Credit: KAIST
Cancer pedigree analysis reveals the mutations in RB1 and TP53 genes play a key role in treatment-resistant, cancer cell-type transformation during EGFR inhibitor therapy for lung cancers.
Research led by Korean medical scientists has discovered that a specific type of drug resistance mechanism to EGFR inhibitor therapy in lung cancer is predisposed by mutations in two canonical cancer-related genes: RB1 and TP53. Published in Journal of Clinical Oncology on May 12, the study also found those mutations can be detectable in patients' tumors at the point of clinical diagnosis. Therefore, it can be used as strong markers in clinic for predicting poor outcome for the targeted treatment for lung adenocarcinoma.
Lung adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer, and about 15% of patients in Western countries and 50% of patients in Asian countries have mutations in the EGFR gene, which is critical for the development of lung cancer. Patients with lung adenocarcinoma harboring the EGFR mutation show favorable responses to EGFR inhibitors such as erlotinib (Tarceva) or gefitinib (Iressa), but ultimately relapse with drug-resistant tumors. Since the initial report in 2006, it has been known that in about 5~15% of patients, the lung adenocarcinoma cells undergo a mysterious transformation into a very different cancer cell type called "small cell lung cancer," a much more aggressive lung cancer subtype, common in cigarette smokers.
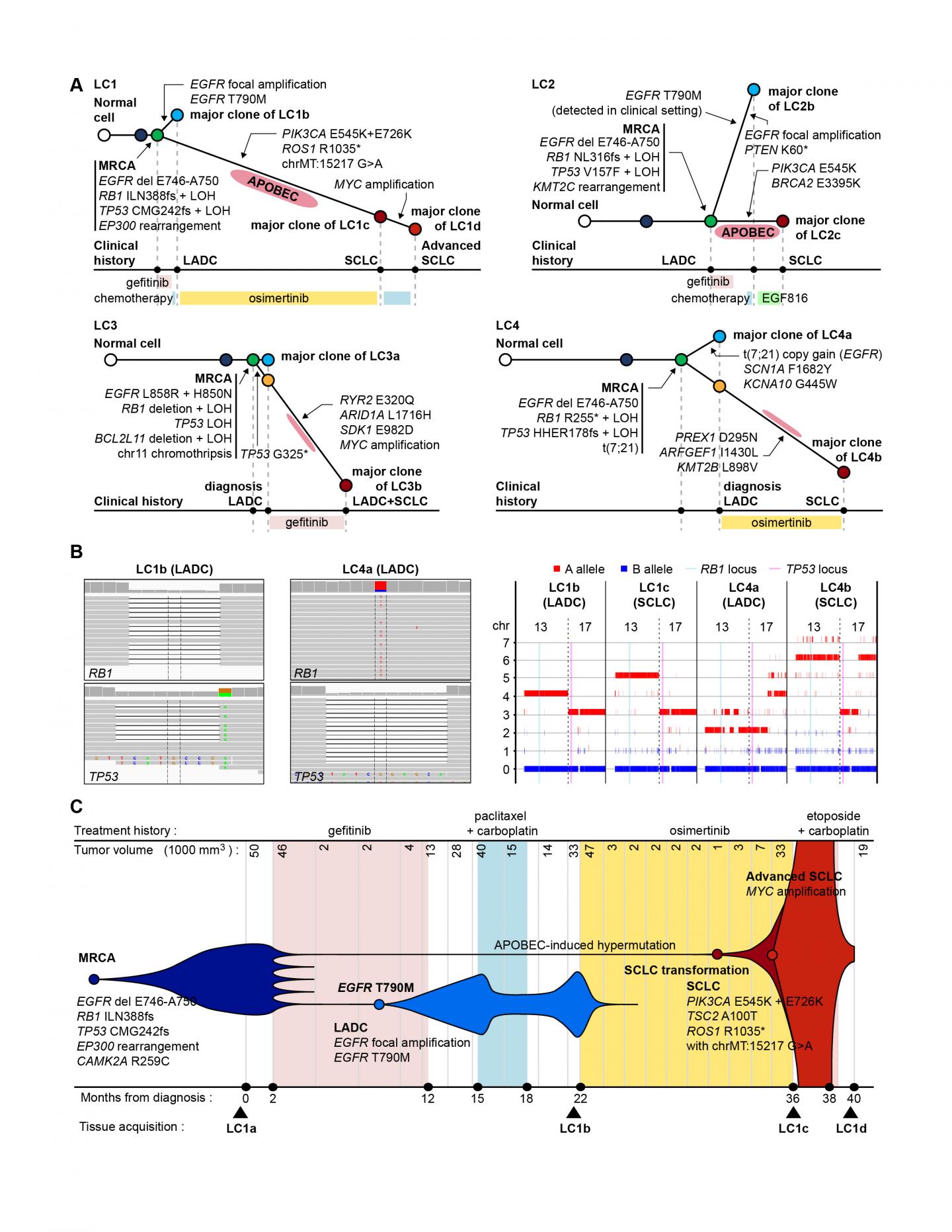
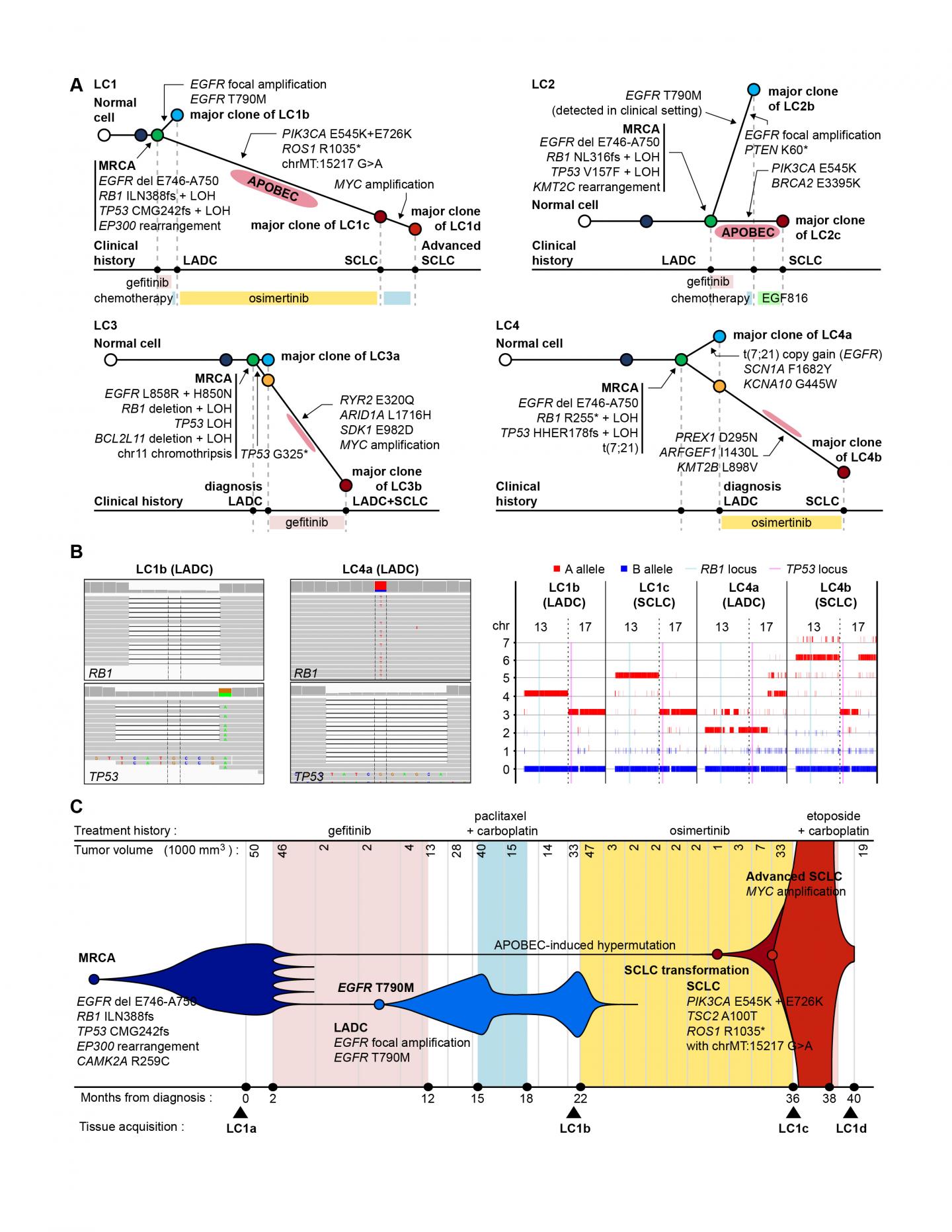
To find out the genetic basis of this process, the researchers compared the genome sequences of multiple cancer tissues acquired during the treatment courses of patients whose tumors underwent small-cell transformation. They reconstructed the cancer cell pedigree by comparing mutations between cancer tissues, and identified that RB1 and TP53 genes are completely inactivated by mutations already in their lung adenocarcinoma tissues.
"We tried to compare the somatic mutational profile of pre-EGFR inhibitor treatment lung adenocarcinomas and post-treatment small cell carcinomas and to reconstruct the pedigrees of the cancer evolution in each patient. Strikingly, both copies of RB1 and TP53 genes were already inactivated at the stage of lung adenocarcinomas in all sequenced cases," said Dr. Jake June-Koo Lee, the first author from KAIST.
They further pursued the clinical implications of RB1 and TP53 inactivation by investigating 75 EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma tissues from patients who received EGFR inhibitor therapy, including patients with small-cell transformation. In this analysis, the lung adenocarcinomas with a complete inactivation of both RB1 and TP53 genes tended to have a 43-times greater risk of transformation into small cell lung cancer during their EGFR inhibitor treatment courses.
Dr. Young Seok Ju, the co-last author from KAIST, explained, "This study shows the power of entire genome analyses to better understand the mechanisms underlying mysterious phenomenon encountered in clinic. Upon accurate bioinformatics, we are finding cancer-specific somatic mutations from the whole-genomes of patients' cancer cells. These mutations allow us to track the evolution of cancer cells throughout the extraordinary clinical course of a special set of lung cancers."
The complete inactivation of both RB1 and TP53 tumor suppressor genes is found in a minor (
"We are actively investigating patient tumor tissues to develop optimal surveillance plans and treatment options for patients with lung adenocarcinomas more prone to small-cell transformation," said Dr. Tae Min Kim, the co-last author from Seoul National University Hospital.
The researchers are implementing their findings into lung cancer clinics by screening the RB1 and TP53 mutational status in lung adenocarcinoma patients receiving EGFR inhibitor treatment, and following their treatment courses to develop a treatment strategy for those patients.
###
This research (doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.71.9096) was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2013H1A2A1032691 to J.-K.L., NRF-2014R1A2A2A05003665 to Y.T.K.); Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (K-16-L03-C02-S02 to J.L.); and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, which was funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare (HI14C1234 to T.M.K., HI16C2387 to Y.S.J.)
Media Contact
Younghye Cho
[email protected]
82-423-502-294
@KAISTPR
http://www.kaist.edu/english/
Original Source
http://www.kaist.ac.kr/_prog/_board/?code=ed_news&mode=V&no=65185&upr_ntt_no=65185&site_dvs_cd=en&menu_dvs_cd=060101 http://dx.doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.71.9096