Credit: Toshikazu Kawagoe
A Japanese research group has revealed that elderly people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) have a particularly weakened ability to memorize human faces in the short term when compared to healthy elderly people. MCI patients also had a different gaze behavior when trying to memorize a face. This research may lead to the early detection of dementia.
Alzheimer's disease is considered to be the most common type of dementia, and early detection of preliminary stages is important to halt its progression into a more serious form of the disease. MCI, which is thought to be a preliminary stage of Alzheimer's, is a state in which cognitive functions, such as memory or thinking ability, decrease at a level that do not affect daily life.
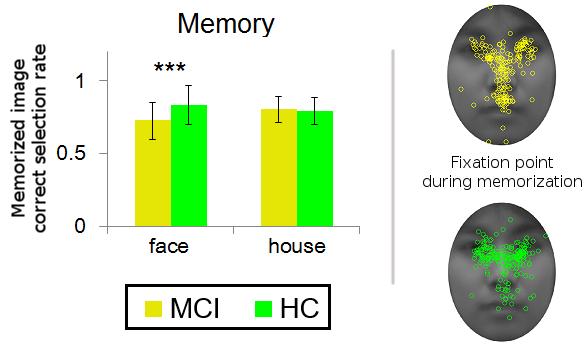
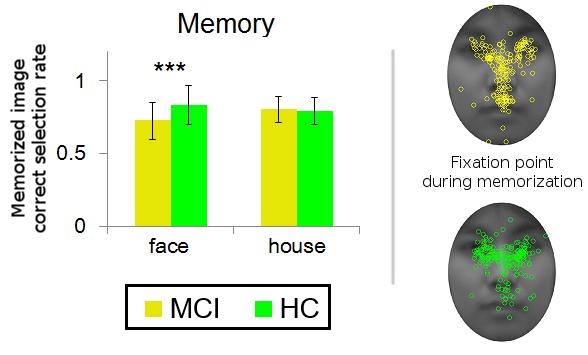
Brain imaging studies show that areas of the brain for memory and visually processing human faces in people with MCI are structurally and functionally transformed. To investigate these specific and yet unstudied areas, a research group from Kumamoto University in Japan conducted comparative experiments with normal elderly subjects and MCI patients (18 each) using a delayed-matching task with face and house stimuli in independent blocks. In each block, they asked subjects to remember a single image and then, after a short delay, select a memorized image from a set new of images. The researchers also recorded subject gaze trends during the image memorization process.
Their experiments revealed that the memorization performance of MCI patients was lower for facial images than for house images, but found no performance difference in normal subjects. The research also showed that, during the memorization process, MCI patient gaze concentration on the eyes of an image decreased but the time spent looking at the mouth increased in comparison to normal subjects. In essence, MCI patients had reduced short-term memorization ability and a different gaze pattern for faces when compared to normal people.
"Looking at the eyes is important for remembering the entirety of the face," said Emeritus Professor Kaoru Sekiyama. "MCI patients probably have an abnormality in the cognitive processing of faces due to the deterioration of brain function. It is possible that the distributed gaze pattern is compensation for this decreased function. We hope to shed some light on this possibility in future work."
This research result was posted online in the journal Scientific Reports on 30 October 2017.
###
[Source]
Kawagoe, T., Matsushita, M., Hashimoto, M., Ikeda, M., & Sekiyama, K. (2017). Face-specific memory deficits and changes in eye scanning patterns among patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Scientific Reports, 7(1). doi:10.1038/s41598-017-14585-5
Media Contact
J. Sanderson, N. Fukuda
[email protected]
http://ewww.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/en/news/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14585-5