Credit: CNIC
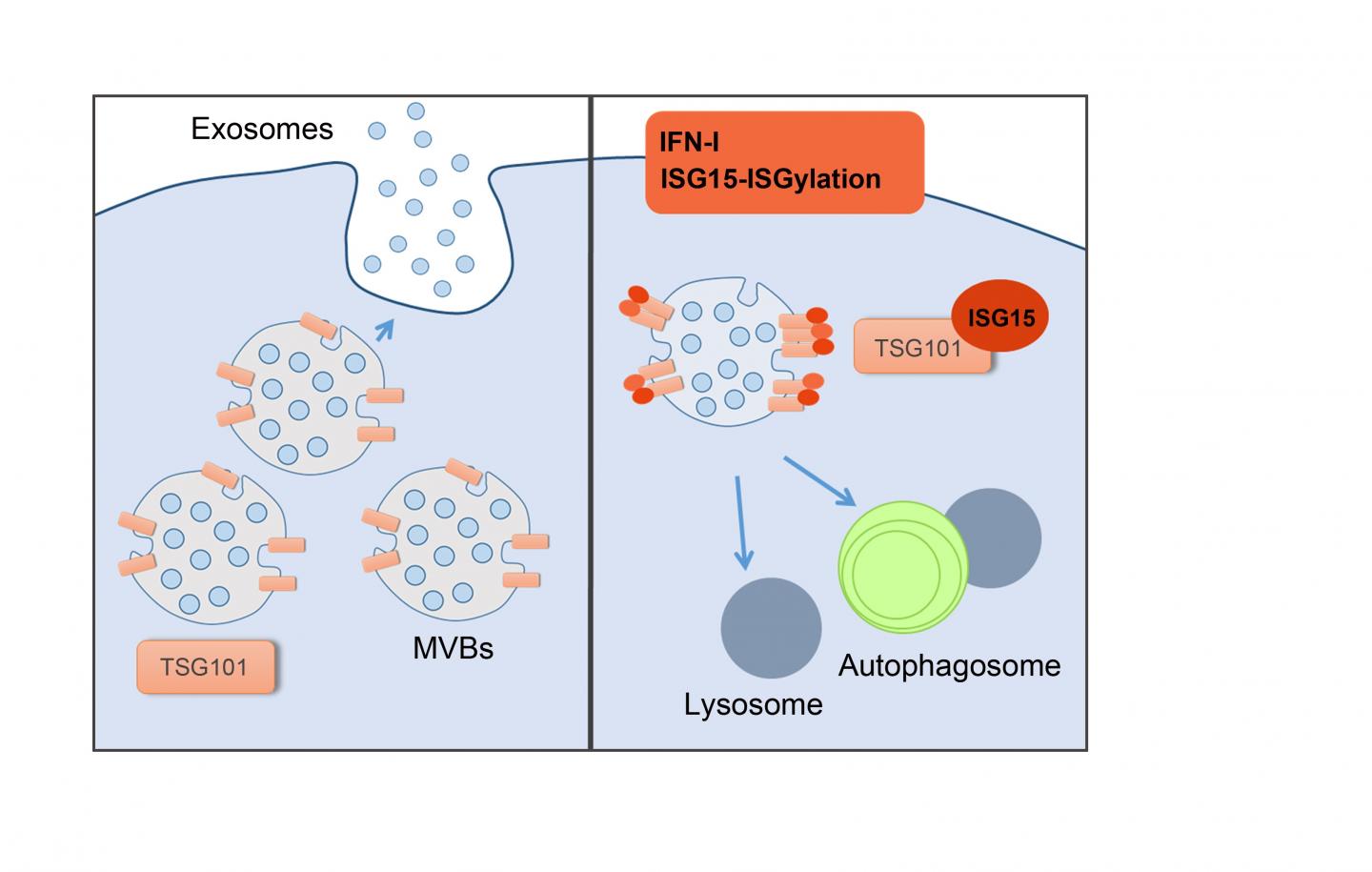
A team of scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (CNIC), led by Prof. Francisco Sánchez-Madrid, has characterized a cell signal that impedes intercellular communication and could play a central role in biomedical strategies such as gene therapy, vaccine design, and immunotherapy. The study, published today in Nature Communications, characterizes a signal that impedes the secretion of nanovesicles called exosomes. Cells secrete exosomes as a means of intercellular communication; however, certain viruses can use exosomes as "Trojan horses" to facilitate their propagation and entry into neighboring cells.
The signal, called ISGylation, has in the past been viewed mainly as an antiviral signal, although some studies show that it can also be activated by other stimuli such as a lack of oxygen, aging, or cancer. "In these situations, the secretion of exosomes, and therefore communication between cells, can be affected by this modification," explains Dr. Carolina Villarroya.
The research team is dedicated to decoding the processes that control exosome secretion and exploring potential biomedical applications. As Dr. Sánchez-Madrid explains, "as well as acting as messengers in intercellular communication, exosomes are potential tools for gene therapy, vaccine design, and immunotherapy." Several clinical trials are underway to assess new treatments using this approach.
The Nature Communications article describes how an antiviral signal activates the programmed degradation of proteins involved in exosome degradation. According to Villarroya, this signal "marks specific proteins located in endosomes, the place where exosomes are formed. This mark redirects these proteins toward the degradation pathway and impedes exosome secretion." Sánchez-Madrid points out that this newly identified mechanism, through which cells defend themselves against infection by activating the degradation of their own proteins, "could also be exploited by external agents for their propagation."
###
The study was carried out by CNIC-UAM scientists Carolina Villarroya, Francesc Baixauli, Irene Fernández, María Mittelbrunn, Daniel Torralba, and Olga Moreno, in collaboration with Susana Guerra (UAM) and Carles Enrich (IDIBAPS).
Media Contact
Fatima Lois
[email protected]
34-639-282-477
@@CNIC_CARDIO
http://www.cnic.es