This news release is available in German.
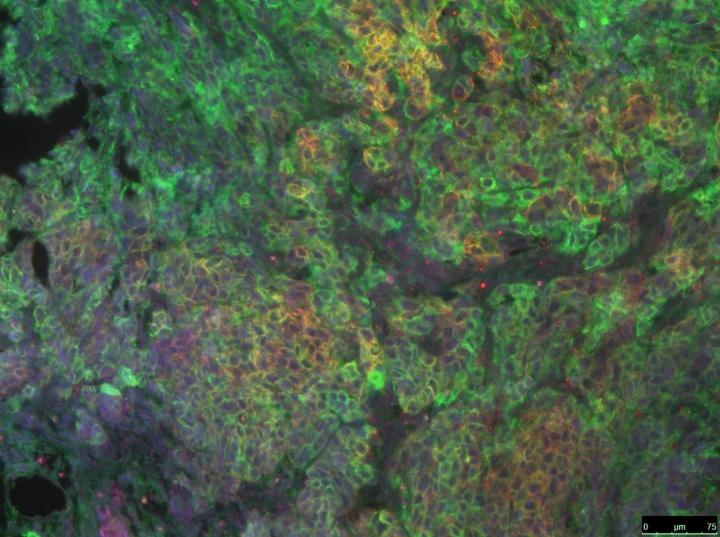
Due to their rapid metastatic spread, pancreatic tumors are among the most aggressive types of cancer. Only three to five percent of patients have a survival rate of five years. A team of KIT researchers has now established the basis for new therapeutic approaches. In the Gastroenterology journal they report that in various pancreatic cancer mouse models CD44v6-specific peptides do not only inhibit the spread of tumor cells, but may even lead to the regression of already existing metastases. (DOI 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.10.020).
"We think that these peptides have a high potential for tumor therapy, above all for the treatment of pancreatic cancer with its aggressive metastases," Véronique Orian-Rousseau of the Institute of Toxicology and Genetics (ITG) of KIT says. The CD44v6 protein was discovered in the 1990s by KIT. It acts as a co-receptor for so-called receptor tyrosine kinases, such as MET or VEGFR-2, that depend on CD44 for their activation. These enzymes largely influence the activities of tumor cells. MET accelerates their proliferation, migration, and invasion. VEGFR-2 promotes angiogenesis, i.e. the formation of new blood vessels required to supply the tumor. Hence, they are decisive for the growth and spread of tumor cells.
In pre-clinical studies on animals and using various pancreatic cancer models, KIT scientists proved for the first time that the co-receptor function of CD44v6 drives the metastatic spreading. Interestingly, small segments of the CD44v6 protein (called v6pep) turned out to be successful inhibitors of metastasis in animal experiments. The researchers assume that they interfere with the three-dimensional protein structure of CD44v6 and inactivate it in this way. Peptide treatment of tumor-bearing animals led to a reduction of tumor load and to the inhibition of metastasis. Moreover, already existing metastases regressed or disappeared completely: "This is the most remarkable result with respect to pancreatic cancer, the diagnosis of which mostly is possible after the formation of metastases only," Orian-Rousseau says. In the animal experiments the survival time increased dramatically. The v6pep peptides were found to be much more effective than Crizotinib and Pazopanib, tyrosine kinase inhibitors directed against MET and VEGFR2 respectively. The evaluation of data of patients suffering from pancreatic cancer shows that metastasis and shorter survival times correlate with an increased level of CD44v6 and MET.
"This means that we have made an important step forward in basic research that will help the development of anti-cancer drugs," the scientist explains. Clinical studies that are planned to be made in cooperation with the KIT spinoff "amcure GmbH" in late 2016 will reveal whether the peptides will be effective in human patients.
###
Inhibition of Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Pancreatic Cancer Models by Interference with CD44v6 Signaling, Gastroenterology, Alexandra Matzke-Ogi et al., DOI:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.10.020, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S001650851501519X.
For further information, please contact: Kosta Schinarakis, PKM – Science Scout, Phone: +49 721 608 41956, Fax: +49 721 608 43658, E-mail: [email protected]
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is a public corporation pursuing the tasks of a Baden-Wuerttemberg state university and of a national research center of the Helmholtz Association. The KIT mission combines the three core tasks of research, higher education, and innovation. With about 9,400 employees and 24,500 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
Since 2010, the KIT has been certified as a family-friendly university.
This press release is available on the internet at http://www.kit.edu.
The photo of printing quality may be downloaded under http://www.kit.edu or requested by mail to [email protected] or phone +49 721 608-4 7414. The photo may be used in the context given above exclusively.