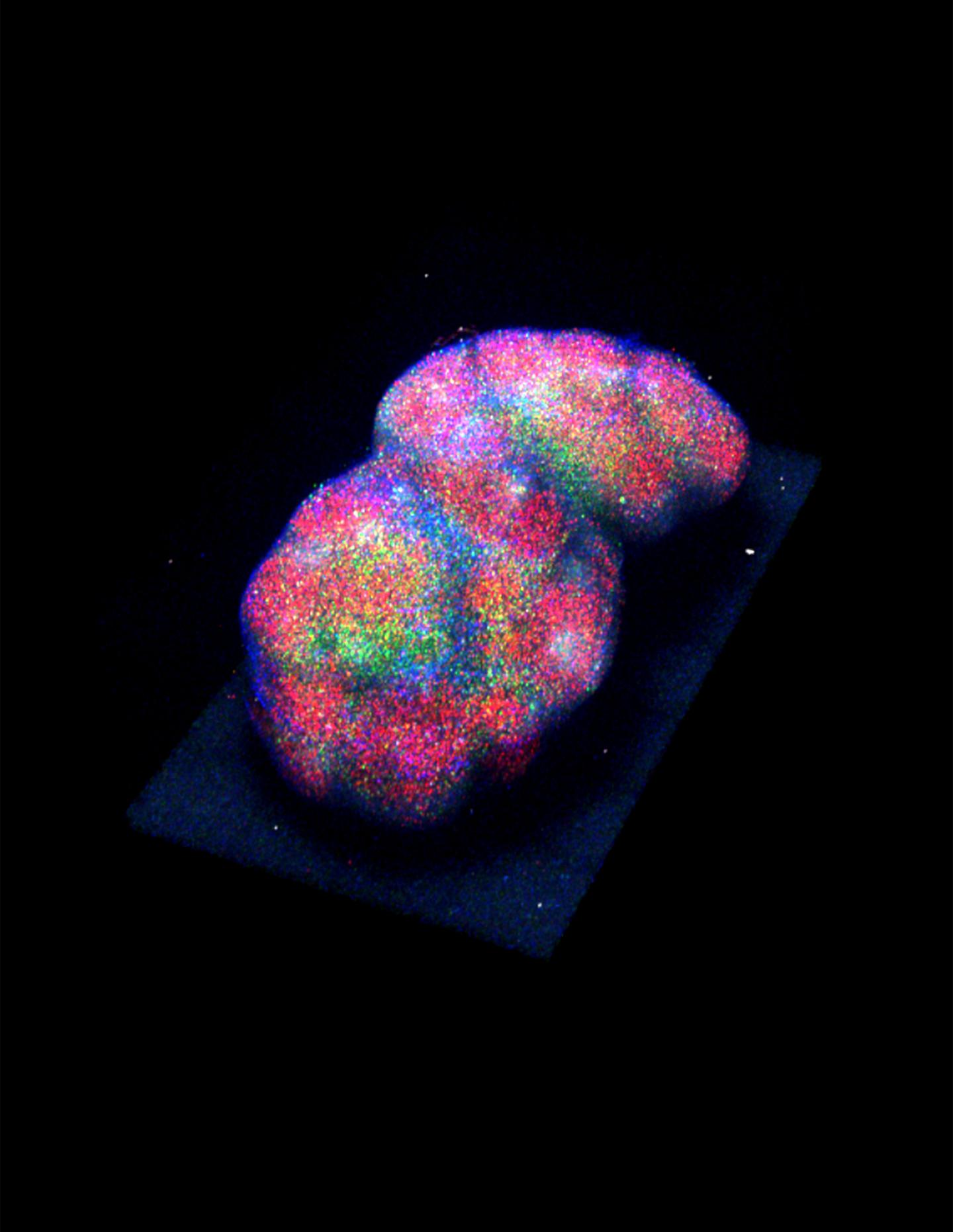
On their way around the body, T and B cells pass through lymph nodes, where specialized cells may present them with antigen molecules captured from bacteria or other pathogens. The T and B cells then reenter the bloodstream in search of these pathogens so that they can kill them and fight off infection. Previous studies have suggested that number of T and B cells present in the bloodstream varies over the course of the day.
Kazuhiro Suzuki and colleagues from the WPI Immunology Frontier Research Center at Osaka University found that, in mice, the number of T and B cells in the blood peaked during the day and decreased during the night, when they accumulated in lymph nodes instead. This daily, or circadian, cycle of immune cell trafficking was regulated by the neurotransmitter noradrenaline, released from adrenergic nerves innervating the lymph nodes. The nerves secreted more noradrenaline at night, activating β2-adrenergic receptor molecules on the surface of T and B cells that impede the cells' exit from lymph nodes.
Mice mounted a stronger immune response if they were injected with antigens at night, when more of their T and B cells were exposed to antigen-presenting cells in lymph nodes. This makes sense, Suzuki and colleagues note, because mice are nocturnal creatures and are therefore more likely to encounter pathogens when they are active during the night. Accordingly, the daily cycle may be flipped in humans, whose T and B cells appear to accumulate in lymph nodes during the day, when adrenergic nerves are thought to be more active.
###
Suzuki, K., et al. 2016. J. Exp. Med. http://dx.doi.org/10.1084/jem.20160723
About The Journal of Experimental Medicine
The Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM) features peer-reviewed research on immunology, cancer biology, stem cell biology, microbial pathogenesis, vascular biology, and neurobiology. All editorial decisions are made by research-active scientists in conjunction with in-house scientific editors. JEM provides free online access to many article types from the date of publication and to all archival content. Established in 1896, JEM is published by The Rockefeller University Press. For more information, visit jem.org.
Follow us on Twitter at @JExpMed and @RockUPress.
Media Contact
Ben Short
[email protected]
212-327-7053
@RockUPress
http://www.rupress.org/