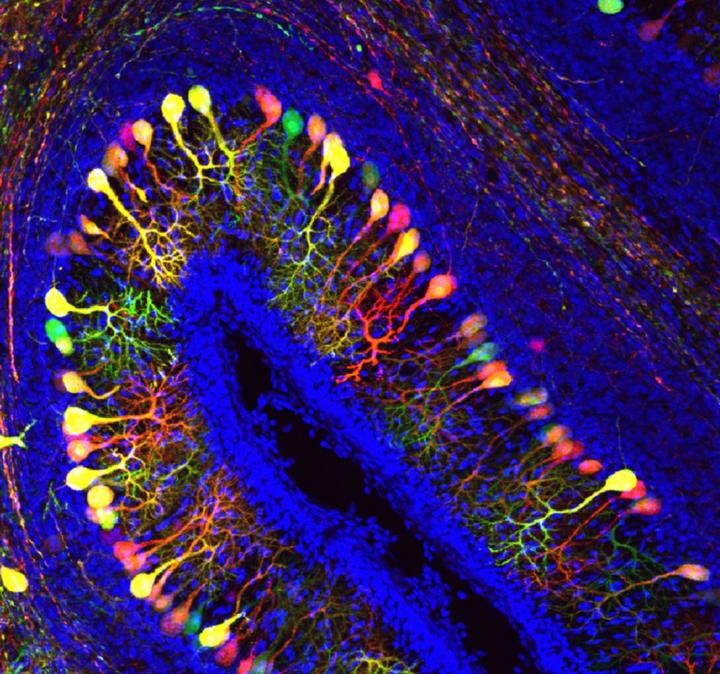
Credit: KU Leuven Lab of Comparative Endocrinology – Joke Delbaere & Pieter Vancamp
Thyroid hormones are very important for the development of the brain. And when the transporters of these hormones are not functioning properly, the consequences for the development of the cerebellum or 'the little brain' are very serious. These are the findings of a study by researchers from KU Leuven (University of Leuven, Belgium) and King's College London.
Thyroid hormones control our everyday metabolism, but they're already crucial before birth: they are essential for the development of the organs, including the brain. "These hormones ensure that different cell types originate in the brain at the right moment, move to the right place, and make the right connections," explains Professor Veerle Darras from the Lab of Comparative Endocrinology at KU Leuven. "Until the thyroid is fully developed, a foetus depends on the mother's hormones. If the mother-to-be doesn't produce enough thyroid hormones, this has a negative impact on the brain development of the foetus from a very early stage."
Determining whether the thyroid is properly functioning is typically done by measuring the amount of hormones in the blood. Unfortunately, this is not always a good indicator. "This proved to be the case with the rare Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome (AHDS), a hereditary condition of the nervous system that only affects boys. These children suffer from severe mental retardation and locomotor deficits. Doctors looked for possible thyroid hormone deficiencies but, surprisingly, the level of hormones in the blood was abnormally high. The problem turned out to be in the transporters that bring the hormones from the blood to the inside of the cell. Due to a genetic mutation an important transporter – MCT8 – is deactivated in patients with AHDS."
To find out more about this mutation Professor Darras's team examined what happens in a chicken embryo when this transporter is deactivated in a part of the little brain, PhD student Pieter Vancamp continues. "The little brain is important for locomotion. A thyroid hormone deficiency impairs its development, but the role of the transporters was not yet known. In our study, we noticed relatively quickly that some important proteins – necessary for the development of brain cells – were not produced in sufficient amounts in the part of the brain with no active transporter. In a later stage, we noticed that the Purkinje cells – nerve cells located in the cortex of the little brain – have less dendritic branches. Therefore, brain cell signalling goes haywire, and problems arise in other cells as well."
The results show that thyroid hormones are essential for embryonic development right from the start. "The earlier things go wrong, the harder it is to repair the damage after birth. Newborns are always screened for thyroid problems with the heel prick, but it's better to test the mothers-to-be as early as possible. Unfortunately, this does not yet happen in all hospitals. For the Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome, in particular, our study raises questions about possible prenatal treatments with variants of thyroid hormones: these can enter the cell without the transporter. But this is still an experimental treatment – one that is only being tested after birth."
###
Media Contact
Veerle Darras
[email protected]
32-163-23985
@LeuvenU
http://www.kuleuven.be/english/news?