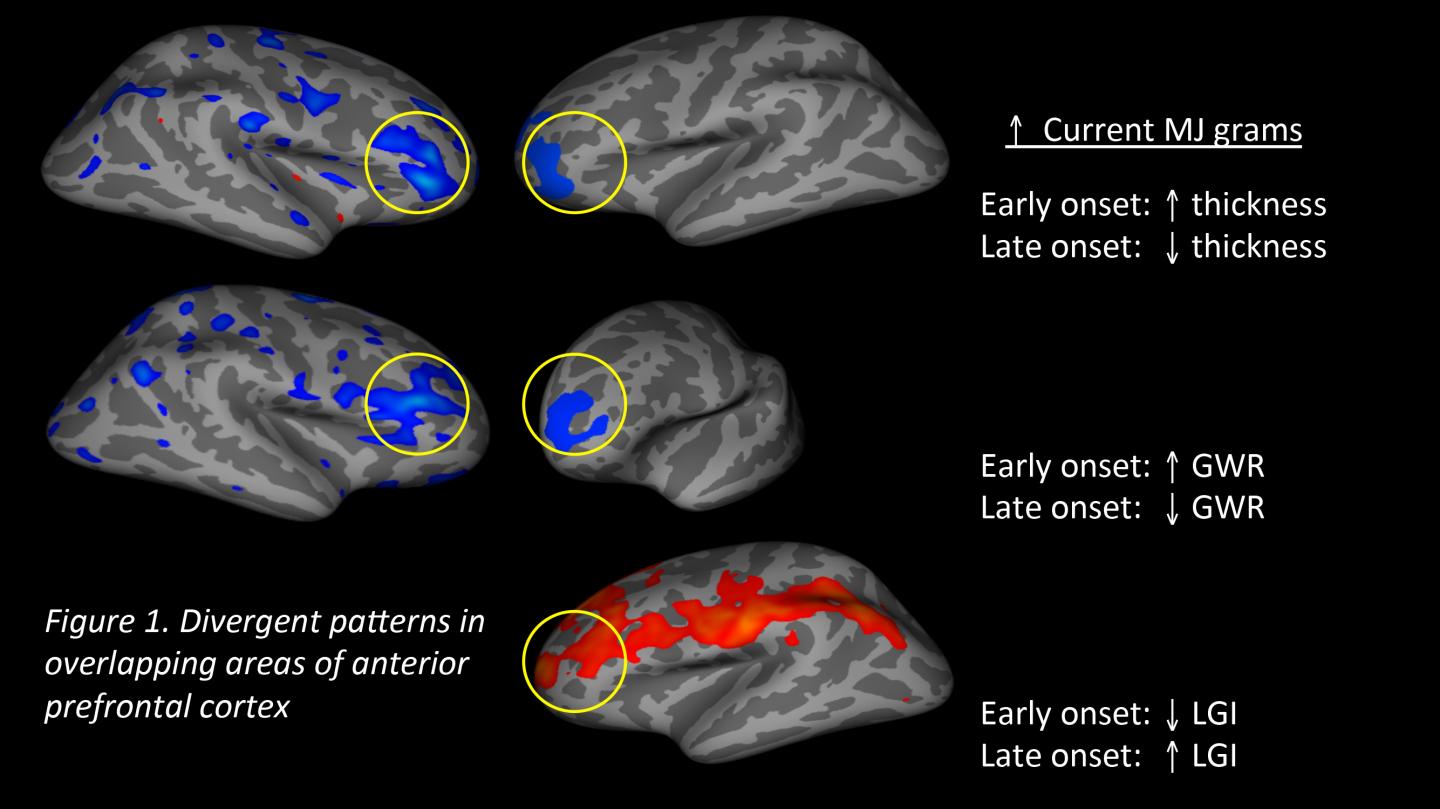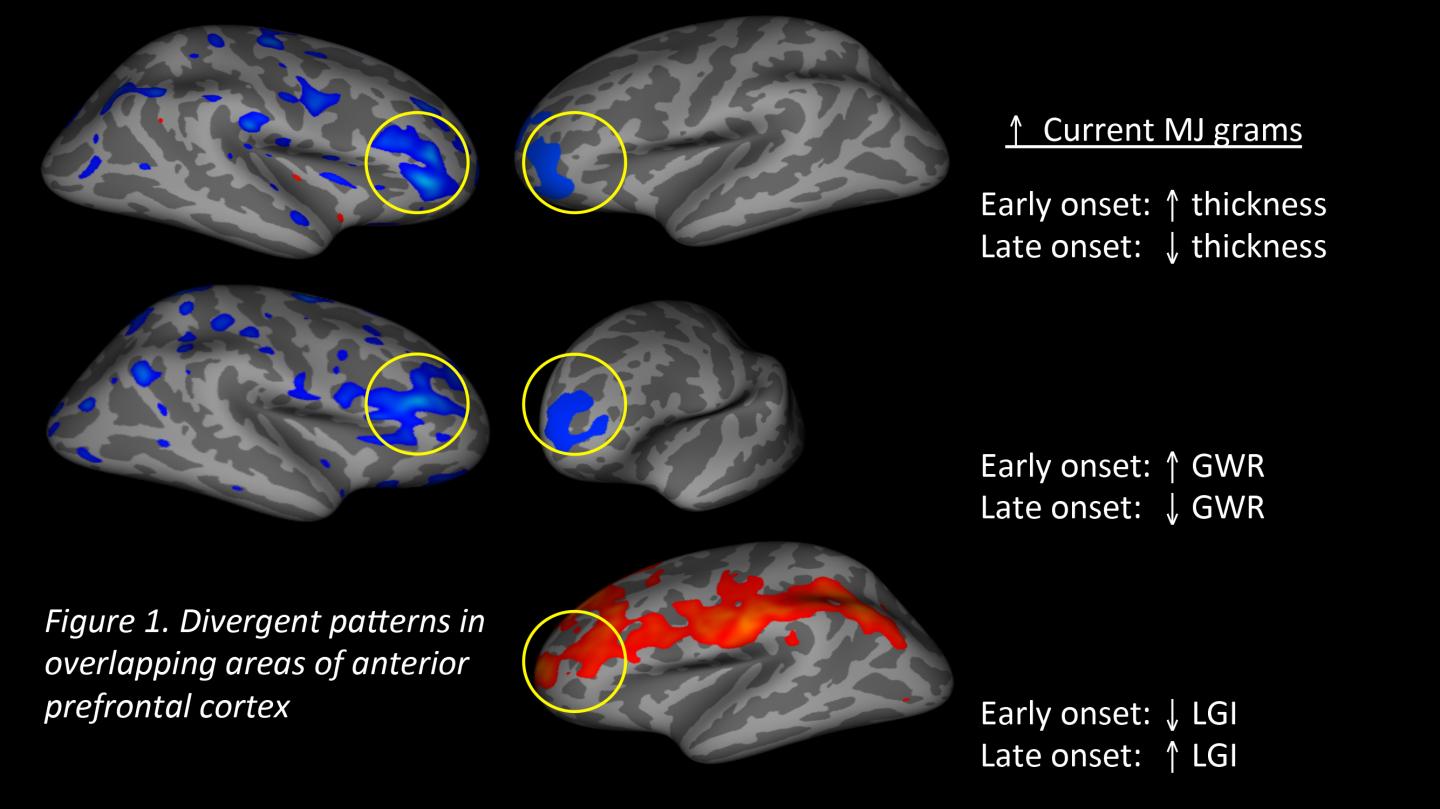
IMAGE: These are divergent patterns in overlapping areas of anterior prefrontal cortex.
Credit: Center for BrainHealth
The age at which an adolescent begins using marijuana may affect typical brain development, according to researchers at the Center for BrainHealth at The University of Texas at Dallas. In a paper recently published in Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, scientists describe how marijuana use, and the age at which use is initiated, may adversely alter brain structures that underlie higher order thinking.
Findings show study participants who began using marijuana at the age of 16 or younger demonstrated brain variations that indicate arrested brain development in the prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain responsible for judgment, reasoning and complex thinking. Individuals who started using marijuana after age 16 showed the opposite effect and demonstrated signs of accelerated brain aging.
"Science has shown us that changes in the brain occurring during adolescence are complex. Our findings suggest that the timing of cannabis use can result in very disparate patterns of effects," explained Francesca Filbey, Ph.D., principal investigator and Bert Moore Chair of Behavioral and Brain Sciences at the Center for BrainHealth. "Not only did age of use impact the brain changes but the amount of cannabis used also influenced the extent of altered brain maturation."
The research team analyzed MRI scans of 42 heavy marijuana users; twenty participants were categorized as early onset users with a mean age of 13.18 and 22 were labeled as late onset users with a mean age of 16.9. According to self-reports, all participants, ages 21-50, began using marijuana during adolescence and continued throughout adulthood, using cannabis at least one time per week.
According to Filbey, in typical adolescent brain development, the brain prunes neurons, which results in reduced cortical thickness and greater gray and white matter contrast. Typical pruning also leads to increased gyrification, which is the addition of wrinkles or folds on the brain's surface. However, in this study, MRI results reveal that the more marijuana early onset users consumed, the greater their cortical thickness, the less gray and white matter contrast, and the less intricate the gyrification, as compared to late onset users. These three indexes indicate that when participants began using marijuana before age 16, the extent of brain alteration was directly proportionate to the number of weekly marijuana use in years and grams consumed. Contrastingly, those who began using marijuana after age 16 showed brain change that would normally manifest later in life: thinner cortical thickness, stronger gray and white matter contrast.
"In the early onset group, we found that how many times an individual uses and the amount of marijuana used strongly relates to the degree to which brain development does not follow the normal pruning pattern. The effects observed were above and beyond effects related to alcohol use and age. These findings are in line with the current literature that suggest that cannabis use during adolescence can have long-term consequences," said Filbey.
Filbey notes that a longitudinal study would be necessary to establish a causal relationship between brain alterations and marijuana use. Her future studies will explore cognitive and behavioral changes associated with structural brain change and consider the different patterns of development within the adolescent period and how these patterns could lead to non-linear effects.
###
Media Contact
Shelly Kirkland
[email protected]
972-883-3221
@BrainHealth
http://www.brainhealth.utdallas.edu/