This news release is available in German.
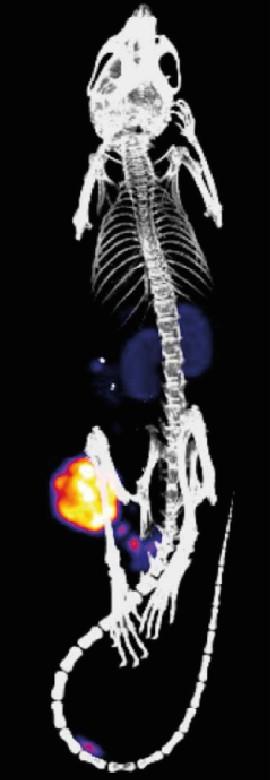
An international team from four EU countries plans to use an innovative concept to improve the use of companion diagnostics in disease and develop new approaches to therapy in the long term. The idea is to combine the use of nanomedicines and short half-life radionuclides for imaging purposes in the living organism. First the nanomedicines, in the form of synthetic nanoparticles or antibodies, are introduced in the body where they actively or passively accumulate in certain organisms or cells. The second stage involves the delivery of a radioactive substance. Where the substance encounters the nanoparticles, a rapid chemical reaction occurs and the two bind together, while the remainder of the substance is eliminated from the body. With the help of an imaging technique, it is now possible to precisely pinpoint where the nanoparticles are located, to what extent they have accumulated at the target site, and what effect they are having on the disease pathology. The EU is funding the project to the tune of EUR 6 million over the next five years. Participating are physicians and clinicians from Copenhagen, chemists at TU Wien, and Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), together with commercial partners from Austria and the Netherlands. The project was launched with the clear ambition of transferring the technology into clinical practice.
The research consortium aims at improving companion diagnostics and, at the same time, reducing exposure of patients to radioactivity to an absolute minimum. Companion diagnostics are tools in the form of medical devices that are used to assess medications in advance and can help determine which patients are likely to benefit from a treatment. For example, it is already possible to treat HER2-positive breast cancer using antibody therapy with relatively high therapeutic success rates. However, only about 20 percent of all breast tumors are HER2-positive and the treatment is very expensive. It is thus advisable to first establish whether a patient is HER2-positive before initiating the therapy. Companion diagnostics can thus be used to determine if an individual patient is suitable for a specific form of therapy and would benefit from it or whether an alternative form of treatment should be preferred. In addition, the outcome of the therapy can be subsequently visualized. It is thus possible that the project may also contribute towards the future development of medicines that are more effective, more rapid, and less expensive.
"The system we are proposing would allow us to do far more than simply determine exactly where the nanoparticles are in the body," explained polymer chemist Dr. Matthias Barz of the Institute of Organic Chemistry at Mainz University, who is involved in the project. "There is the imaging factor that will allow us to see where our nanoparticles with their specific function are located in the body. And, eventually, it should at some point be possible to use our approach in radiotherapy — making it truly unique."
###
The two cooperation partners in Mainz, Dr. Matthias Barz and Professor Rudolf Zentel, are contributing their expertise in the production of microparticles of nanoparticles with specific functions. The European Union is making EUR 300,000 available over the next three years to fund their project.