Credit: Osaka University
The Cardiovascular Surgery Group at Osaka University succeeded in minimally invasive treatment of a patient with acute heart failure due to medical treatment-resistant cardiogenic shock by making use of Impella*, a percutaneous auxiliary artificial heart, for the first time in Japan. This method is anticipated as a new therapy for treating patients with acute heart failure due to medical treatment-resistant cardiogenic shock.
Medical treatment-resistant cardiogenic shock is very difficult to treat and mechanical circulatory support is necessary in many cases. Conventional mechanical circulatory support devices, such as intra-aortic balloon pumping (IABP) and percutaneous cardiopulmonary support (PCPS), may not be able to fully improve hemodynamics and reduce load on left ventricular myocardium because of problems during circulatory support, such as blood pressure maintenance and retrograde blood flow (blood pressure must be continuously monitored and retrograde blood flow increases afterload on the left ventricle).
In addition, temporary/durable left ventricular assist device allow for blood flow support and anterograde blood flow and can provide satisfactory circulatory support in many cases; however, they required invasive surgical techniques for their use, and patients with cardiogenic shock at the acute stage could not endure the surgical stress.
A group of researchers led by Professor SAWA Yoshiki at the Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University, treated a patient with acute heart failure due to medical treatment-resistant cardiogenic shock by using Impella, which is minimally invasive and can provide satisfactory circulatory support with blood flow support and anterograde blood flow, significantly improving the patient's hemodynamics.
This method, which provides sufficient circulatory assistance with minimum invasion, will become a new therapy for treating patients with acute heart failure due to medical treatment-resistant cardiogenic shock. The growth in the proper use of this technique in Japan will save more patients with acute heart failure and improve treatment outcome.
###
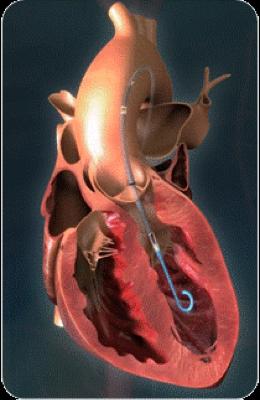
*Impella devices
Impella, a minimally invasive option that does not require open heart surgery, is a ventricular assist device with a catheter-mounted microaxial rotary blood pump and a catheter that is inserted percutaneously and via an artery. The pump catheter inserted and placed in the left ventricle sucks in blood from its tip by rotating an impeller in the pump at a high speed and pumps the blood out from the outlet at the ascending aorta, thereby supporting anterograde blood flow in the systemic circulation.
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
@osaka_univ_e
http://www.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
Original Source
http://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en/research/2017/20171026_1