Credit: Houston Methodist
A new study shows that a 70-year-old malaria drug can block immune cells in the liver so nanoparticles can arrive at their intended tumor site, overcoming a significant hurdle of targeted drug delivery, according to a team of researchers led by Houston Methodist.
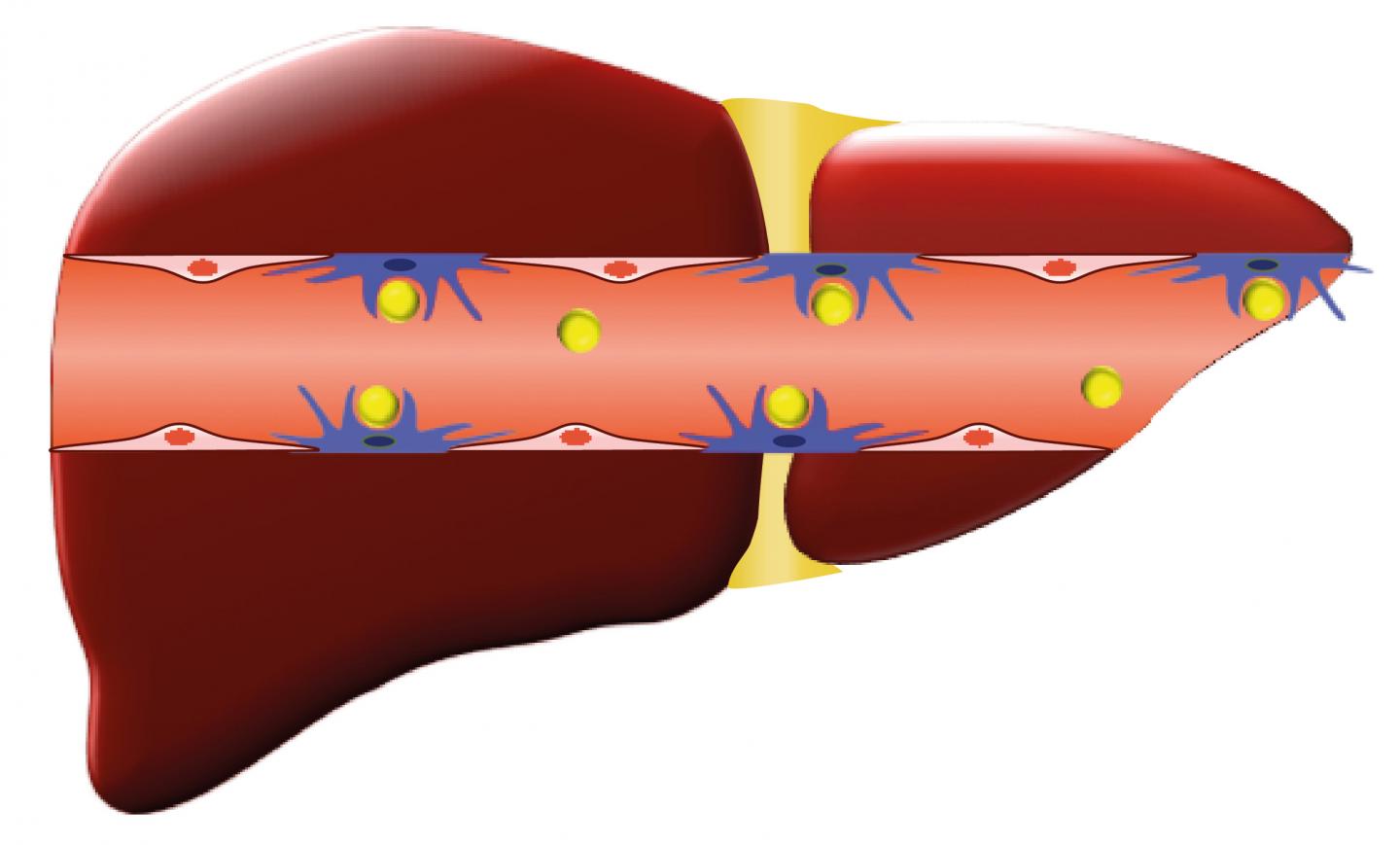
Many cancer patients do not respond to chemotherapies because the drugs never reach the cancer cells. Even in nanomedicine, which is one of the best new methods for delivering drugs to a tumor, only about one percent of a dose of nanoparticles will successfully arrive at the intended tumor site, while the rest are filtered out by the immune cells of the liver and spleen.
Using chloroquine, the researchers not only increased the circulation of nanoparticles in the body, but also reduced the body's filtration of nanoparticles, as well as improved drug delivery to breast tumors. The study was recently published in Scientific Reports, a research journal from the Nature Publishing Group.
Led by Mauro Ferrari, Ph.D., president and CEO of the Houston Methodist Research Institute, and Joy Wolfram, Ph.D. (now at Mayo Clinic's campus in Jacksonville, Florida), the research showed that chloroquine interfered with immune cells called macrophages, which are used by the body to identify microscopic foreign objects and destroy them.
In this study, mice models received injections of chloroquine, followed by an injection of nanoparticles. Chloroquine decreased the macrophages' ability to clean up the nanoparticles. The findings are significant, because the nanoparticles not only remained in circulation, but also accumulated in mouse tumors, as well as in the lungs of healthy mice, suggesting that the approach also may enhance treatment for lung diseases.
Chloroquine was invented in the 1940s for the prevention and treatment of malaria. Since it mildly suppresses the immune system, the drug also is used in some autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Apart from this research, the drug is also being studied in other cancers, such as triple-negative breast cancer and pancreatic cancer.
Ferrari, considered one of the founders of nanomedicine and transport oncophysics (the physics of mass transport within a cancer lesion), says researchers and clinicians need to understand the limitations of transport mechanisms to identify effective immunotherapy treatments for patients.
###
The research was funded by the Houston Methodist Research Institute, the Ernest Cockrell Jr. Distinguished Endowed Chair, the U.S. Department of Defense (W81XWH-09-1-0212, W81XWH-12-1-0414), the National Institutes of Health (U54CA143837, U54CA151668, U54CA210181), Nylands nation Finland, Victoriastiftelsen Finland, and the Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas (RP121071).
The study's other authors include S. Nizzero, H. Liu, F. Li, G. Zhang, Z. Li, H. Shen, and E. Blanco (Houston Methodist Research Institute, Houston, TX).
To speak with Mauro Ferrari, Ph.D., contact Gale Smith, Houston Methodist, at 281.627.0439 or [email protected] For more information about Houston Methodist, visit houstonmethodist.org. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook.
For more information: J. Wolfram, S. Nizzero, H. Liu, F. Li, G. Zhang, Z. Li, H. Shen, E. Blanco and M. Ferrari., A chloroquine-induced macrophage-preconditioning strategy for improved nanodelivery, Scientific Reports (Online Oct. 23, 2017). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-14221-2.
Media Contact
Gale Smith
[email protected]
281-627-0439
@MethodistHosp
http://methodisthealth.com
Original Source
http://www.houstonmethodist.org/newsroom/age-old-malaria-treatment-found-to-improve-nanoparticle-delivery-to-tumors/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14221-2