Credit: Thevaranjan et al./Cell Host & Microbe 2017
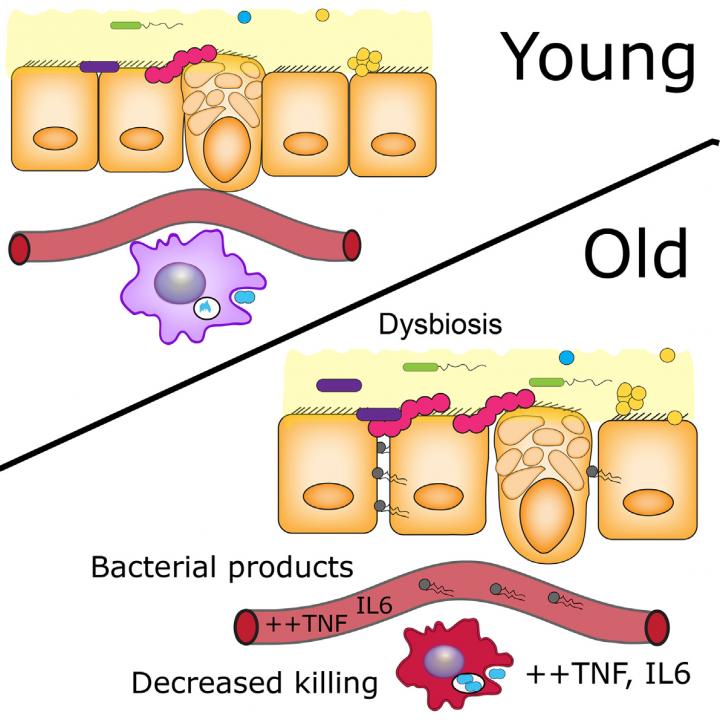
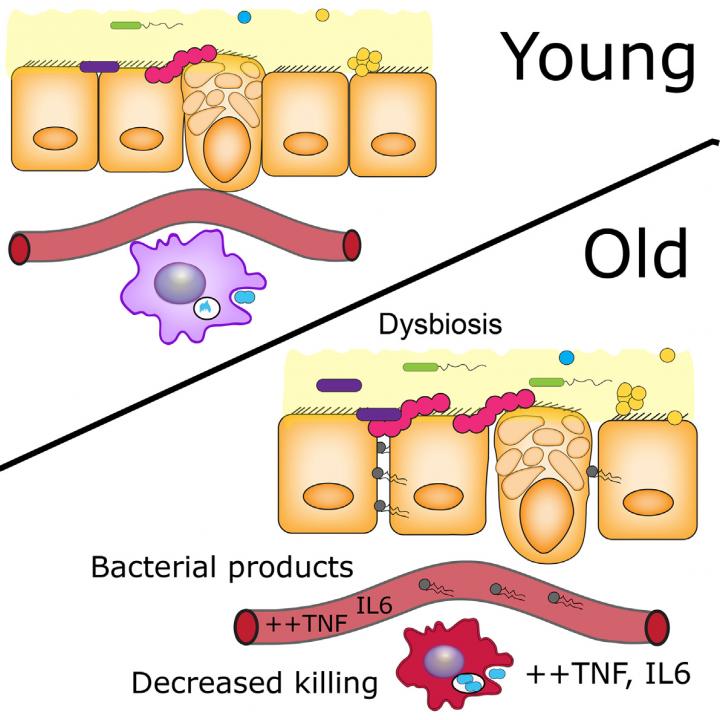
Inflammation increases with age and is a strong risk factor for death in the elderly, but the underlying cause has not been clear. A study published April 12 in Cell Host & Microbe reveals that gut microbes are one of the culprits behind age-associated inflammation and premature death in mice. Imbalances in the composition of gut microbes in older mice cause the intestines to become leaky, allowing the release of bacterial products that trigger inflammation and impair immune function.
"To date, the only things you can do to reduce your age-associated inflammation are eat a healthy diet, exercise, and manage any chronic inflammatory conditions to the best of your ability," says senior author Dawn Bowdish (@MsMacrophage) of the Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research at McMaster University. "We hope that in the future we will be able use drugs or pre- or probiotics to increase the barrier function of the gut to keep the microbes in their place and reduce age-associated inflammation and all the bad things that come with it."
Age is associated with an increase in levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and other pro-inflammatory cytokines in the bloodstream and tissues. Individuals with high levels of these inflammatory molecules are more likely to be frail, hospitalized, and less independent; are more susceptible to certain types of infections; and have a variety of chronic, late-life diseases such as dementia and cardiovascular disease, as well as higher death rates. Some have proposed that age-associated inflammation is caused by accumulating wear and tear on our immune cells, while others have suggested that it is caused by immune cells dealing with chronic viral infections. But evidence supporting these hypotheses has been elusive, and the underlying cause of age-associated inflammation has remained unknown.
Bowdish and her colleagues raised mice in germ-free conditions and compared them to their conventionally raised counterparts. Strikingly, the germ-free mice did not show an age-related increase in intestinal permeability or in levels of bacterial products or pro-inflammatory cytokines in the bloodstream, in contrast to conventionally raised mice. Moreover, a higher proportion of germ-free mice lived to the ripe old age of 600 days, and macrophages derived from older germ-free mice maintained anti-microbial activity. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that age-related changes in the gut microbiome weaken the intestinal barrier, leading to the release of bacterial products that promote inflammation, impair immune function, and reduce lifespan.
Additional experiments showed that the relationship between inflammation and the microbiome is bidirectional. In TNF-deficient mice, which are protected from inflammation, age-related changes in the composition of gut microbes were not observed. Moreover, treatment with an anti-TNF drug approved for human use reversed age-related changes in the microbiome.
"We assume that this is because if we reduce inflammation, we improve immune function, and if we improve immune function, we maintain the ability to farm a healthy gut microbiota, but we don't know for sure yet," Bowdish says. "We also believe that targeting age-associated inflammation will improve immune health and are investigating repurposing drugs that are already on the market and developing novel strategies or therapeutics to this effect."
In future studies, Bowdish and her collaborators will try to identify the good bacteria that maintain gut integrity with age as well as the bad bacteria that cause the gut to become leaky. They are also trying to understand how early in life some of these changes in the microbiota start occurring so that they could try to intervene before they are severe enough to alter immune function.
In the end, this research could lead to new strategies for manipulating the microbiome to improve intestinal health and decrease age-associated inflammation. "Since age-associated inflammation is linked to so many aspects of unhealthy aging, we predict that these strategies could help keep us healthy, active, and independent as we age," Bowdish says.
###
The authors were supported by an Ontario Graduate Scholarship, the Canadian Thoracic Society, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Ontario Ministry of Research and Innovation, the McMaster Immunology Research Centre, and the M.G. DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research.
Cell Host & Microbe, Thevaranjan and Puchta et al.: "Age-associated microbial dysbiosis promotes intestinal permeability, systemic inflammation and macrophage dysfunction" http://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe/fulltext/S1931-3128(17)30112-9
Cell Host & Microbe (@cellhostmicrobe), published by Cell Press, is a monthly journal that publishes novel findings and translational studies related to microbes (which include bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses). The unifying theme is the integrated study of microbes in conjunction and communication with each other, their host, and the cellular environment they inhabit. Visit: http://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact [email protected]
Media Contact
Joseph Caputo
[email protected]
617-397-2802
@CellPressNews
http://www.cellpress.com